Today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants explores the latest developments relevant to the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping India’s socio-political and economic landscape. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.

Contents
- 1 Olympics boxing gender testing controversy
- 2 Legal challenges to the Great Nicobar infrastructure project
- 3 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 4 Highest-ever organ transplants in India
- 5 International Conference of Agricultural Economists
- 5.1 Why in the news?
- 5.2 About International Conference of Agricultural Economists (ICAE):
- 5.3 International Conference of Agricultural Economists 2024:
- 5.4 Key Highlights of PM Modi’s Speech:
- 5.5 How to Reduce Landslide Risks
- 5.6 Why in the news?
- 5.7 Possible Causes of Landslide in Wayanad:
- 5.8 Landslide Prevention Techniques/Measures:
- 5.9 Initiatives Taken by the Government to Mitigate Landslide Risks:
- 6 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- 7 Maritime Partnership Exercise
- 8 Price Monitoring System App
- 9 Article 311 of Indian Constitution
- 10 Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) Scheme
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Olympics boxing gender testing controversy
Tags: GS-2, IR- International sports events- Olympics- Gender Controversy
Why in the news?
- Imane Khelif, a 25-year-old welterweight from Algeria, qualified for the quarterfinals of the Olympic women’s boxing tournament by defeating Italy’s Angela Carini in the round of 16, a fight that lasted just 46 seconds.
- Following her victory, Khelif faced a wave of abuse, with many accusing her of being a “biological man” with an “unfair advantage” over Carini.

- Some even wrongly identified Khelif as a transgender woman.
- The participation of trans women and women with certain “masculine” biological characteristics, such as higher testosterone levels, in women’s sports has long been a subject of polarising debate.
Background: The Controversy
- Boxers Failed Gender Eligibility Test Conducted by International Boxing Association (IBA)
- In 2023, Imane Khelif and Chinese Taipei boxer Lin Yu-ting were banned from competing in the IBA’s World Championship in New Delhi after failing a confidential “gender eligibility” test.
- The IBA stated that the boxers did not meet the criteria to compete in the female category.
- Both Boxers Are Competing in Paris Olympics
- Both boxers are now competing at the Paris Olympics, as the International Olympic Committee (IOC) derecognized the IBA over governance and financial issues.
- The IOC-appointed unit governing the competition in Paris only requires the gender stated in an athlete’s passport for eligibility, and Khelif’s passport identifies her as female.
- Response by IOC
- Following Khelif’s win and the subsequent abuse, the IOC stated that all Olympic boxers complied with eligibility and entry regulations.
- It noted that both Khelif and Lin have competed in women’s competitions for many years, including the Tokyo 2020 Games.
- The IOC also criticised the IBA’s decision to ban the two women as arbitrary and not following proper procedure.
Gender Eligibility: A Contentious Issue in Women’s Sports:
- Organization of Sports Based on Sex
- Modern sports are organised on the basis of sex, with men and women competing in different categories.
- This is because men, on average, have certain physiological advantages over women.
- Sex Is Determined Based on Chromosomes
- Sex is determined based on chromosomes, which carry genes. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes — 22 are identical in men and women; one, the sex chromosome, is different.
- The XX sex chromosomes result in the development of female sex organs, and XY in male sex organs.
- The SRY gene, found on the Y chromosome, is responsible for the production of testosterone.
- Link Between Testosterone and Athletic Performance
- Many studies have supported the link between testosterone and athletic performance.
- The difference in circulating testosterone between adults likely explains most, if not all, sex differences in sporting performance due to testosterone’s effects on muscle mass, strength, bone size, strength (density), and circulating haemoglobin.
- DSD and Swyer Syndrome:
- Some people born with female reproductive organs may also carry the XY chromosome, in what is known as Swyer syndrome.
- This syndrome is one of many “Disorders of Sex Development”, or DSDs.
- Swyer syndrome, also known as 46 XY gonadal dysgenesis, is a rare genetic condition where individuals have one X and one Y chromosome in each cell (typically associated with males) but develop female reproductive structures.
- People with Swyer syndrome are genetically male but phenotypically female, meaning they have a female appearance and female external genitalia.
- This is at the heart of the debate surrounding gender eligibility in women’s sports.
- Many argue that to prevent some athletes from having an unfair advantage in women’s sports, women with DSDs must not be allowed to compete with other women.
- They claim that DSDs facilitate greater testosterone production and other consequent athletic advantages.
Steps Taken by Sports Federations to Address This Matter
Sports Federations Have Their Own Eligibility Criteria
- In 2021, the IOC decided to allow international sports federations to develop their own eligibility rules based on an “evidence-based approach” considering principles of “fairness”, “inclusion”, “non-discrimination”, “no presumption of advantage”, and “prevention of harm.”
- Previously, the IOC required women athletes who had transitioned from male to female to have testosterone levels below 10 nanomoles per litre (nmol/L).
- World Athletics still uses testosterone levels as an eligibility criterion, requiring DSD athletes to maintain levels below 2.5 nmol/L for at least 24 months before competing.
- This is stricter than the pre-2023 requirement of 5 nmol/L for events ranging from 400 meters to a mile, with no restrictions on other events.
- FINA, the world swimming body, the International Cycling Union, and the International Rugby Union have all implemented varying degrees of bans on trans women athletes.
Debate Goes On
- There is still much unknown about the impact of testosterone on sporting performance.
- Many question whether women born with higher levels of testosterone have any different advantage compared to people with other genetic advantages, such as LeBron James’ height or Michael Phelps’ large, fin-like hands.
Source: IE
Legal challenges to the Great Nicobar infrastructure project
Tags: GS-3, Ecology & Environment- Biodiversity- Great Nicobar Island Project- Government Policies & Interventions
Why in the news?
- Recently, The Central government’s Rs 72,000 crore Great Nicobar Island (GNI) infrastructure project includes constructing an airport for civilian and defence use, an international container transshipment terminal, and a township.
- The project has faced legal challenges in the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and the Calcutta High Court.
- Recently, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Limited (ANIIDCO), the project’s implementing agency, submitted conclusions from a high-powered committee (HPC) formed by NGT in 2023.
- The HPC concluded that the proposed transshipment port does not fall within the Island Coastal Regulation Zone-IA (ICRZ-IA), where ports are prohibited.
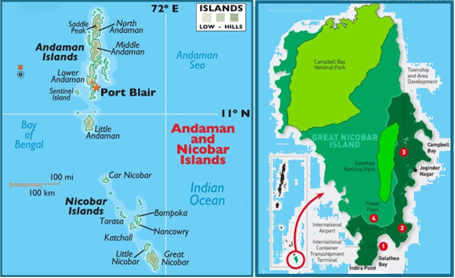
Great Nicobar Island:
- Geographical Location
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, a sparsely inhabited 910-sq-km patch of mainly tropical rainforest in the southeastern Bay of Bengal.
- Indira Point on the island is India’s southernmost point, located 90 nautical miles (<170 km) from Sabang at the northern tip of Sumatra, the largest island of the Indonesian archipelago.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands consist of 836 islands, divided into two groups: the Andaman Islands located in the north and the Nicobar Islands situated in the south.
- These groups are separated by the 150-kilometre wide 10° Channel.
- Ecosystem and Population
- Great Nicobar has two national parks and a biosphere reserve.
- It is home to small populations of the Shompen, Onge, Andamanese, and Nicobarese tribal peoples, as well as a few thousand non-tribal settlers.
What is the Great Nicobar Island Project?
About:
- Launch and Location: The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) project, launched in 2021, is a mega project to be implemented at the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Components: It involves developing a trans-shipment port, an international airport, township development, and a 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant on the island.
Rationale:
- The project was implemented following a NITI Aayog report that identified the potential to leverage the island’s advantageous position.
- It is approximately equidistant from Colombo (Sri Lanka) to the southwest and Port Klang (Malaysia) and Singapore to the southeast.
Features:
- Implementation: The mega infrastructure project is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- Key Developments: It includes an International Container Trans-shipment Terminal (ICTT) and a greenfield international airport.
- Strategic Location: Close to the Malacca Strait, the main waterway connecting the Indian Ocean to the Pacific. The ICTT is expected to position Great Nicobar as a major player in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a key hub for cargo transshipment.
- Site: The proposed site for the ICTT and power plant is Galathea Bay on the southeastern corner of Great Nicobar Island, an area without human habitation.
Strategic Importance:
- Military Deployment: The project aims to facilitate the deployment of additional military forces, larger warships, aircraft, missile batteries, and troops.
- Surveillance and Security: Enhancing surveillance and building a strong military deterrence on Great Nicobar is vital for India’s national security.
- Regional Significance: The island’s proximity to the Malacca Strait is crucial for India’s maritime strategy, allowing participation in the global cargo transshipment economy.
- Geopolitical Context: The Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean regions are crucial for India’s strategic and security interests, particularly due to increasing Chinese military presence.
- Chinese Naval Influence: India is concerned about China expanding its naval forces in key Indo-Pacific choke points such as the Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok Straits.
- Regional Military Concerns: China’s efforts to build a military facility on the Coco Islands, located just 55 km north of India’s Andaman & Nicobar Islands, raise significant concerns for India’s maritime security.
What are the legal challenges to the GNI Project?
- Grounds for Appeals:
- In 2022, environmental activists challenged the environmental and Coastal Regulation Zone clearances granted to the project.
- They highlighted the impact on the Shompen and Nicobarese tribal communities and the ecological sensitivity of the Island Coastal Regulation Zone (ICRZ-IA).
- Threat to Island Ecology:
- The port project could destroy coral reefs and threaten species like the Nicobar Megapode bird and leatherback turtles in Galathea Bay.
- The project affects about 15% of the island’s land mass, leading to one of the largest forest diversions in a unique rainforest ecosystem.
- The proposed port is in a seismically volatile zone that experienced significant subsidence during the 2004 tsunami.
- NGT’s Response and Formation of HPC
- The NGT formed a high-powered committee (HPC) to revisit the project’s green clearance due to concerns about coral conservation, the port’s location in a prohibited area, and limited baseline data.
- The HPC concluded that the proposed port does not fall in the ICRZ-IA.
- Recent Petitions
- In May 2024, Kothari filed two petitions before the NGT’s eastern bench.
- The first challenged the exclusion of parts of the project from ecologically sensitive areas as per the 2019 CRZ notification.
- The second accused the MoEFCC of contempt for not updating the NGT on the HPC’s findings and failing to act as directed.
- ANIIDCO filed a counter affidavit, while MoEFCC requested more time to respond.
- High Court Cases
- The activists also filed a writ petition in the Calcutta High Court challenging the NGT’s April 2023 order.
- The petition argued that the NGT special bench overstepped its jurisdiction and failed to adequately consider the project’s environmental impact, delegating decision-making to the HPC.
- It contended that the NGT should have directly evaluated the clearances and not relied on the committee.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q:1 Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q:2 Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q:3 In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
(a) Nilgiri Hills
(b) Nicobar Islands
(c) Spiti Valley
(d) Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)
Source: IE
Highest-ever organ transplants in India
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- Biotechnology- Health
Why in the News?
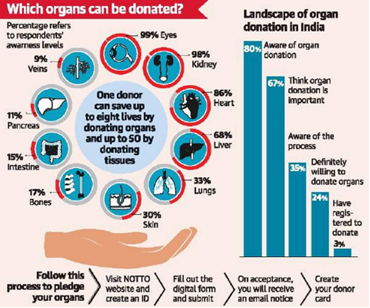
- India achieved a record 18,378 organ transplants in 2023, as reported by the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO), with 10% of these transplants going to foreign nationals.
- This marks the highest number of organ transplants in the country’s history, ranking India third globally in organ transplants and second in corneal transplants.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO):
- About: NOTTO is a national-level organisation under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Functions: It coordinates the procurement and distribution of organs and tissues and maintains a registry for organ and tissue donations and transplants across India.
Regulatory Frameworks Guiding Organ Transplantation in India
- Legislation:
- The Transplantation of Human Organs Act (THOA), 1994: This act regulates organ transplantation, prohibits organ commercialization, and legalises brain death, allowing deceased donations.
- Rules and Amendments: The act’s rules were last amended in 2014, expanding the scope to include tissue transplants.
- Institutions:
- National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO): Coordinates organ donation activities and sets policy guidelines and protocols.
- Organ Transplant Rules:
- 2023 Guidelines Update: Removed the 65-year age limit for deceased donor registration. Removed domicile criteria for registering for organ transplants, allowing patients to register and receive transplants in any state.
- Registration and ID: Patients are allotted a unique ID by NOTTO, which remains valid across different hospitals and states.
- Fee Regulations: States are prohibited from charging fees for organ transplant registration.
- Organ Transport Policy: A uniform policy is being developed, with coordination from seven ministries and NITI Aayog, involving nodal officers from each ministry and state-level coordination.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Status of Organ Transplants:
- Growth: Organ transplants have more than tripled in the past decade. In 2023, India performed 18,378 transplants, with kidney transplants being the most common.
- Global Ranking: India ranks third globally in organ transplants and second in corneal transplants.
- Deceased Organ Donations:
- Milestone: In 2023, India surpassed 1,000 deceased organ donations for the first time, with deceased-donor transplants increasing from 837 in 2013 to 2,935 in 2023.
- Gender Trends in Organ Donation:
- Living Donors: Females (9,784) outnumbered males (5,651) as living donors in 2023.
- Deceased Donors: Males (844) outnumbered females (255) among deceased donors.
- Recipients: Women constituted 30% of organ transplant recipients.
- Transplants to Foreign Nationals:
- Statistics: There were 1,851 transplants for foreign nationals, with Delhi-NCR accounting for 78%.
- Allocation Criteria: Foreign nationals receive organs from deceased donors only when no matching Indian patients are available.
- Irregularities: Allegations of irregularities in transplant approvals for foreign nationals were reported, particularly involving Myanmar nationals purchasing kidneys.
- Organ Donation Rate:
- Current Rate: Less than 1 per million population.
- Need for Improvement: Increased deceased organ donations are necessary to meet the rising demand, driven by the increase in non-communicable and lifestyle diseases.
Source: IE
International Conference of Agricultural Economists
Tags: GS-3, Economic – Growth & Development- Agriculture Sector
Why in the news?
- Recently, the triennial conference organised by the International Association of Agricultural Economists (IAAE) was held from 02 to 07 August 2024 in India after 65 years.

About International Conference of Agricultural Economists (ICAE):
- Organiser: International Association of Agricultural Economists (IAAE).
- Purpose: Facilitates the exchange of knowledge and innovations in agricultural economics, addressing global challenges like food security, rural development, and sustainability.
- Participants: Academics, researchers, government officials, industry professionals, and international organisation representatives.
- Sessions and Topics: Includes keynote addresses, plenary sessions, panel discussions, and paper presentations on agricultural policy, market dynamics, trade, environmental impacts, technological advancements, and rural development.
- Global Impact: Shapes agricultural policies and practices by providing evidence-based insights and recommendations, promoting economic principles to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Frequency and Location: Held every three years in different locations around the world, emphasising its global scope and reach.
International Conference of Agricultural Economists 2024:
- Dates and Location: Held in India from August 2 to 7, 2024, returning to the country after 65 years.
- Theme: “Transformation Towards Sustainable Agri-Food Systems,” focusing on sustainable agriculture amidst global challenges such as climate change, resource degradation, rising production costs, and conflicts.
- Objectives: Highlights India’s proactive approach to global agricultural challenges, showcases advancements in agricultural research and policy, and provides a platform for young researchers and professionals to network and strengthen partnerships.
- Impact: Aims to influence policy making on national and global scales and exhibit India’s progress in digital agriculture and sustainable agri-food systems.
- Participation: Approximately 1,000 delegates from 75 countries.
Key Highlights of PM Modi’s Speech:
- Welcome: PM Modi welcomed delegates from 75 countries, highlighting India’s deep agricultural roots and scientific basis of ancient agricultural practices.
- Diversity and Transformation: Emphasised India’s diverse agro-climatic zones and its transformation from a food-insecure nation to a major global producer.
- Sustainable Farming: Stressed the importance of sustainable and climate-resilient farming practices, including natural farming and climate-resilient crop varieties.
- Global Welfare Commitment: Reiterated India’s commitment to global welfare and sharing agricultural innovations and experiences.
- Initiatives: Discussed initiatives like Soil Health Cards, solar farming, e-NAM, and PM Kisan Samman Nidhi to modernise Indian agriculture.
- Digital Technology: Highlighted the use of digital technology for real-time crop surveys, land digitization, and promoting drone use in farming.
- Nutrition and Water Scarcity: Acknowledged the nutrition challenge, water scarcity, and climate change, presenting millet (Shri Anna) as a solution.
- Millet Promotion: Expressed willingness to share India’s millet basket with the world, noting the celebration of the International Year of Millets.
- Conference Impact: Expressed confidence in the conference fostering learning and collaboration towards sustainable agri-food systems.
Source: IE
How to Reduce Landslide Risks
Tags: GS Paper – 3, Disaster Management- Landslide, National Landslide Risk Management Strategy
Why in the news?
- Recently, Massive landslides struck the Wayanad district in northern Kerala, resulting in a death toll of 215 and significant destruction.
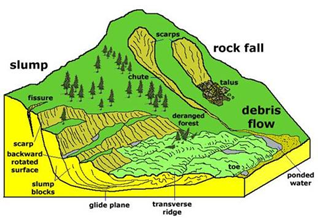
Possible Causes of Landslide in Wayanad:
- Natural Factors:
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) Findings: Approximately half of Kerala’s land area is prone to landslides.
- Heavy Rainfall and Slope: In Wayanad, 31.54% of the area is highly susceptible to landslides due to heavy rainfall and the region’s slope.
- Anthropogenic Factors:
- Increasing Construction Activities: The rise in tourism, including homestays and monsoon tourism, has led to extensive construction of resorts, artificial lakes, and quarrying in eco-sensitive zones (ESZ), heightening landslide risks.
- Changes in Crop Patterns: A 62% reduction in forest cover and a 1,800% increase in plantation areas since the 1950s have weakened topsoil stability, previously maintained by forest roots.
- Climate Change: Altered rainfall patterns and warming of the Arabian Sea have led to more intense and concentrated rainfall, increasing the risk of landslides.
- Issues with Landslide Warnings:
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) issues colour-coded rainfall warnings, but the week before the landslides, the alert was a non-critical yellow.
- The GSI is working on an early warning system for landslides, but it is still in development and may take several years to implement fully.
Landslide Prevention Techniques/Measures:
- Regulatory Measures:
- Banning/Regulating Construction in ESZs: The Gadgil panel report (2011) recommended declaring the Western Ghats as an ESZ to prevent harmful construction activities.
- Institutional Upgrades:
- Enhanced Weather Prediction: IMD should adopt new technologies to improve weather forecasts and warnings.
- Engineering Solutions:
- Slope Stabilization: Adding structural elements to slopes to enhance stability.
- Grading and Terracing: Modifying the slope’s shape and gradient to mitigate landslide risk.
- Soil Reinforcement: Strengthening soil by adding materials to increase slope stability.
- Natural Solutions:
- Vegetation Control: Planting trees, shrubs, or grasses to stabilise soil, absorb excess water, and reduce erosion.
- Mulching: Applying organic or inorganic material to the soil surface to retain moisture and prevent erosion.
- Bioengineering Techniques: Combining plants and engineering methods to stabilise slopes.
- Water Management: Managing water flow to allow gradual infiltration into the soil.
- Monitoring and Preparedness:
- Early Warning Systems: Implementing systems to provide timely alerts and information for landslide risk mitigation.
- Emergency Preparedness: Preparing communities for potential landslide events to minimise risks and enhance response effectiveness.
Initiatives Taken by the Government to Mitigate Landslide Risks:
- National Landslide Risk Management Strategy (2019): A comprehensive strategy covering hazard mapping, monitoring, early warning systems, awareness programs, capacity building, regulations, and mitigation measures.
- Landslide Risk Mitigation Scheme (LRMS): An upcoming scheme providing financial support for site-specific landslide mitigation projects, disaster prevention, R&D in monitoring, and early warning system development.
- Flood Risk Mitigation Scheme (FRMS): An upcoming scheme focused on developing model flood shelters, river basin-specific flood early warning systems, and digital elevation maps for inundation models and early evacuation warnings.
- National Guidelines on Landslides and Snow Avalanches: Guidelines from the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) addressing hazard assessment, vulnerability analysis, risk management, structural and non-structural measures, institutional mechanisms, and community participation.
- Landslide Atlas of India: A document by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) detailing landslide occurrences and damage assessments in India’s landslide-prone areas.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains:
Q:1 Differentiate the causes of landslides in the Himalayan region and Western Ghats. (2021)
Q:2 The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation. (2016)
Source: DC
Maritime Partnership Exercise
Tags: GS – 2, International Treaties & Agreements Bilateral Groupings & Agreements, GS – 3, Security Challenges & their Management in Border Areas
Why in the news?
- Recently, a Maritime Partnership Exercise (MPX) was conducted between India and Russia in St. Petersburg.

Maritime Partnership Exercise:
- About:
- The MPX was held in St. Petersburg to celebrate the 328th Russian Navy Day.
- Participating Ships: INS Tabar (India) and Soobrazitelny (Russia).
- It marked a milestone in India-Russia maritime cooperation, highlighting both nations’ commitment to regional peace, stability, and security.
- The exercise included complex naval manoeuvres such as communication drills, Search & Rescue operations, and Replenishment at Sea, showcasing high professionalism and interoperability.
- Significance:
- The exercise underscored the strong bilateral naval ties between India and Russia.
- It reflects India’s dedication to fostering global naval partnerships and enhancing maritime cooperation.
Key Facts about INS Tabar:
- Type: Stealth frigate built in Russia for the Indian Navy.
- Class: Third of the Talwar-class frigates.
- Commissioned: April 19, 2004, in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Capabilities: Handles air, surface, and sub-surface missions; operates independently or as part of a larger naval task force.
- Affiliation: Part of the Indian Navy’s Western Fleet, based in Mumbai under the Western Naval Command.
Source: PIB
Price Monitoring System App
Tags: GS-3, Economy- PDS, Buffer Stock & Food Security- Market Scheme
Why in the news?
- On August 4, 2024, the Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution & New and Renewable Energy launched Version 4.0 of the Price Monitoring System (PMS) Mobile app.

About the App:
- Agency: Managed by the Price Monitoring Division (PMD) in the Department of Consumer Affairs.
- Purpose: Monitors prices of selected essential commodities.
- Initial Launch: The PMS App was launched in 2021 to enhance the quality of price data by facilitating daily price reporting from various centers.
- Price Data Sources: Retail and wholesale prices are collected daily from 550 centers via State Civil Supplies Departments using the PMS App.
Commodities Monitored:
- Existing: 22 essential commodities including Rice, Wheat, Sugar, Oil, Tea, Milk, and more.
- New Additions: 16 new items such as Bajra, Jowar, Ghee, Butter, Brinjal, and Banana.
- Coverage: The 38 commodities now monitored cover about 31% of the total Consumer Price Index (CPI) weights, up from 26.5% with the previous 22 commodities.
Significance:
- The data collected aids in formulating policy decisions and provides insights on CPI inflation for the Government, RBI, and analysts.
Article 311 of Indian Constitution
Tags: GS-2, Polity & Governance- Indian Constitution- Article
Why in the news?
- The Jammu and Kashmir Lieutenant-Governor recently invoked Article 311 to terminate the services of six government employees.

About Article 311:
- Purpose: Provides procedural safeguards and protections against arbitrary dismissal, removal, or reduction in rank of government employees.
- Safeguards:
- Inquiry Requirement: Government employees cannot be dismissed, removed, or reduced in rank without an inquiry.
- Opportunity to Defend: Employees must be informed of the charges and given a chance to defend themselves.
- Authority: Only the appointing authority or someone of equal or higher rank can remove a civil servant.
- Grounds for Action:
- Efficiency: Unsatisfactory performance or conduct affecting government efficiency.
- Moral Turpitude: Involvement in corruption, bribery, fraud, or similar offences.
- Procedure:
- Formulation of Charges: Clear charges must be formulated against the employee.
- Opportunity to Respond: Employees must be given a chance to respond and present their defence.
- Conducting Inquiry: An impartial inquiry must be conducted.
- Consideration of Report: The inquiry report must be considered before making a decision.
- Decision-making: The decision must be reasoned, fair, and communicated to the employee.
- Exceptions:
- Security of the State: Immediate action can be taken if deemed necessary for state security, bypassing the inquiry process.
- Public Service Efficiency: The President or Governor can dispense with the inquiry for efficiency reasons.
- Probationary Employees: Probationary employees can be dismissed without an inquiry.
- Judicial Review:
- Decisions under Article 311 are subject to judicial review, and remedies may include reinstatement, back wages, or other appropriate reliefs.
Source: TH
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) Scheme
Tags: GS-2, Polit & Governance- Govt. Policies & Incentive – Womens Schemes
Why in the news?
- The Centre is considering not extending the Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) scheme beyond its March 2025 deadline.
About the MSSC Scheme:
- Introduction:
- Announced in Budget 2023 as a one-time scheme.
- Available for a two-year period, concluding in March 2025.
- Aimed at women and girls of all age groups.
Key Features:
- Deposit Facility:
- Maximum deposit limit of ₹2 lakh per account.
- Minimum deposit of ₹1000, with subsequent deposits in multiples of ₹100.
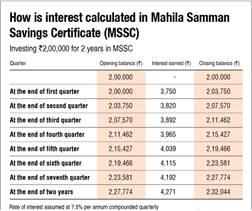
- Interest Rate:
- Fixed interest rate of 7.5% per annum.
- Interest is compounded quarterly and credited to the account.
- Tenure:
- 2-year lock-in period from the date of account opening.
- Partial withdrawal of up to 40% of the balance permitted after one year.
- Account Opening:
- Open to individual women.
- Minor accounts can be opened by guardians.
- Multiple accounts allowed with a minimum gap of three months between openings.
- Total deposit across all accounts cannot exceed ₹2 lakh.
- Objective:
- To promote formal financial savings among women.
- Tax Benefits:
- No tax benefits are associated with this scheme.
Source: BS
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

