The Geo-Calculus of the Moscow Visit is all about understanding the strategic importance and implications of India’s Prime Minister visiting Moscow. This visit isn’t just a simple diplomatic trip; it’s a complex calculation involving geopolitical factors, economic interests, and international relations. By meeting Russian leaders, the Indian PM aims to strengthen ties, discuss key issues like trade and defense, and navigate the delicate balance of global politics. This visit could reshape alliances and influence future collaborations, making it a significant event on the world stage.

Tags: GS-2, IR- India and its Neighborhood – Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Contents
- 0.1 Why in the News?
- 0.2 Context:
- 0.3 Evolution of Indo-Russia Relations:
- 0.4 Assessment of the Conflict in Ukraine:
- 0.5 Keeping Russia from China:
- 0.6 Geo-Economic Thrust:
- 0.7 What India Needs to Do?
- 1 Conclusion:
- 2 UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 3 FAQs
- 4 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Why in the News?
- Two weeks after PM Modi’s visit to Russia, the U.S. and Europe continue to respond to the close rapport between Modi and President Putin.
- The visit during the Ukraine conflict faced criticism from Ukrainian President Zelenskyy and disappointment from U.S. officials.
- India has emphasized its right to choose its foreign policy while ensuring its core worldview remains unchanged.
Context:
- Prime Minister’s Visit:
- Significance: Modi’s visit to Russia, his first in his third term, has generated notable reactions from the U.S. and Europe.
- International Reactions: The evident camaraderie between Modi and Russian President Vladimir Putin has faced criticism from Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and various U.S. officials.
- Global Reactions:
- U.S. Concerns: The U.S. State Department, National Security Adviser, and U.S. Ambassador to India have expressed disappointment over the visit, reflecting concerns about its geopolitical implications.
- India’s Stance:
- Freedom of Choice: Despite global reactions, New Delhi has emphasised its “freedom of choice” in foreign policy, asserting that India’s worldview remains unchanged.
- Geopolitical Messaging: The visit has conveyed significant geopolitical messages and highlighted India’s nuanced diplomatic balancing act.
- Diplomatic Dynamics:
- Timing and Context: The visit’s timing amid ongoing global tensions underscores India’s delicate diplomatic balancing on the world stage.
- Strategic Implications: The visit suggests potential shifts in India’s foreign policy approach, emphasising the need to understand both the explicit outcomes and the broader strategic context.
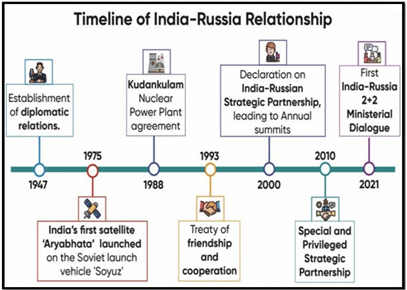
Evolution of Indo-Russia Relations:
- Historical Background:
- Cold War Era Alliance: India and the Soviet Union had a strong strategic, military, economic, and diplomatic relationship during the Cold War.
- Post-Soviet Continuity: Russia continued the robust ties with India after the Soviet Union’s dissolution, maintaining a Special Strategic Relationship.
- Political Relations:
- Annual Commissions: The IRIGC-TEC and IRIGC-MTC commissions meet annually to discuss trade, economic, scientific, technological, cultural, and military-technical cooperation.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Trade Figures: India’s bilateral trade with Russia reached around USD 13 billion in 2021-22, up from USD 8.14 billion in 2020-21.
- Trading Partner Rank: Russia has become India’s seventh-largest trading partner, rising from the 25th position in 2021.
- Defence and Security Relations:
- Joint Military Exercises: India and Russia regularly conduct the Tri-Services exercise ‘INDRA’ and collaborate on military programs like BrahMos missiles and Sukhoi Su-30MKI aircraft.
- Military Hardware: India has acquired significant military hardware from Russia, including the S-400 Triumf, Kamov Ka-226 helicopters, and INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier.
- Science and Technology:
- Historical Collaboration: Soviet assistance was crucial in establishing Indian institutions such as IIT Bombay and the early Indian space program.
- Current Projects: Ongoing collaboration includes basic sciences, Gaganyaan manned spaceflight program, nanotechnologies, and quantum computing.
Assessment of the Conflict in Ukraine:
- Timing of the Visit:
- Visit’s Timing: Modi’s visit to Russia, two years after the Ukraine war began, reflects an evolving assessment of the conflict’s progression.
- Initial Response:
- Public Messaging: Modi initially avoided the 2022 and 2023 India-Russia summits, focusing on his statement at the SCO summit in Uzbekistan about “this era is not of war.”
- Conflict Evolution:
- Current Situation: The visit must be seen in the context of the Ukraine conflict’s evolution, with Russia maintaining control over eastern Ukraine despite earlier setbacks.
- Frozen Conflict:
- Peace Process: With Western nations pushing for peace, New Delhi appears to anticipate a frozen conflict, influencing its foreign policy.
- U.S. Political Dynamics:
- Political Changes: Modi’s visit could be a strategic adjustment considering potential changes in U.S. political leadership and a reduced commitment to Ukraine.
- Joint Statement Nuances:
- Language and Diplomacy: The joint statement’s reference to the conflict “around Ukraine” and appreciation for peace proposals reflects a strategic diplomatic balance.
Keeping Russia from China:
- Geopolitical Signalling:
- Prioritising Engagement: Modi’s visit to Moscow, instead of attending the SCO Summit in Astana, highlights India’s strategic intent to prioritise engagement with Russia.
- China-Russia Dynamics:
- Contrasting Messages: This contrasts with Western efforts urging China to reduce support for Russia, showcasing India’s intent to maintain close ties with Russia amid tensions with China.
- Indo-Pacific Concerns:
- Balancing Act: India balances its partnerships in the Indo-Pacific with the need to maintain relations with Russia, reflecting complex strategic calculations.
- U.S. Actions:
- Strategic Reassessment: Recent U.S. initiatives, such as AUKUS and “Quad Plus,” prompt India to reassess its strategic positioning within these evolving alliances.
- Quad’s Utility:
- Effectiveness: India seeks to reinvigorate the Quad (India, Japan, Australia, U.S.) amidst shifting global dynamics, questioning the partnership’s effectiveness.
- Strategic Autonomy:
- Diplomatic Options: The visit underscores India’s strategic autonomy, demonstrating its diverse diplomatic options beyond any single alliance.
Geo-Economic Thrust:
- Economic Context:
- Trade Relations: Modi’s visit must be viewed within a geo-economic context, focusing on sustaining and enhancing India-Russia trade relations amidst Western sanctions.
- Trade Growth:
- Surge in Trade: India-Russia trade has surged, driven by discounted Russian oil imports. Developing effective payment mechanisms is crucial to sustaining this growth.
- Joint Vision Statement:
- Trade Measures: The Modi-Putin summit outlined a Joint Vision statement on trade by 2030, focusing on circumventing Western sanctions and enhancing bilateral economic cooperation.
- Far East Cooperation:
- Energy and Commodities: Cooperation in Russia’s Far East aims to boost energy supplies and commodity exports, leveraging the Chennai-Vladivostok maritime corridor.
- Investment Strategies:
- Mutual Investments: Both nations aim for mutual investments, highlighted by significant deals such as Rosneft’s stake in India’s Vadinar refinery and Indian stakes in Russian oil fields.
- Sanction Dynamics:
- Avoidance of Sanctions: U.S. and European sanctions have largely avoided targeting these transactions, allowing continued economic ties and anticipating future deals.
What India Needs to Do?
- Strengthen Diplomatic Channels: Enhance engagements with both Russia and Western countries to maintain a balanced foreign policy, ensuring India’s strategic autonomy.
- Promote Strategic Autonomy: Assert independence in foreign policy decisions, maintaining relationships with major powers based on national interests.
- Expand Economic Cooperation: Develop mechanisms to sustain and grow trade relations with Russia, focusing on energy and commodities while navigating Western sanctions.
- Diversify Energy Sources: Secure long-term energy agreements with Russia and explore new energy corridors like the Chennai-Vladivostok maritime route.
- Invest in Joint Ventures: Encourage investments between Indian and Russian sectors, focusing on mutual benefits in oil, gas, and infrastructure.
- Leverage Multilateral Forums: Use platforms like BRICS, SCO, and the G20 to foster dialogue and cooperation with Russia and other key global players.
- Enhance Defence Collaboration: Continue defence cooperation with Russia, focusing on technology transfer, joint exercises, and diversification of military hardware.
- Support Peace Initiatives: Engage in global efforts to resolve the Ukraine conflict, promoting peace proposals that align with international law and the UN Charter, while balancing relations with both Russia and Ukraine.
Conclusion:
Prime Minister Modi’s visit to Russia underscores India’s strategic autonomy and long-term commitment to bilateral ties with Russia. Despite global reactions and uncertainties, the visit highlights India’s nuanced diplomatic approach, focusing on enhancing strategic and economic relations while maintaining diverse diplomatic options.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q:1 Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Ans: B
Mains
Q:1 What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)
Source: TH
FAQs
Q: What does “Geo-Calculus of the Moscow Visit” mean?
- Answer: “Geo-Calculus of the Moscow Visit” refers to the strategic and geopolitical considerations behind a political leader’s visit to Moscow. It involves analyzing the potential impacts and motivations of the visit on international relations and political alliances.
Q: Why is the Moscow visit important for India?
- Answer: The Moscow visit is important for India because it helps strengthen diplomatic and economic ties with Russia. It can lead to new agreements on trade, defense, energy, and other areas, which are crucial for India’s national interests and global standing.
Q: What are the key goals of the Moscow visit?
- Answer: The key goals of the Moscow visit typically include enhancing bilateral relations, securing strategic partnerships, discussing mutual interests in global politics, and negotiating trade deals. It’s also an opportunity to address any existing issues and explore new areas of cooperation.
Q: How does the Moscow visit affect global geopolitics?
- Answer: The Moscow visit can influence global geopolitics by shifting alliances and power balances. It can impact relations with other countries, especially those watching the dynamics between India and Russia. It also sends signals about India’s foreign policy priorities and its stance on international issues.
Q: What are the potential challenges during the Moscow visit?
- Answer: Potential challenges during the Moscow visit include managing differing national interests, navigating complex international relationships, and ensuring that agreements made are beneficial and sustainable. There can also be external pressures and reactions from other global players monitoring the visit.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

