
Sustainable development once hailed as the guiding principle for global progress, found itself at a crossroads in recent years. Amidst pressing environmental challenges, socio-economic inequalities, and geopolitical tensions, the pursuit of sustainability seemed to falter, veering off course from its intended trajectory. However, amidst the setbacks and stagnation, there emerges a renewed sense of urgency and determination to steer the course back on track. As the world grapples with the repercussions of climate change, resource depletion, and social injustices, the imperative for sustainable development has never been clearer. Now, more than ever, there is a collective call to action to reinvigorate efforts towards a future where prosperity is not at the expense of the planet or its people. It’s time to reclaim the promise of sustainable development and forge a path towards a more equitable, resilient, and harmonious world.
Contents
Topic: Sustainable Development back on track
Tags: GS Paper – 3, Inclusive Growth — Environmental Pollution & Degradation — Conservation — International Treaties & Agreements
GS 2:Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
GS 3: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Context:
- The United Nations Summit on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) convened in New York to evaluate advancements towards the 17 SDGs established in Agenda 2030, which was ratified by the UN General Assembly in 2015.
- Progress towards SDGs has been slow, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and other crises, particularly in environmental and biodiversity-related goals.

United Nations Summit Overview:
- The UN summit in New York (September 18-19) focused on evaluating the progress of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Adopted in 2015, the Agenda-2030 set forth 17 SDGs with 169 targets, aiming for completion by 2030.
- Though the program is non-binding, it represents a global commitment to shift towards sustainable development.
- The summit underscored the collaborative international effort required to achieve these goals.
- The session provided a platform for nations to reassess and recommit to the SDGs amidst varying degrees of progress.
What is Sustainable Development?
- Development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs’.
- This most widely accepted definition of Sustainable Development was given by the Brundtland Commission in its report Our Common Future (1987).
- Sustainable development (SD) calls for concerted efforts towards building an inclusive, sustainable and resilient future for people and the planet.
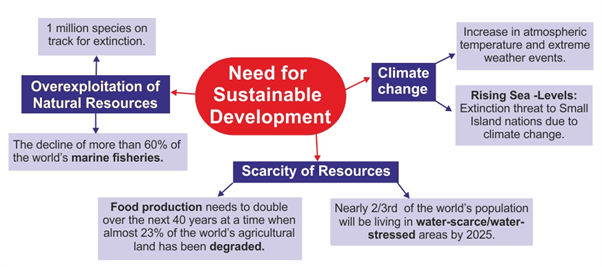
Core Elements of Sustainable Development:
- Sustainable development encompasses three fundamental elements: economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection. Achieving harmony among these elements is essential.
- Economic Sustainability: Sustainable economic growth, alongside the attainment of sustainable livelihoods and the integration of appropriate technology, plays a pivotal role in sustainable development. It emphasises living in harmony with nature while fostering economic progress.
- Environmental Sustainability: It prioritises the protection and prudent utilisation of natural resources. Aspects such as environmental conservation, investment in renewable energy, water conservation, promotion of sustainable transportation, and innovation in eco-friendly construction contribute to advancing environmental sustainability.
- Social Sustainability: Social sustainability promotes gender equality and the holistic development of individuals, communities, and cultures to ensure a fair and equitable quality of life, encompassing healthcare and education on a global scale.
- Economic Sustainability: Economic sustainability focuses on fostering inclusive economic growth that benefits all members of society without causing harm to the environment.
The Sustainable Development Goals back on track after the covid -19:
- Global Cooperation and Partnerships: As of April 2024, COVAX has delivered over 2.8 billion doses to 144 countries, contributing to the recovery from the pandemic and advancing health-related SDGs.
- Digital Transformation and Innovation: According to the International Telecommunication Union, by the end of 2021, over 4.9 billion people were using the internet, facilitating access to essential services and education, thereby supporting SDGs related to health and education.
- Green Recovery and Climate Action: The International Renewable Energy Agency reported that renewable energy capacity grew by over 260 gigawatts in 2021, contributing to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and advancing SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
- Social Protection and Resilience Building: The World Bank estimates that as of 2022, over 200 countries have introduced or adapted social protection programs in response to the pandemic, providing critical support to vulnerable populations and contributing to progress on SDGs related to poverty reduction and social equity.
- Addressing Inequalities and Leaving No One Behind: According to the United Nations Development Programme, as of 2022, over 150 countries have implemented measures to address disparities exacerbated by the pandemic, such as expanding access to healthcare and social services, contributing to SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
- Rebuilding Sustainable Economies: The International Labour Organization reported that as of 2021, over 100 countries have adopted policies to promote green employment and sustainable economic recovery, supporting progress towards SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production.
Global issues Related to Sustainable Development:
- Poverty and Inequality: The presence of a significant population living in poverty and income disparity undermines the objectives of SDG 1 (No Poverty) and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequality), posing substantial challenges to global development efforts.
- Environmental Degradation: Striking a balance between economic growth and environmental preservation is critical, as severe challenges such as deforestation and pollution directly impact progress towards SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
- Education and Healthcare: Disparities in access to education and healthcare services, as well as variations in their quality and infrastructure, hinder the achievement of SDG 4 (Quality Education) and SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), representing significant obstacles to human development.
- Urbanisation: The rapid pace of urbanisation brings about various challenges, including strain on infrastructure and environmental resources, thus impeding progress towards SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
- Gender Equality: Persistent gender discrimination poses a formidable challenge to the realisation of SDG 5 (Gender Equality), perpetuating inequalities in access to opportunities and resources worldwide.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Ensuring food security while promoting sustainable agricultural practices is a complex endeavour, particularly in the face of challenges such as water scarcity and the impacts of climate change, which directly affect progress towards SDG 2 (Zero Hunger).
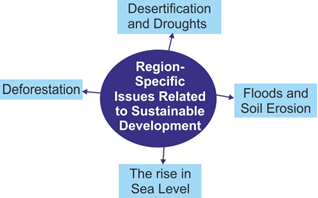
Way forward:
- To operationalize sustainable development, a unified focus is crucial, integrating the efforts of diverse stakeholders globally. Recognizing the diversity across geography, society, economics, and technological capabilities is essential.
- Developed nations must shift their production and consumption behaviours, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and plastics. Encouraging investments, both public and private, that align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is imperative.
- Protecting environmental resources such as the atmosphere, rainforests, and oceans is vital for their role in providing ecosystem services. Collaboration among all stakeholders is necessary for their conservation, restoration, and sustainable utilisation.
- Overhauling the food system requires changes in infrastructure, cultural norms, societal attitudes, and policies. This transformation is essential to move away from the current unsustainable practices.
- Achieving the 2030 goals demands a deeper, faster, and more ambitious response. This entails unleashing a comprehensive social and economic transformation.
- Attaining a more optimistic future necessitates significant shifts in development policies, incentives, and actions. Embracing these changes is crucial for steering towards sustainability and achieving the desired outcomes.
Conclusion:
Hence, the year 2024 represents a pivotal moment in our journey towards sustainable development. By embracing this opportunity and taking decisive action, we can overcome the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic and accelerate progress towards achieving the SDGs. Together, let us commit to building a future that is more equitable, resilient, and sustainable for generations to come.
UPSC PYQ
Prelims
Q:1 Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the ‘Club of Rome’.
- The Sustainable Development Goals have to be achieved by 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: b)
Q:2 With reference to ‘Agenda 21’, sometimes seen in the news, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is a global action plan for sustainable development.
- It originated in the World Summit on Sustainable Development held in Johannesburg in 2002.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Q:3 The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE), a UN mechanism to assist countries in transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at (2018)
- The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
- The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
- The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris
- The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
Answer: b)
Mains:
Q:1 Define the concept of carrying capacity of an ecosystem as relevant to an environment. Explain how understanding this concept is vital while planning for sustainable development of a region. (2019)
Source: (TH)
FAQs
Q: What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable Development is a holistic approach to meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses economic, social, and environmental dimensions, aiming for a balanced and equitable future.
Q: Why is Sustainable Development Important?
Sustainable Development is crucial for ensuring a harmonious coexistence between humanity and the planet. It promotes responsible resource management, reduces poverty, fosters social inclusion, and mitigates environmental degradation, ultimately striving for a more resilient and prosperous global society.
Q: How Can Sustainable Development Be Achieved?
Achieving Sustainable Development requires collaborative efforts across governments, businesses, communities, and individuals. This involves implementing policies and practices that promote renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, conservation of natural resources, equitable access to education and healthcare, and the protection of biodiversity and ecosystems.
Q: What are Some Challenges to Sustainable Development?
Challenges to Sustainable Development include inadequate access to resources, socio-economic disparities, unsustainable consumption patterns, climate change, environmental degradation, and political barriers. Overcoming these challenges necessitates innovative solutions, effective governance, and a collective commitment to change.
Q: What Role Can Individuals Play in Advancing Sustainable Development?
Individuals can contribute to Sustainable Development through everyday actions such as reducing energy consumption, conserving water, minimizing waste, supporting ethical and eco-friendly products, advocating for sustainable policies, participating in community initiatives, and raising awareness about the importance of sustainability. By making conscious choices, individuals can collectively drive positive change towards a more sustainable future.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

