
The Swiss Peace Summit stands as a beacon of diplomatic prowess and global cooperation, bringing together leaders, thinkers, and advocates from around the world to address pressing issues of conflict resolution, peacebuilding, and sustainable development. Nestled amidst the serene landscapes of Switzerland, renowned for its neutrality and commitment to peace, this summit serves as a platform for dialogue, innovation, and collaboration, aimed at forging pathways towards a more harmonious and equitable world. With its rich history of hosting pivotal diplomatic negotiations and its reputation as a hub for humanitarian efforts, Switzerland provides an ideal backdrop for the convergence of minds and the cultivation of solutions to the most complex challenges facing humanity. As delegates gather in this idyllic setting, they embark on a collective journey towards fostering understanding, fostering dialogue, and laying the groundwork for lasting peace.
Tags: GS Paper – 2, Russia-Ukraine- Bilateral Groupings & Agreements- Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India’s Interests
Prelims: New START treaty, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Black Sea Food grain initiative.
Mains: Impacts of Russia-Ukraine conflict on India, Global impacts.
Contents
Context:
- Switzerland announced it would host a major summit in June as a “first step” for lasting peace in the Russia-Ukraine war.
- More than 100 countries, including India and Russia, are invited to participate.
- Earlier, Turkey was able to negotiate the Black Sea grain deal, which allowed the movement of grains from Ukraine through the Black Sea.
Russia – Ukraine Conflict Background:
- Post the disintegration of the Soviet Union, Ukraine gained independence in 1991. Ukraine was a member of the Soviet Union until 1991 when it disintegrated, and Russia has tried to maintain the country in its orbit since then.
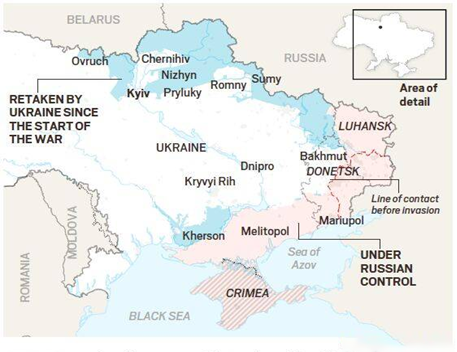
- In 2014, a separatist insurgency started in Ukraine’s eastern industrial heartland, Donetsk Basin, also known as Donetsk Basin.
- Russia further gained a maritime advantage in the region due to its invasion and annexation of Crimea. As a result, both the US and the EU have pledged to safeguard the integrity of Ukraine’s borders.
Reasons for Russian Aggression:
- Economic Factors
- Russia aimed for Ukraine’s membership in the Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC), a free trade agreement established in 2015, due to Ukraine’s significant market size and advanced agricultural and industrial sectors. However, Ukraine declined to join the agreement.
- Geo-Political and Strategic Factors
- Russia perceives NATO’s eastward expansion, which it terms “enlargement,” as a threat to its interests. It has demanded written security guarantees from NATO.
- Additionally, NATO, led by the U.S., has proposed installing missile defence systems in Eastern Europe, including Poland and the Czech Republic, to counter Russia’s intercontinental-range missiles.
Russia’s Demands:
- Expansion Ban: Russia demands a halt to further NATO expansion, particularly including countries like Ukraine and Georgia that share borders with Russia.
- Military Deployment: Russia urges NATO to reduce its military deployments to 1990s levels and to prevent the deployment of intermediate-range missiles near Russia’s borders.
- Military Cooperation: Russia calls for NATO to limit its military collaboration with Ukraine and other former Soviet republics.
Response from the West:
- NATO Policy: The U.S. maintains NATO’s “open-door policy,” signalling continued membership inductions.
- Support for Ukraine: The U.S. commits to providing training and weapons to Ukraine.
- Discussion on Missile Deployment: The U.S. is open to discussing missile deployments and mutual reductions in military exercises in Eastern Europe.
- Germany’s Warning: Germany warns Russia that the Nord Stream 2 pipeline project could be halted if Russia invades Ukraine.
- Economic Sanctions: The U.S. threatens Russia with new economic sanctions in case of any invasion attempts against Ukraine.
Demands of Russia and Ukraine:
- Ukraine’s 10-point plan:
- It focuses on:
- Restoring Ukraine’s territorial integrity,
- Withdrawal of Russian troops and cessation of hostilities,
- Restoration of Ukraine’s state borders with Russia.
- Other demands include the release of prisoners and food security.
- Russia 12-point plan
- Russia rejected the Ukrainian plan; however, it supports the Chinese 12-point plan.
- It focuses on hostilities and protecting civilians but makes no mention of Russia returning territory.
- It also stressed that “The security of a region should not be achieved by strengthening or expanding military blocs”, indirectly referring to NATO expansion.
- Russia has maintained its aims of “denazification, demilitarisation, and neutral status” of Ukraine.
India’s Stand:
- Call for Peaceful Resolution: India advocates for a peaceful resolution of the situation through sustained diplomatic efforts, aiming for long-term peace and stability in the region and beyond.
- Abstention from UN Votes: India abstained from voting in the UN General Assembly on resolutions condemning Russia’s actions in Ukraine, maintaining a stance of neutrality.
- Voting Patterns: In 2020, India voted against a Ukraine-sponsored resolution in the UN General Assembly, reflecting its neutrality and adaptation to the post-2014 status quo on Ukraine.
Way Forward:
- Reviving Diplomatic Efforts: The US and other Western countries are expected to revive the peace process through diplomatic channels, although this process may be time-consuming.
- Emphasis on Dialogue: Experts recommend increased dialogue between the West and Russia, focusing on the issues surrounding Ukraine.
- Normandy Format Allies: Ukraine should work with its Normandy Format allies, France and Germany, to persuade Russia to withdraw support for proxies and facilitate the region’s safe reintegration into Ukraine.
- Geoeconomic Approach: Preventing Russian military expansion in Ukraine could involve geoeconomic measures, such as leveraging trade relations, including the Nord Stream pipeline.
- Addressing Internal Disturbances: Addressing internal disturbances in Ukraine is crucial for reviving the Minsk II agreement and fostering peace in the region, thereby easing tensions.
FAQs
1. What is the Swiss Peace Summit?
The Swiss Peace Summit is an annual gathering held in Switzerland, bringing together global leaders, policymakers, activists, and scholars to discuss pressing issues related to peacebuilding, conflict resolution, and humanitarian efforts.
2. When and where does the Swiss Peace Summit take place?
The Swiss Peace Summit typically occurs in Switzerland, known for its neutrality and commitment to peace. It usually takes place in the summer months, providing a conducive environment for constructive dialogue and collaboration.
3. Who attends the Swiss Peace Summit?
The Summit attracts a diverse range of participants, including heads of state, diplomats, representatives from international organizations such as the United Nations, civil society leaders, academics, and grassroots activists. This diversity fosters inclusive discussions and innovative approaches to peacebuilding.
4. What are the key themes addressed at the Swiss Peace Summit?
Themes vary from year to year but often include topics such as conflict prevention, peace mediation, post-conflict reconstruction, human rights, gender equality in peace processes, and the role of technology in peacebuilding. The Summit aims to tackle both longstanding challenges and emerging issues in the field of peace and security.
5. What outcomes result from the Swiss Peace Summit?
The Summit serves as a platform for exchanging ideas, sharing best practices, and forging partnerships to advance peace and stability globally. Participants often collaborate on joint initiatives, endorse declarations or resolutions, and commit to concrete actions aimed at promoting peace, justice, and sustainable development.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

