
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Report Links Wildlife Trafficking to Organized Crime
- 2 Surrogacy Law
- 3 Road Accidents in India
- 3.1 In News
- 3.2 Key Findings of the “Road Accidents in India-2022” report are as follows:
- 3.3 What is the current condition of India’s road network?
- 3.4 To mitigate road accidents, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has implemented a range of measures:
- 3.5 Initiatives related to road safety encompass International and Indian efforts:
- 4 President Terminates Services of an Indian Army Major
- 4.1 In News
- 4.2 What ethical issues were associated with the actions of the Army Major and the subsequent decision to terminate their service?
- 4.3 Articles 309, 310, and 311 of the Indian Constitution pertain to the regulation and governance of civil services.
- 4.4 What are some key clauses in the Army Act, 1950?
- 5 OECD Report Highlights Taxation of Indian Farmers
- 6 India-Bangladesh Jointly Inaugurated Major Development Projects
- 7 Kozhikode and Gwalior in UNESCO Creative Cities Network
- 8 India’s Widening Tax Base
- 9 Bolivia
- 10 Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary
- 11 Sustainability Bond
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Report Links Wildlife Trafficking to Organized Crime
Tag: GS-2 Polity
In News
The Wildlife Justice Commission (WJC) has published a 2023 report highlighting the increasing intersection of wildlife crime with various other forms of organized crime.
Key Takeaways from The Study
- Unveiling of strong links between wildlife trafficking and various organized crime activities, such as protection rackets, extortion, murder, money laundering, illicit drugs, tax evasion, and corruption.
- Additionally, it recognizes illegal sand mining as an environmental crime, with detrimental consequences like erosion, aquifer damage, and violence by sand mafias.
- The report offers case studies from different regions showcasing convergence between crimes, and it underscores the urgency of studying and integrating crime convergence into strategies for combatting both wildlife and organized crime, aiming to provide typologies and strategies for law enforcement and policymakers to address transnational organized crime more effectively.
About Organised Crime
- Organized crime activities refer to actions conducted collectively or individually by members of a criminal gang or syndicate, with the aim of gaining financial or other advantages.
Types of Organized Crime:
- These activities encompass organized gang criminality, racketeering, syndicate crime, drug trafficking, cybercrime, human trafficking, money laundering, violence, people smuggling, extortion, and counterfeiting.
- These criminal operations typically operate discreetly, taking advantage of gaps in law enforcement and regulations.
Legal Status in India Regarding Organized Crime:
- At the national level, India lacks a specific law to address organized crime.
- Existing laws, such as the National Security Act of 1980 and the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act of 1985, are inadequate as they primarily target individuals rather than criminal groups or enterprises.
- Several Indian states, including Gujarat, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh, have enacted their own laws to combat organized crime, such as the Gujarat Control of Organised Crime Act of 2015, the Karnataka Control of Organised Crime Act of 2000, and the Uttar Pradesh Control of Organised Crime Act of 2017.
- India is also a signatory to various international conventions and treaties, including the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC), the United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC), and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC).
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2017) Q.Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC): TRAFFIC is a bureau under United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The mission of TRAFFIC is to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature. Which of the above statements is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) Mains (2019) Q. Coastal sand mining, whether legal or illegal, poses one of the biggest threats to our environment. Analyse the impact of sand mining along the Indian coasts, citing specific examples. |
Source: DTE
Surrogacy Law
Tag: GS-2 Issues Related to Women, Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Arising Out of Design & Implementation of Policies, Social Empowerment
In News
The Delhi High Court has raised concerns regarding the linkage between marital status and eligibility for surrogacy as per the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act of 2021.
About Surrogacy
- Surrogacy is an arrangement where a woman, known as the surrogate, agrees to carry and deliver a child on behalf of another person or couple, who are the intended parents.
- The surrogate, sometimes referred to as a gestational carrier, becomes pregnant and gives birth to the child for the intended parent/s.
Altruistic Surrogacy:
This type of surrogacy involves no financial compensation for the surrogate mother, except for covering her medical expenses and providing insurance during the pregnancy.
Commercial Surrogacy:
Commercial surrogacy, on the other hand, entails surrogacy or related procedures carried out in exchange for financial rewards or benefits, whether in cash or other forms, that exceed the basic medical expenses and insurance coverage.
The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act of 2021 outlines the following provisions:
Eligibility for Surrogacy:
- Widows or divorcees aged 35 to 45, and legally married couples, can opt for surrogacy if they have a medical requirement for it.
- The intended couple must be a legally married Indian man and woman.
- The man’s age should be between 26 and 55 years, and the woman’s age should be between 25 and 50 years.
- They should not have any biological, adopted, or surrogate child from previous arrangements.
Ban on Commercial Surrogacy:
- The law prohibits commercial surrogacy, and violations can lead to a prison sentence of up to 10 years and a fine of up to Rs 10 lakhs.
Altruistic Surrogacy:
- The law permits only altruistic surrogacy, where no financial transactions occur, and the surrogate mother has a genetic connection to those seeking a child.
Challenges with the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act of 2021 include:
- The Act’s ban on commercial surrogacy shifts from a rights-based approach to a needs-based approach, potentially limiting women’s autonomy in making reproductive choices and their right to parenthood, despite intending to prevent the exploitation of poor women and protect the child’s right to be born.
- The Act reinforces traditional patriarchal norms by not recognizing the economic value of women’s work, impacting women’s fundamental rights to reproduce under Article 21 of the constitution.
- Altruistic surrogacy involving a friend or relative as the surrogate mother can lead to emotional complications for both the intending parents and the surrogate child, risking relationships during and after the surrogacy period.
- Altruistic surrogacy limits the choice of surrogate mothers, as very few relatives may be willing to undergo the surrogacy process.
- Altruistic surrogacy lacks third-party involvement, which can help intended couples and surrogate mothers navigate the complex process and ensure financial support during surrogacy.
- Unmarried women, single men, live-in partners, and same-sex couples are excluded from availing surrogacy services, which amounts to discrimination based on marital status, gender, and sexual orientation, denying them the right to form a family according to their choice.
Recent Developments
- The recent changes made by the Supreme Court include an amendment to the law that bans the use of donor gametes in surrogacy, requiring “intending couples” to use their own gametes.
- A legal challenge was filed, claiming that this amendment violates a woman’s right to parenthood.
- The Supreme Court interpreted “genetically related” to mean related to the husband and emphasized that gestational surrogacy decisions are “woman-centric,” based on a woman’s inability to become a mother due to medical or congenital conditions.
- The Court clarified that when specific medical or congenital conditions apply, the child must be related to the intended couple, particularly the husband.
- Additionally, the Supreme Court temporarily halted the enforcement of Rule 7 of the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, which had prohibited the use of donor eggs in surrogacy.
- This decision allowed a woman with Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) Syndrome, a rare congenital disorder affecting the female reproductive system, to undergo surrogacy using a donor egg.
The Path Ahead
- India can create a strong legal structure for surrogacy by giving priority to inclusivity, ethical considerations, and advancements in medical practices.
- This framework should uphold the rights of individuals, promote the welfare of everyone involved, and provide assistance to those wanting to build families using assisted reproductive technologies.
Source: IE
Road Accidents in India
Tag: GS- 3 GS- 2 Infrastructure, Government Policies & Interventions
In News
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has released a report titled “Road Accidents in India-2022,” highlighting alarming patterns in road accidents and resulting fatalities.
Key Findings of the “Road Accidents in India-2022” report are as follows:
- In 2022, India witnessed 4,61,312 road accidents, resulting in 1,68,491 fatalities and 4,43,366 injuries, showing significant increases of 11.9% in accidents, 9.4% in fatalities, and 15.3% in injuries compared to the previous year.
- Road accidents were distributed as follows: 32.9% on National Highways and Expressways, 23.1% on State Highways, and 43.9% on other roads. Fatalities were spread similarly, with 36.2% on National Highways, 24.3% on State Highways, and 39.4% on other roads.
- Young adults aged 18-45 constituted 66.5% of victims in 2022, and individuals in the working age group of 18-60 made up 83.4% of road accident fatalities.
- Rural areas accounted for 68% of road accident deaths, while urban areas contributed 32% to the total accident deaths in the country.
- Two-wheelers were the leading category in both total accidents and fatalities for the second consecutive year, with light vehicles (cars, jeeps, and taxis) in second place.
- Two-wheeler riders were the most affected road users, representing 44.5% of persons killed in road accidents in 2022, followed by pedestrians at 19.5%.
- Tamil Nadu had the highest number of road accidents (13.9%), while Uttar Pradesh had the highest number of fatalities (13.4%).
- In international comparison, India had the highest number of total persons killed in road accidents, followed by China and the United States. Venezuela had the highest rate of persons killed per 1,00,000 population.
What is the current condition of India’s road network?
- In 2018-19, India’s road density was relatively high at 1,926.02 per 1,000 sq.km of area, surpassing that of many developed countries, despite the fact that surfaced/paved roads accounted for only 64.7% of the total road length, which was comparatively lower than developed nations.
- National Highways constituted 2.09% of the total road length in 2019, with the remaining road networks comprising State Highways (2.9%), District Roads (9.6%), Rural Roads (7.1%), Urban Roads (8.5%), and Project Roads (5.4%).
To mitigate road accidents, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has implemented a range of measures:
- The Ministry conducts awareness campaigns through various media platforms and supports road safety advocacy initiatives by providing financial assistance to relevant agencies.
- Road safety is integrated into road design from the planning stage, and Road Safety Audits (RSAs) are mandated for all highway projects at every stage. Additionally, the Ministry has enforced the mandatory provision of airbags for front seat passengers in vehicles.
- The Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act of 2019 is in place to strengthen road safety regulations. Electronic monitoring and enforcement of road safety rules are conducted through devices like speed cameras, body-wearable cameras, and dashboard cameras to ensure compliance with road safety rules and regulations.
International efforts:
- Brasilia Declaration on Road Safety (2015)
- This declaration, signed at the Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety in Brazil, includes India as a signatory.
- It aims to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 3.6, which targets a 50% reduction in global road traffic accident deaths and injuries by 2030.
- Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030
- Adopted by the UN General Assembly, this resolution sets an ambitious goal of preventing at least 50% of road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- It aligns with the holistic approach emphasized in the Stockholm Declaration.
- International Road Assessment Programme (iRAP)
- iRAP is a registered charity committed to saving lives by improving road safety worldwide.
Indian Efforts:
- Motor Vehicles Amendment Act, 2019
- This Act increases penalties for traffic violations, addresses issues like defective vehicles and juvenile driving, and establishes a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund for compulsory insurance coverage of road users in specific accident scenarios.
- It also provides for the creation of a National Road Safety Board by the Central Government.
- The Carriage by Road Act, 2007
- This Act regulates common carriers, limiting their liability and determining the value of goods delivered to them.
- It helps ascertain their liability for loss or damage to goods due to their negligence or criminal actions.
- The Control of National Highways (Land and Traffic) Act, 2000
- This Act regulates land within National Highways, their right of way, and traffic on National Highways.
- It also addresses the removal of unauthorized occupation on these highways.
- National Highways Authority of India Act, 1998
- This Act establishes an authority responsible for the development, maintenance, and management of National Highways, along with related matters.
Source: PIB
President Terminates Services of an Indian Army Major
Tag: GS-2 Polity
In News
The President of India has removed an Indian Army Major serving in a Strategic Forces Command (SFC) unit due to their engagement in significant national security violations, as identified in an Army investigation.
What ethical issues were associated with the actions of the Army Major and the subsequent decision to terminate their service?
- An Army inquiry revealed ethical violations by a Major, leading to the termination of their services by the President under legal authority.
- This emphasizes the military’s commitment to ethics, integrity, and national security.
- It also highlights disciplinary actions against others for social media policy violations, reinforcing the importance of a Code of Conduct.
- The incident underscores the Army’s vigilance in safeguarding classified information and upholding moral standards and constitutional duties.
Articles 309, 310, and 311 of the Indian Constitution pertain to the regulation and governance of civil services.
- Article 309 of the Indian Constitution grants the Parliament and State legislatures the authority to regulate the recruitment and terms of service for individuals appointed to public roles related to Union and State affairs.
- Article 310 establishes that civil servants work at the discretion of the President for Union employees and the Governor for State employees, adhering to the “Pleasure Doctrine.”
- However, this governmental power is not absolute.
- Article 311 specifies that no government employee can be dismissed or removed by a lower authority than the one that appointed them.
- Additionally, no civil servant can be dismissed, removed, or demoted without a proper inquiry, including informing the individual of the charges and providing them a fair chance to defend themselves.
- There are exceptions to Article 311 (2), such as when an individual is convicted of a criminal offense, when an inquiry is deemed impractical due to specific reasons recorded in writing, or when the President or Governor determines that, in the interest of state security, an inquiry should not be held.
What are some key clauses in the Army Act, 1950?
- The Army Act covers various aspects of enlistment and terms of service for army personnel, including recruitment procedures, training, and retirement conditions.
- It also establishes a comprehensive framework for maintaining discipline in the army, outlining different offenses and penalties for misconduct.
- Additionally, the Act addresses the legal framework for conducting courts-martial to try military personnel accused of offenses, defining various types of courts-martial.
- It ensures the legal rights and safeguards of individuals facing court-martial, including the right to legal representation, the right to remain silent, and the right to appeal.
- The Act allows for the detention of military personnel in specific situations, such as when they pose a threat to army security or discipline.
- Furthermore, the Armed Forces Tribunal Act of 2007 creates the Armed Forces Tribunal, a specialized judicial body for hearing appeals and petitions related to military matters.
- The Act also includes miscellaneous provisions concerning the protection of witnesses, the appointment of Judge Advocates, and rules for administering oaths.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2018) Q. With reference to the election of the President of India, consider the following statements: The value of the vote of each MLA varies from State to State. The value of the vote of MPs of the Lok Sabha is more than the value of the vote of MPs of the Rajya Sabha. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (a) Prelims (2022) Q2. Consider the following statements: (2022) A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India. When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent. A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
Source: IE
OECD Report Highlights Taxation of Indian Farmers
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News
The most recent report from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 2023 has highlighted the issue of implicit taxation imposed on Indian farmers during the year 2022.
Key Findings of Report
- In 2022, India had a significant negative Market Price Support (MPS), accounting for over 80% of such taxes globally among 54 countries analysed in the OECD report.
- While total implicit taxation on farmers across these countries was around USD 200 billion, India imposed a staggering USD 169 billion in implicit taxation on its farmers, resulting in a major negative net support of 15% of gross farm receipts.
- India’s attempt to offset negative MPS through budgetary transfers, like subsidies for various inputs and programs like Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN), was insufficient due to domestic marketing regulations and trade policies.
- In 2022, India implemented export policies, including bans, duties, and permits, impacting various agricultural commodities.
- While these policies aimed to stabilize domestic prices, they reduced farmers’ incomes and affected India’s status as a global agricultural producer.
- The OECD report noted that producer support to the agricultural sector in the 54 countries averaged USD 851 billion annually from 2020 to 2022, with a significant portion considered potentially distorting.
- Emerging economies had both positive support and implicit taxation, while OECD countries had less potentially distorting policies and did not implicitly tax producers.
About OECD
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an intergovernmental economic organization established in 1961, headquartered in Paris, France, with 38 member countries, including the most recent additions, Colombia and Costa Rica.
- While India is not a member, it maintains a significant economic partnership with the OECD.
- The organization produces various reports and indices, including “Government at a Glance” and the “OECD Better Life Index,” with the aim of promoting economic progress and international trade among its predominantly high-income and highly developed member nations.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2020) Q. In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies Social Capital development Free electricity supply to farmers Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 5 only (b) 1, 3, and 4 and 5 only (c) 2, 3 and 6 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 Ans: C Prelims (2017) Q. What is/are the advantage/advantages of implementing the ‘National Agriculture Market’ scheme? It is a pan-India electronic trading portal for agricultural commodities. It provides the farmers access to nationwide market, with prices commensurate with the quality of their produce. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither1 nor 2 Ans: C Mains (2020) Q. What are the main constraints in transport and marketing of agricultural produce in India? |
Source: DTE
India-Bangladesh Jointly Inaugurated Major Development Projects
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News
The Indian Prime Minister and the Prime Minister of Bangladesh jointly inaugurated three significant development projects in Bangladesh, which were assisted by India.
The major projects that were inaugurated and their significance
- The inauguration of three major Indian-assisted development projects in Bangladesh marked a significant milestone in the bilateral relationship between the two countries.
- These projects include the Akhaura-Agartala Cross-Border Rail Link, the Khulna-Mongla Port Rail Line, and the Maitree Super Thermal Power Project, with each project addressing key areas of connectivity enhancement, energy security, and bilateral cooperation, underlining the collaborative efforts in line with India’s “Neighbourhood First policy.”
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2017) Q. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim. River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta. River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
Source: ET
Kozhikode and Gwalior in UNESCO Creative Cities Network
Tag: GS-1 Art and culture
In News
UNESCO added 55 new cities to its Creative Cities Network, including Kozhikode, Kerala, recognized as the ‘City of Literature,’ and Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, designated as the ‘City of Music.’
Importance of Kozhikode and Gwalior
- Kozhikode, Kerala, becomes India’s first ‘City of Literature’ recognized by UNESCO, celebrating its rich literary tradition, hosting major literary events, and being home to numerous libraries and renowned writers.
- Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, is designated the ‘City of Music,‘ following Varanasi, with its historical significance as the birthplace of Tansen, the Gwalior Gharana, and the renowned Tansen Sangeet Samaroh music festival, highlighting its musical heritage.
Source: PIB
India’s Widening Tax Base
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News
The recent release of income tax return statistics by the Income Tax Department, covering assessment years 2019-20 to 2021-22, provides valuable insights into evolving tax compliance trends.
What are the Key Insights from the Latest Income Tax Returns Statistics?
- The recently released income tax return statistics for the assessment year 2021-22 reveal a 5.6% increase in tax filings, with 6.75 crore taxpayers submitting their returns, although approximately 2.1 crore taxpayers paid taxes without filing returns.
- The taxpayer base has been steadily growing from 5.87 crore in AY 2018-19 to 6.75 crore in AY 2021-22, but the percentage of taxpayers with nil tax liability has also increased to 66% in the latter year.
- The data shows a shift of individual taxpayers toward higher income brackets, with the top 1% earners contributing less proportionately and the bottom 25% earners contributing more.
- Critics argue that this has led to a widening wealth gap in India, as the top 1% income earners’ share of income has increased while the income growth for the bottom 25% has lagged behind, posing concerns about economic fairness and the financial struggles of the middle class.
About The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)
- The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is a legally established body operating under the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963.
- It functions within the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance. CBDT serves a dual purpose:
- It provides significant input for the formulation of direct tax policies and strategies in India,
- It also supervises the enforcement and application of direct tax regulations through the Income Tax Department. CBDT is headed by a chairman and comprises six members.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2021) Q. Which one of the following effects of creation of black money in India has been the main cause of worry to the Government of India? (a) Diversion of resources to the purchase of real estate and investment in luxury housing. (b) Investment in unproductive activities and purchase of precious stones, jewellery, gold, etc. (c) Large donations to political parties and growth of regionalism. (d) Loss of revenue to the State Exchequer due to tax evasion. Ans: (d) |
Source: IE
Bolivia
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News
Bolivia has chosen to sever diplomatic ties with Israel as a means of expressing its strong disapproval and condemnation of the Israeli military offensive happening in the Gaza Strip.
About Bolivia
- Bolivia is a landlocked country in South America.
- La Paz is the administrative capital, and Sucre is the constitutional capital.
- It’s known for its diverse landscapes, including the Andes Mountains and the Amazon Rainforest.
- Bolivia has a rich indigenous culture and a history of indigenous political movements.
- The country is famous for the Uyuni Salt Flats, one of the world’s largest salt deserts.
- Bolivia’s official languages include Spanish, Quechua, and Aymara.
- Evo Morales, Bolivia’s first indigenous president, held office for nearly 14 years.
- The country is known for its vibrant festivals and traditional music and dance.
- Bolivia’s economy relies on agriculture, mining, and natural gas production.
- Political and social challenges have marked Bolivia’s recent history, including disputes over resource distribution and indigenous rights.
Source: IE
Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News
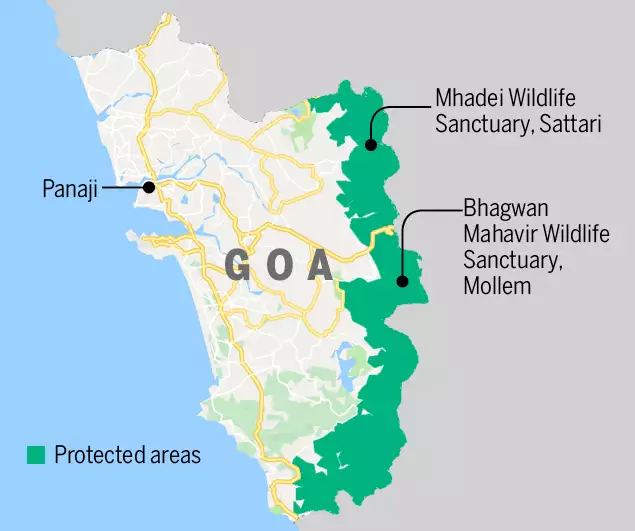
The Goa bench of the Bombay High Court has ordered the Goa government to declare a tiger reserve in the Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary and adjoining regions within a three-month period.
About Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary
- The Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the North Goa District, specifically in the Sanguem taluka near Valpoi town.
- Due to the presence of Bengal Tigers, it’s eligible for declaration as a tiger reserve under Project Tiger.
- This sanctuary has earned recognition as an International Bird Area due to its diverse avian population, including species like the Nilgiris wood-pigeon, Malabar parakeet, Malabar grey hornbill, Grey-headed Bulbul, Rufous babbler, White-bellied blue-flycatcher, and Crimson-backed sunbird.
- Herpetologists are drawn to this sanctuary because of its rich variety of snakes, including all of India’s ‘big four’ venomous snakes: the Indian krait, Russell’s viper, Saw-scaled viper, and Spectacled cobra.
- Established in 1999, the sanctuary has made Goa the sole Indian state to fully protect the Western Ghats within its boundaries.
- It boasts the three highest peaks in Goa, namely Sonsogod (1027 meters), Talavche Sada (812 meters), and Vageri (725 meters), with “Vageri” meaning ‘the abode of the tiger.’
- The Mhadei River, known as the Mandovi River downstream, originates in Karnataka, passes through the Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary, and flows into the Arabian Sea at Panaji, Goa.
- The sanctuary functions as a catchment area for the river, although much of the region has undergone changes due to agricultural and human activities, replacing its natural vegetation with cashew and kumeri cultivation.
Source: IE
Sustainability Bond
Tag: GS-3 Economics
In News
The Export-Import Bank of India (India Exim Bank) has introduced its inaugural $1 billion sustainability bond with a ten-year tenure on the Sustainable Bond Market (SBM) platform of the London Stock Exchange (LSE).
About Sustainability Bond
- A sustainability bond is a type of bond issued by governments, organizations, or institutions to raise funds for projects and activities that have a positive impact on social, environmental, or economic sustainability.
- The proceeds from sustainability bonds are typically earmarked for initiatives related to environmental conservation, social development, or other sustainable objectives.
- These bonds are designed to attract investors who are interested in supporting projects that promote sustainability and responsible business practices.
- Sustainability bonds are part of the broader category of green bonds, social bonds, and sustainable finance instruments that align financial markets with sustainable development goals.
The significance of sustainability bonds in India
Financing Sustainable Initiatives:
- Sustainability bonds enable organizations and government bodies in India to raise funds for projects and activities focused on environmental protection, social development, and economic sustainability.
- These initiatives can address critical issues like renewable energy, clean water, affordable housing, healthcare, and more.
Attracting Responsible Investors:
- Sustainability bonds attract socially responsible and environmentally conscious investors who are looking to align their investments with their values.
- It helps in channelling investments towards projects that have a positive impact on society and the environment.
Meeting ESG Objectives:
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are increasingly important for investors and stakeholders.
- Issuing sustainability bonds can help Indian entities demonstrate their commitment to ESG principles and sustainability goals.
Fulfilling National Priorities:
- Sustainability bonds can be used to address specific national priorities in India, such as renewable energy development, clean water supply, sanitation, affordable healthcare, and other sectors critical for the country’s sustainable growth.
Global Recognition:
- Listing sustainability bonds on international platforms, like the London Stock Exchange’s Sustainable Bond Market, provides global visibility and recognition for Indian entities committed to sustainability.
Supporting the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Sustainability bonds align with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, and by issuing these bonds, India can contribute to achieving these global goals.
Raising Awareness:
- Sustainability bonds raise awareness about critical sustainability challenges in India and encourage stakeholders to work together towards finding innovative solutions.
Source: LM

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

