Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is more than just a buzzword; it’s about companies taking responsibility for the social, environmental, and economic impacts of their actions. When businesses engage in CSR, they contribute to positive changes in society, such as improving education, healthcare, and the environment. The social impact of CSR is significant because it helps address critical issues, supports communities, and promotes sustainable development. By investing in social causes, companies not only enhance their public image but also play a vital role in creating a better, more equitable world.

Tags: GS – 3, Economy- Skill Development– Education– Inclusive Growth
For Prelims: Corporate Social Responsibility, Amendments to the Companies Act, National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT), Transforming Indian Education: Towards Long-Term Vision
For Mains: Social impact of CSR spending, Issues related to CSR expenditure
Contents
Context:
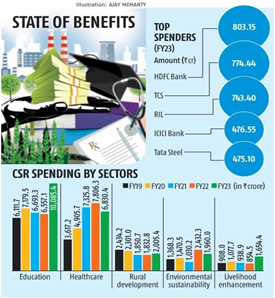
- Government data for FY23 revealed that education received the largest share of corporate social responsibility (CSR) expenditure, totaling Rs 10,085 crore.
- This has sparked debate over the uneven distribution of CSR funds across sectors and regions.

Recent Developments in CSR Expenditure:
- Overview:
- Total CSR expenditure rose from Rs 26,579.78 crore in FY22 to Rs 29,986.92 crore in FY23.
- The number of CSR projects increased from 44,425 to 51,966.
- Companies outside the public sector contributed 84% of the total CSR expenditure.
- Sector-Wise Expenditure:
- Education accounted for one-third of the CSR spend in FY23.
- CSR spending on vocational skills increased slightly to Rs 1,164 crore from Rs 1,033 crore.
- Technology incubators received the least funding, with Rs 1 crore compared to Rs 8.6 crore the previous year.
- Health, rural development, environmental sustainability, and livelihood enhancement also received notable CSR funds.
- Spending on animal welfare surged from Rs 17 crore in FY15 to over Rs 315 crore in FY23.
- CSR expenditure under the Prime Minister Relief Fund dropped to Rs 815.85 crore in FY23, down from Rs 1,698 crore in FY21 and Rs 1,215 crore in FY22.
- Contributions to disaster management fell by 77%, and spending on slum development decreased by 75%.
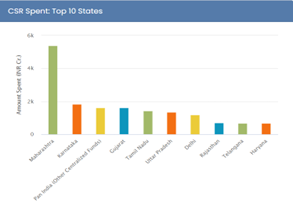
- Region-Wise Expenditure:
- Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Gujarat received the most CSR funding, while North Eastern states, Lakshadweep, and Leh and Ladakh received the least.
What is CSR?
- About:
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) involves corporate initiatives to assess and address the company’s impact on the environment and social welfare.
- It is a self-regulating model that promotes social accountability, considering economic, social, and environmental impacts.
- India mandates CSR spending under clause 135 of the Companies Act, 2013, whereas most countries have voluntary CSR frameworks.
- Norway and Sweden transitioned from voluntary to mandatory CSR models.
- Applicability:
- CSR provisions apply to companies with:
- Net worth over Rs 500 crore
- Turnover over Rs 1,000 crore
- Net profit over Rs 5 crore
- Such companies must spend at least 2% of their average net profits from the last three financial years on CSR activities.
- CSR provisions apply to companies with:
- Types of Corporate Social Initiatives:
- Corporate Philanthropy: Donations through corporate foundations.
- Community Volunteering: Company-organised volunteer activities.
- Socially-Responsible Practices: Producing ethical products.
- Cause Promotions and Activism: Funded advocacy campaigns.
- Cause-Based Marketing: Donations linked to sales.
- Corporate Social Marketing: Funded behaviour-change campaigns.
- Eligible Sectors:
- CSR activities include hunger and poverty eradication, education, gender equality, disease prevention, environmental sustainability, and government relief funds for socio-economic development and disadvantaged groups.
Issues Pertaining to CSR Compliance:
- Geographical Disparity:
- CSR spending is concentrated in industrial states like Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, while North Eastern states, Lakshadweep, Leh, and Ladakh receive less funding.
- CSR Allocation Trends:
- Data shows nearly 75% of CSR funds are focused on education, health (including sanitation and water), and rural poverty, with minimal spending on livelihood enhancement.
- PSU vs Non-PSU Spending:
- Non-PSUs contribute 84% of CSR expenditure, while PSUs contribute only 16%, highlighting a disparity between the two sectors.
- Strategic Misalignment:
- Many companies integrate CSR with business strategies, prioritising profits over genuine social impact, thus undermining the purpose of CSR.
- Finding the Right Partners:
- Challenges include identifying effective partners and selecting impactful, scalable, and sustainable projects.
- Issues of Transparency:
- Companies report a lack of transparency from local implementing agencies regarding program disclosures, audits, impact assessments, and fund utilisation.
Ways to Enhance the Effectiveness of CSR Expenditure:
- Enhancing CSR Engagement and Oversight:
- Align CSR with local government programs like the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) to boost community involvement.
- The government should ensure effective implementation and leverage AI for oversight. NGOs can support successful implementation in remote areas.
- Addressing Sectoral and Geographical Disparity:
- Invest in high-impact education and technology projects focused on skill development and livelihood enhancement.
- Develop CSR programs for underserved regions and incentivize spending in less-funded areas.
- PSU vs Non-PSU Spending Disparity:
- Encourage PSUs to increase their contributions and promote joint CSR initiatives between PSUs and non-PSUs.
- Company Roles and Governance:
- Conduct regular reviews, set clear objectives, and update governance roles.
- Establish new SOPs for fund utilisation, impact assessments, and detailed checklists.
Conclusion
To maximise CSR impact, companies should align with local government programs, address regional and sectoral disparities, and ensure transparency. Strengthening collaboration between PSUs and non-PSUs and investing in innovative projects will drive sustainable social change and contribute to India’s socio-economic development.
Source: BS
FAQs
Q: What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- Answer: Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is when companies take responsibility for the social, environmental, and economic impact of their activities. This often includes initiatives like charitable donations, community development projects, and sustainable business practices.
Q: How does CSR benefit society?
- Answer: CSR benefits society by addressing social issues like poverty, education, healthcare, and environmental conservation. Companies that engage in CSR can help improve living conditions, provide job opportunities, and support local communities.
Q: Can CSR make a real difference in people’s lives?
- Answer: Yes, CSR can make a significant difference. For example, when a company funds educational programs or builds schools, it helps improve access to education. Similarly, CSR initiatives focused on healthcare can lead to better medical facilities and healthier communities.
Q: How do companies benefit from CSR?
- Answer: Companies benefit from CSR by building a positive reputation, earning customer trust, and fostering employee satisfaction. Engaging in CSR can also attract investors and create a loyal customer base who appreciate the company’s commitment to social good.
Q: What are some examples of successful CSR initiatives?
- Answer: Successful CSR initiatives include companies providing clean drinking water to rural areas, supporting women’s empowerment programs, reducing their carbon footprint, and investing in renewable energy. These actions not only help the environment and communities but also set a standard for other businesses to follow.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

