
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Research agenda for AMR
- 2 Solar Geoengineering to counter global warming
- 3 Trafficking in Border Areas
- 4 Article 355 and Article 226
- 5 Mo Jungle Jami Yojana
- 6 eSARAS mobile app
- 7 Gucchi Mushroom
- 8 Lord Lansdowne
- 9 Bharat 6G Alliance
- 10 Pichavaram region
- 11 Bogibeel in Dibrugarh
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Research agenda for AMR
Tag: GS Paper-2: Health; Government Policies and Interventions.
In News:
The ‘Quadripartite’ comprising the United Nations (UN) Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) released One Health Priority Research Agenda on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
About the research agenda for AMR:
- It will serve as a guide for countries, research institutes and funding bodies to support One Health AMR research.
- It will also allow policymakers, researchers, and the multidisciplinary scientific community to collaborate across sectors.
- It defined ‘One Health’ as an integrated, unifying approach that aims to sustainably balance and optimise the health of people, animals and ecosystems.
- The concept acknowledges the health of humans, domestic and wild animals, plants, and the larger environment, including ecosystems, are inextricably linked and interdependent.
- At this One Health interface, addressing global health issues necessitates a multi-sectoral, multidisciplinary response to AMR.
- Using a mixed-methods approach, global experts have identified five key pillars as well as three cross-cutting themes, namely gender, vulnerable populations, and sustainability.
What are the five key pillars of the research agenda?
Transmission
- This pillar focuses on the environment, plant, animal, and human sectors where AMR transmission, circulation and spread occur. This includes what drives this transmission across these areas, where these interactions occur, and the impact on different sectors.
Integrated surveillance
- This pillar aims to identify cross-cutting priority research questions in order to improve common technical understanding and information exchange among One Health stakeholders. The surveillance aims for harmonisation, effectiveness, and implementation of integrated surveillance with a focus on LMICs.
Interventions
- This pillar focuses on programmes, practises, tools, and activities aimed at preventing, containing, or reducing the incidence, prevalence, and spread of AMR. This also calls for the best use of existing vaccines, as well as other One Health-related measures to reduce AMR.
Behavioural insights and change
- The priority research areas under this pillar are concerned with comprehending behaviour across various groups and actors involved in the development and spread of AMR at the One Health interface. It focuses on research addressing human behaviour that affects AMR, including ways to combat it.
Economics and policy
- From a One Health standpoint, this pillar addressed investment and action in AMR prevention and control. This pillar also takes into account the cost-effectiveness of an AMR investment case, financial sustainability, and long-term financial impact.

The agenda at the regional and national levels requires tailoring and the development of specific research questions.
Source: Down to Earth
Solar Geoengineering to counter global warming
Tags: GS – 3: Environment (Global Warming)
Why in News:
The United States of America is looking for a controversial tool i.e., Solar Geoengineering to counter global warming.
Solar Geoengineering:
- Solar Geoengineering describes a set of proposed approaches to reflect sunlight (back to space) to rapidly cool the Earth.
- It is also known as Solar Radiation Management (SRM).
The major approaches within solar geoengineering are as follows:
- Stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI): It involves injecting tiny reflecting particles, known as aerosols, into the upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB): It would use sea salt to stimulate cloud formation over the ocean, which would also help reflect sunlight in the region.
- High-albedo crops and buildings: Painting roofs and roads in white, covering glaciers and deserts with reflective plastic sheeting, putting white or pale-coloured plastic floating panels over oceans or lakes, and planting genetically engineered paler crops have all been proposed to reflect sunlight into space.
- Ocean mirror: An “ocean mirror” is a less popular choice for reducing the impact of sunlight.
- Cloud thinning: To “remove” cirrus clouds from the atmosphere would be one less-examined method of minimizing the impact of sunlight on the Earth’s surface.
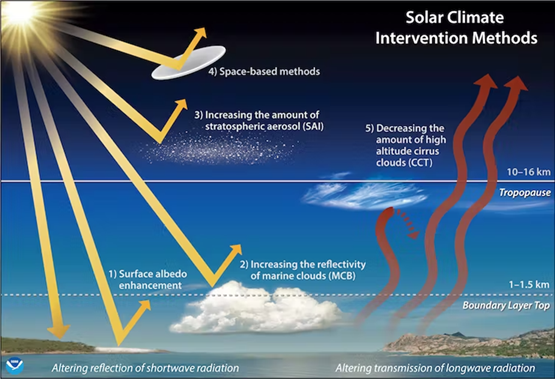
- Space mirrors/sunshades: To send into orbit giant mirrors made of wire mesh; or to send trillions of light and small mirrors, to deflect sunlight back to space.
Why is SRM method being considered:
- The Paris Agreement’s target requires limiting global temperature increase well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C.
- Nations need to bring net global CO2 emissions to zero by no later than mid-century.
Concerns with Solar Geoengineering:
- SRM deployment may also increase climate change damage or introduce a range of new risks to people and ecosystems, including risks to human health and global biodiversity.
- Research to scope the risks and potential of solar geoengineering has mostly been conducted through computer-based modelling and natural observations (volcanic eruption).
- The technology may become an excuse to slow emissions reductions and nations would stop moving toward a low-carbon economy.
Way Forward:
Its impacts will be on the entire globe, so certain provisions like Effective international governance, Mechanisms for oversight, Ways to involve the public in decision-making, etc. should be considered before taking steps further.
Source: Down to Earth
Trafficking in Border Areas
Tags: GS – 3: Internal Security (Security challenges and management in border areas)
Why in News:
Recently, the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India, has approved a scheme that aims to provide financial assistance to states and Union Territories to establish protection and rehabilitation homes for victims of trafficking.
Human Trafficking:
- It is the illegal trade and exploitation of individuals through force, coercion, or deception for various purposes such as forced labour, sexual exploitation, and organ trafficking.
- It involves the recruitment, transportation, harbouring, or receipt of people by means of threat, fraud, or abduction for the purpose of exploitation.
- India is both a source and destination country for human trafficking.
Major Provisions of the scheme:
- To provide financial aid to states and Union Territories in order to establish protection and rehabilitation homes for victims of trafficking.
- The government has allocated funds from the Nirbhaya Fund to support the strengthening of anti-human trafficking units in every district across all states and Union Territories.
- The funding has been extended to all states and Union Territories, including AHTUs in Border Guarding Forces like the BSF (Border Security Force) and SSB (Sashastra Seema Bal).
- As of now, 788 AHTUs, including 30 in border guarding forces, are functional.
- The trafficking victims in the border areas will also be produced before the child welfare committees to declare them fit for availing sponsorship as per the Mission Vatsalya Scheme.
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 23 prohibits human trafficking and begar (forced labour without payment).
- Article 24 forbids the employment of children below the age of 14 years in dangerous jobs like factories and mines.
National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB) data:
- According to NCRB, 2,189 cases of human trafficking were filed in 2022, involving 6,533 victims (4,062 – female, 2,471 – male, and 2,877 – minors).
Source: The Hindu
Article 355 and Article 226
Tags: GS-2 Indian Polity
In News:
Madras High Courts dismiss a writ petition in pursuance of High Court’s power to issue a direction for invocation of Article 355 of the Constitution
About Article 355 and Article 226:
Article 355:
- It enjoins upon the Centre a duty to protect States against external aggression and internal disturbance.
- It ensures that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the constitutional provisions.
- It has been inspired by Article IV (4) of the US Constitution and Section 61 of the Australian Constitution Act.
- It was not in original draft constitution and was later introduced by B.R. Ambedkar to emphasize constitutional obligation for Centre’s interference in provincial affairs.
- The scope of Article 355 is wide enough for the Union to provide assistance even without a specific request from the State Government.
- However, it requires a case of large-scale public disorder endangering the security of the State for it to be considered an internal disturbance.
Article 226:
- It pertains to the writ jurisdiction of High Courts under the Constitution.
- It does not grant High Courts the power to issue a direction to the Centre to invoke Article 355.
- The High Court’s jurisdiction is limited to issuing writs for enforcement of fundamental rights and other purposes.
- Accordingly, High Courts cannot use it as a mechanism to compel the Centre to fulfil its duties under Article 355.
Major writs under Article 226:
- Habeas Corpus: It is used to secure the release of a person who has been illegally detained or imprisoned to ensure that the detained individual’s fundamental right to personal liberty is protected.
- Mandamus: It is issued to a public official, government, or statutory authority to perform a specific duty when there is a clear legal right and a corresponding duty of the authority to act.
- Prohibition: It prevents an inferior court or tribunal from exceeding its jurisdiction or acting contrary to the principles of natural justice in order to maintain the hierarchical authority of the court system.
- Certiorari: It orders the transfer of a case from a lower court to a higher court for review to ensures that the lower court has not acted beyond its jurisdiction or violated principles of natural justice.
- Quo Warranto: It is used to challenge the legality of a person holding a public office and asks the holder of the office to justify their right to hold that position.
Source: The Hindu
Mo Jungle Jami Yojana
Tags: GS-2: Government Policies
In News:
Odisha government announces state forest rights scheme “Mo Jungle Jami Yojana” to benefit over 7 lakh households
About Mo Jungle Jami Yojana:
- The Mo jungle yojana has been introduced by the Odisha government through state budget 2023-24 to effectively implement the Forest Rights Act, 2006 in the state.
- The scheme targets over 7 lakh tribal families and 32,000 villages across 30 districts of Odisha with a total cost of the scheme is Rs 38.76 crore.
- It establishes a state program management unit (SPMU) at the Tribal Research Institute, Bhubaneswar to promote awareness campaigns and training of officials and field functionaries.
- It will also establish Forest Rights Cells across districts for assessment, monitoring, and review of the scheme’s implementation.
- The scheme aims to make Odisha the first state to be “FRA compliant” by implementing all provisions of the Forest Rights Act.
- It focuses on individual forest rights, community forest rights (CFR), habitat rights for particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTG), and conversion of forest and unsurveyed villages.
- It will provide ownership of land and access to forest resources to beneficiaries according to their entitlements.
- It will work for conversion of unsurveyed, forest, and zero area villages into revenue villages for improved infrastructure and services.
- Overall, the scheme is expected to provide better access to tribals the critical forest resources and will promote collective action for resource conservation.
Source: Down to Earth
eSARAS mobile app
Tags: General Studies –2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) has launched the eSARAS mobile app to support the marketing of products made by women in self-help groups (SHGs).
About:

- It is an initiative conceptualized by the DAY-NRLM, Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), towards the marketing of the best, authentic handicrafts and hand-looms.
- This initiative promotes the spirit of Vocal for Local even further with easier marketing of products prepared by SHGs.
- Along with that eSARAS Fulfilment Centre was also inaugurated.
- These centres will be managed by the Foundation for Development of Rural Value Chains (FDRVC – a Not for Profit Company constituted jointly by Ministry of Rural Development and Tata Trust).
- This centre will be used for processing, packaging and shipping of products that customers purchase through the eSARAS Portal and eSARAS mobile App.
- It will handle the logistics required to bring an online order to a customer’s doorstep.
DAY-NRLM scheme:
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) is the flagship program of the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Its aim is promoting poverty reduction through building strong institutions for the poor, particularly women, and enabling these institutions to access a range of financial services and livelihoods.
Source: PIB Gov.
Gucchi Mushroom
Tags: General Studies –3 Environment
Why in news?
Unpredictable weather patterns, early springs, and above-average temperatures have left gucchi mushroom hunters in distress, facing another season of low yield for the second consecutive year.
About:

- The Guchhi mushroom is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae of the Ascomycota.
- They are pale yellow in colour with large pits and ridges on the surface of the cap, raised on a large white stem.
- It has a nutty, earthy and savoury flavour.
- Benefits:
- They are rich in potassium, vitamins and copper. They are also a rich source of vitamin D apart from several B vitamins.
- It is further rich in antioxidants that prevent health issues including heart diseases and diabetes by removing reactive oxygen species that harm the body.
- It has been given a GI tag in year 2021.
- These mushrooms cannot be cultivated commercially.
- Climate change, deforestation, and habitat destruction have also contributed to the rarity of gucchi mushrooms.
- Ideal conditions:
- Mostly grown in clusters on southerly slopes and sunny areas and on logs of decaying wood, leaves or humus soil.
- Thunder and rain to help these mushrooms in sprouting.
- Soil with a limestone base is favourable.
- Day time temperature of 15 to 20 degrees Celsius and Night time temperatures of 5 to 9 degrees Celsius is favourable.
- Location:
- Mostly found in the wild in the mountains of Ramban, Kupwara and Anantnag districts in Jammu and Kashmir.
- These are also found in foothills of Himalayas in forests of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand.
- Conifer forests across temperature regions.
Source: Down to Earth
Lord Lansdowne
Tags: General Studies –1 Morden India History
Why in news?
Recently, The Lansdowne Cantonment Board has decided to rename the hill station of Lansdowne in Uttarakhand, India, as Jaswantgarh in honour of Rifleman Jaswant Singh Rawat.
About:
Lord Lansdowne

- He was a british politician also known as Henry Charles Keith Petty-Firzmaurice.
- During 1888 to 1894, he served as Viceroy of India.
- After this he also served as the Governor General of Canada.
- Lord Lansdowne legitimized the work of the Indian National Congress, recognizing the rise of Indian nationalism as an inevitable byproduct of the British administration.
- He is given credit for supressing Manipur Rebellion of 1891.
- He also perpetuated divide and rule policy and promoted Hindu-Muslim divide.
Various Acts & Commissions in between 1888 to 1894
- The Indian Factory Act, of 1891 was passed when Lord Lansdowne was the Viceroy of India.
- On Aitchison Commission recommendations (1889), Statutory Civil Service was abolished.
- The Age of Consent Act, 1891, was enacted in British India in 1891, raising the age of consent for sexual intercourse for all girls, married or unmarried, from ten to twelve years in all jurisdictions, with violations punishable as rape.
- Lord Lansdowne introduced the Indian Councils Act of 1892, which established additional members in the central and provincial legislative councils and introduced an indirect election system for council members.
- In 1893, a royal commission was issued to inquire into the results of using opium in India, and the possibility of prohibiting it. The commission’s findings favoured the continued use of opium and led to the shelving of the idea of imposing a ban.
- Setting up Durand Commission (1893): Durand Line agreement was signed to secure the north-west and Afghanistan.
Rifleman Jaswant Singh
- Rifleman Jaswantgarh, a member of 4th Battalion of the Garhwal Rifles, is a war hero of 1962 war and a recipient of Maha Vir Chakra.
- He was awarded the second highest gallantry award due to his role against the People’s Liberation Army of China in Battle of Nuranang during 1962 war.
- The battle was fought in the North-East Frontier Agency, current Arunachal Pradesh.
More Information:
- The Cantonment and Regimental Centre for the training of recruits of the Garhwal Rifles was located in a forest area popularly known as Kalundanda.
- On September 21, 1890, Kalundanda was renamed as Lansdowne after the Viceroy.
Source: Indian Express
Bharat 6G Alliance
Tags: General Studies –3 IT & Computers, Indigenization of Technology, Scientific Innovations & Discoveries
Why in news?
Recently, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) under the Ministry of Communications launched the Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA) to foster innovation and leadership in 6G technology, the next frontier of wireless communication.

About:
- Bharat 6G Alliance is a collaborative platform which aims to achieve universal and affordable connectivity, promote indigenous technology, and establish India as a global leader in the telecom sector.
- This platform consists of public and private companies, academia, research institutions, and standards development organizations, aims to lead the development and deployment of 6G technology in India.
- It will forge coalitions and synergies with other 6G Global Alliances, fostering international collaboration and knowledge exchange.
- Aims and Objectives of B6GA:
- To understand the business and societal needs of 6G beyond technology requirements, foster consensus on these needs, and promote high-impact open research and development (R&D) initiatives.
- To bring together Indian startups, companies, and the manufacturing ecosystem to establish consortia that drive the design, development and deployment of 6G technologies in India.
- To facilitate market access for Indian telecom technology products and services, enabling the country to emerge as a global leader in 6G technology.
Other initiatives launched:
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF) scheme was launched by Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) in 2022. USOF is a body under Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
- 5% of annual collections from USOF are available for TTDF for funding R&D in rural-specific communication technology applications and form synergies among academia, start-ups, and industry to build and develop a telecom ecosystem.
Source: PIB Gov.
Pichavaram region
Tags: General Studies – 1 Physical Geography, GS Paper – 3 Environmental Pollution & Degradation, Conservation
Why in news?
Recently, Tamil Nadu Forest Department has drawn up a comprehensive plan for the rehabilitation of coastal habitats by creating bio-shields and restoring degraded mangroves in the Cuddalore district, particularly in the Pichavaram region.
About:
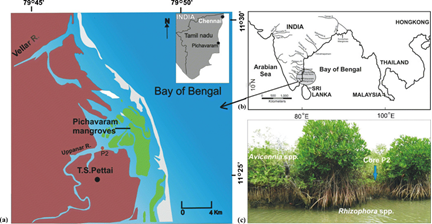
- The Pichavaram mangrove Forest is one of the largest mangrove forests in India covering about 45 sq km of area.
- Pichavaram mangrove forest is located between two prominent estuaries, the Vellar estuary in the north and the Coleroon estuary in the south.
- The Vellar-Coleroon estuarine complex forms the Killai backwater and Pichavaram mangroves.
- It consists of a number of islands interspersing a vast expanse of water covered with mangrove forest.
- It is separated from the Bay of Bengal by a sand bar.
- The Pichavaram mangroves are among the most productive ecosystems in the State, and are a storehouse of biodiversity, supporting 840 species of flora and fauna.
- These includes 115 species of birds, 16 species of mammals, 11 amphibians, 177 species of finfish, 95 species of zooplanktons, 82 phytoplanktons, 35 species of butterflies, 17 snakes and 3 species of seagrass.
Source: The Hindu
Bogibeel in Dibrugarh
Tags: General Studies –3 Infrastructure
Why in news?
Recently, The Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways and Ayush, laid the foundation stone of Inland Waterways Transport (IWT) terminal to be developed at Bogibeel in Dibrugarh, by the bank of the River Brahmaputra (National Waterways 2) in Dibrugarh, Assam.
About:
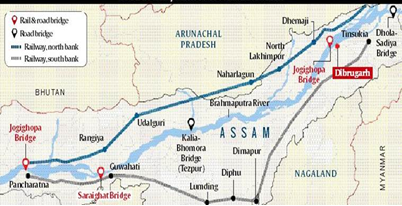
- The Bogibeel Bridge is built over Brahmaputra River at Bogibeel between Dibrugarh and Dhemaji districts of Assam.
- At 4.94 km, the Bogibeel Bridge is the country’s longest road-cum-rail bridge.
- In a comparison of all bridges across water, the Bogibeel comes in at fourth, after the neighbouring Dhola-Sadiya Road bridge (9.15 km), the Patna-Hajipur road bridge (5.75 km), and the Bandra-Worli Sea Link (5.6 km).
More Information:
- The government intends to increase the share of Inland Water Transport (IWT) to 5% as per Maritime India Vision (MIV)-2030.
Source: PIB Gov.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

