The effective management of land and water resources stands as an indispensable pillar in the alleviation of human miseries. As the global population burgeons and environmental challenges escalate, the judicious utilization and preservation of these finite resources become paramount. Land, a finite asset, serves as the foundation for food production, settlement, and various economic activities. Effective land management involves sustainable agricultural practices, afforestation, and urban planning that ensure the equilibrium between human needs and ecological integrity. Simultaneously, water, a vital yet increasingly scarce resource, necessitates meticulous management to meet the burgeoning demands of a growing population. Sustainable water resource management involves efficient distribution, conservation, and pollution mitigation. Access to clean water not only directly impacts public health but also influences agricultural productivity and industrial processes. In regions grappling with water scarcity, equitable and efficient water management can mitigate conflicts and enhance societal well-being. In essence, the effective management of land and water resources is intricately linked to the mitigation of hunger, poverty, and health disparities. A strategic approach to resource management not only safeguards ecosystems but also ensures a resilient foundation for socio-economic development, thereby contributing significantly to the reduction of human miseries on a global scale.
Tag: Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent).
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In Introduction, try to define effective management of land resources and effective management of water resources.
- In Body, elaborate separately, how the effective management of land and water resources will drastically reduce the human miseries.
- Conclude with the solutions, like using nuclear technologies, for effective management of land and water resources.
Answer:
Effective management of land resources is the use of land to meet changing human needs (agriculture, forestry, conservation), by ensuring long-term socioeconomic and ecological functions of the land. Effective management of water resources incorporates the reduction in loss and wastage of water and harvesting, collection, and improved storage of water. The management of land and water are essential for mankind’s survival and to achieve growth and sustainable life.
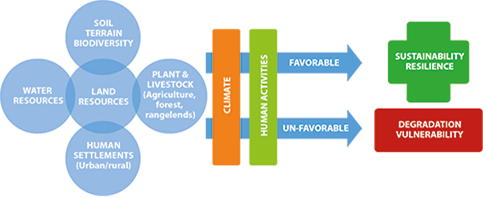
Effective land management can reduce human misery:
- Food Security and Nutrition: According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), about 690 million people suffer from hunger globally, and malnutrition affects around 2 billion people. Sustainable agricultural practices, like crop rotation and organic farming, have the potential to increase crop yields by up to 79%, improving food availability and reducing hunger.
Example: In Malawi, the Sustainable Agriculture Production Programme (SAPP) has been implemented to improve food security and nutrition among smallholder farmers.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) reported that between 2000 and 2022, over 1.4 million people lost their lives due to disasters, and these events affected approximately 6.2 billion people globally. Preserving natural buffer zones, such as mangroves and wetlands, can reduce the impact of coastal flooding by acting as natural barriers.
Example: In Vietnam, the protection and preservation of mangrove forests have been instrumental in reducing the impact of coastal flooding and storm surges.
- Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Services: The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) estimates that we lose approximately 18.7 million acres of forests each year, leading to biodiversity loss and ecological imbalances. Conserving natural habitats, such as old-growth forests and marine protected areas, helps preserve biodiversity and ecosystem services like pollination and water purification.

Example: the Great Barrier Reef contributes significantly to Australia’s economy, generating approximately AU$6.4 billion each year and supporting around 64,000 jobs through industries such as tourism, fishing, and research.
- Sustainable Land Use and Urban Planning: The United Nations projects that by 2050, around 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas. Well-planned and compact cities can reduce the environmental footprint, lower energy consumption, and provide better access to services for urban dwellers.
Example: According to the Singapore Land Authority, as of 2022, approximately 14% of the country’s land area is designated as nature reserves and green spaces.
- Community Resilience and Livelihoods: The International Labour Organization (ILO) states that 80% of the world’s population depends on the informal economy for their livelihoods. Sustainable land management practices can create opportunities for eco-friendly livelihoods, such as ecotourism and sustainable agriculture, helping to reduce poverty and enhance economic stability.
Example: According to the Costa Rican Tourism Institute, eco-tourism is a significant contributor to the country’s economy, accounting for approximately 40% of the total tourism revenue.
Effective water management can reduce human misery:
- Access to Clean Water and Sanitation: According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF, as of 2023, around 785 million people still lack access to improved drinking water sources. Proper water management can improve access to clean and safe water, reducing waterborne diseases and improving overall public health.
Example: In Rwanda, the government has implemented the “Water for Growth” program, which aims to improve access to clean water and sanitation in rural areas.
- Water Scarcity and Stress: The United Nations projects that by 2030, the global demand for water will exceed supply by 40%. As water scarcity and stress continue to increase, effective water management becomes crucial to ensure equitable water distribution and prevent conflicts over water resources.
Example: In Singapore, where water resources are scarce, the government has implemented an innovative water management strategy known as the “Four National Taps.”
- Water-Related Diseases: Unsafe water and poor sanitation are major contributors to water-related diseases, leading to approximately 485,000 diarrheal deaths each year, according to WHO. Effective water management practices, including water treatment and safe disposal of wastewater, can significantly reduce the prevalence of such diseases.
Example: In Bangladesh, where waterborne diseases like cholera are a significant health concern, the introduction of sustainable water management practices has made a positive impact on public health.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Agriculture accounts for around 70% of global water withdrawals, as reported by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). By implementing efficient irrigation techniques and water-saving practices in agriculture, water management can enhance food production and improve food security.
Example: In India, according to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, drip irrigation under the PMKSY has resulted in water savings of up to 40% in some regions, contributing to improved food security and reduced water wastage.
- Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Water management directly impacts aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity. Over-extraction of water from rivers and aquifers can lead to the degradation of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity. Sustainable water management practices can help protect ecosystems, supporting essential services like fish habitats and water purification.
Example: In the Everglades National Park in Florida, USA, sustainable water management practices have been crucial in preserving this unique and biodiverse ecosystem.
Effective management of land and water resources are fundamental to global food security, especially in the face of climate change and increasingly erratic weather. Using nuclear technologies, the development of sustainable land and water management practices can be achieved which will contribute to increasing global agricultural production and food security while conserving natural resources.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


