
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 National Commission for Women (NCW)
- 2 Issues faced by gig workers in India
- 3 India’s ethanol push
- 4 FAO Strategy on Climate Change 2022-2031
- 5 WTO: Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies
- 6 Silvopasture systems
- 7 ‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign
- 8 PM-WANI
- 9 Fluorochemicals
- 10 Hygroelectricity
- 11 Argentina
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
National Commission for Women (NCW)
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Statutory Bodies)
Why in News:
Recently, there is rising demand for a review of working and responses to the National Commission for Women (NCW) due to the cases of molestation and rape of women in Manipur.
National Commission for Women:
- It was set up in 1992 under the National commission for Women Act, 1990.
- It was established to review the constitutional and legal safeguards for women.
- It enjoys all the powers of a civil court.
- It looks into complaints, and takes Suo Motto notice of matters relating to – deprivation of women’s rights, Non-implementation of the laws and Non-compliance of the policy decisions guaranteeing the welfare for women society.
- It tables reports to the central government, every year and at such other times as the commission may deem fit, reports upon the working of those safeguards.
- Each state has its own commission. Manipur State Commission for Women was formed in 2006. They are meant to investigate women’s rights violations.
Reason for ineffectiveness in addressing women issues in Manipur:
- Lack of Proactive Action: The national commission received numerous complaints from Manipur but they merely forwarded to the state commission. This led to the ignorance of those complaints.
- Preference over paperwork than fieldwork: The commissions focus heavily on paperwork, neglecting fieldwork.
- Political influence in Appointments: Members are nominated by the ruling political party. This makes them hesitant to criticize the government, affecting their objectivity.
- Lack of real time engagement: Despite numerous complaints from Manipur, there were no extensive field visits to understand the situation.
Steps to be taken for enhancing its effectiveness:
- Reforms in Appointment Process: Appointments should be done through a committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition and the Chief Justice of India.
- Regular External Audits: Conduct regular social audits by competent agencies.
- Encourage Fieldwork engagement: Commission members should frequently visit areas of concern.
- Define the roles of Chairperson and members.
- Strengthen Collaboration: Instead of an adversarial approach, NCW should work closely with the enforcement agencies to address women’s issues effectively.
- Increase transparency in Reports: Regularly share the commission’s activities and reports with the public.

Source: Indian Express
Issues faced by gig workers in India
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment)
Why in News:
Recently, a parliamentary panel has asked the Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoL&E) to formulate and implement welfare schemes for gig and platform workers and unorganised sector workers at the earliest.
Gig Economy:
- As per the World Economic Forum, gig economy is defined by its focus on workforce participation and income generation via “gigs”, single projects or tasks for which a worker is hired.
- It is a labour market that relies heavily on temporary and part-time positions filled by independent contractors and freelancers rather than full-time permanent employees.
- Gig workers refer to workers outside of the traditional employer-employee relationship.
- There are two groups of gig workers:
- Platform workers: When gig workers use online algorithmic matching platforms or apps to connect with customers, they are called platform workers.
- Non-platform workers: Those who work outside of these platforms are non-platform workers, including construction workers and non-technology-based temporary workers.
- According to the NITI Aayog estimates, nearly 23.5 million workers will be engaged in the gig economy by 2029.
Challenges faced by the Gig Workers:
- The gig workers usually lack basic employment rights such as Minimum wage, overtime pay, medical leave and a statutorily bound resolution of employer-employee disputes.
- They have the characteristics of both employees and independent contractors due to which they fall outside the ambit of statutory benefits under the Minimum Wage Act 1948, EPF Act 1952, Payment of Bonus Act 1965, and the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act 1970.
Proposed Laws for the Gig Workers:
- The Code on Social Security 2020: It has proposed social security schemes for gig workers and platform workers on matters relating to life and disability cover, accident insurance, health and maternity benefits, old age protection, etc.
- The Code has not come into force till now.
- An MoU has been signed between the MoL&E and the National Law School of India University (NLSIU), Bangalore for assistance in framing a new scheme for the gig and platform workers as well as workers in the unorganised sector.
Present Law for the Gig Workers in India:
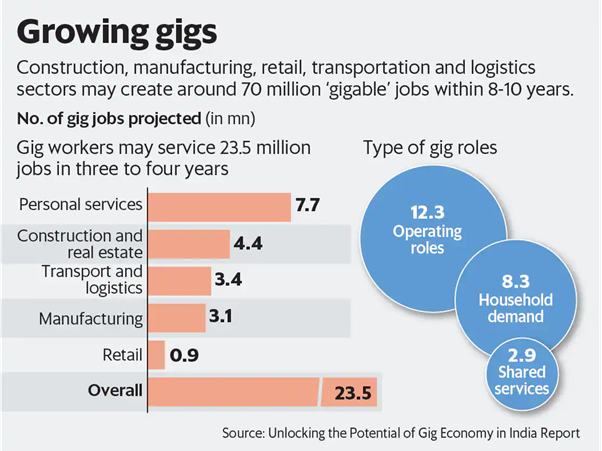
- The Rajasthan Platform-Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Act 2023: Rajasthan has become the first state in the country to pass a law for the welfare of gig workers earning their livelihood through online platforms (Ola, Swiggy, etc).
Source: Indian Express
India’s ethanol push
Tag: GS Paper-3: Growth & development; Environmental Pollution & degradation.
In News:
Diversification from molasses to a range of feedstocks and government’s differential pricing policy for ethanol, has enabled blending rates with petrol to more than double to 11.75% in the past five years.
About India’s ethanol production programme:
- India has rolled out 20% ethanol-blended petrol this year and aims to “cover the entire country by 2025”.
- There are 3 routes to ethanol production from sugarcane.
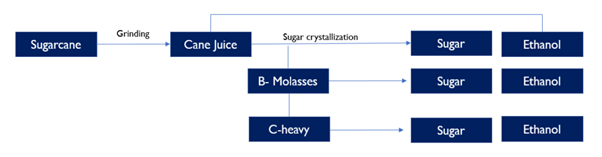
What is the status of feedstock diversification in India?
- India’s ethanol programme is no longer reliant on a single feedstock or crop.
- Earlier, it was molasses and cane.
- Today, it’s also rice, maize and other grains.
- Ethanol yields from grains are actually higher than from molasses.
- However, the process is longer.
- The starch in the grain has to first be converted into sucrose and simpler sugars (glucose and fructose), before their fermentation into ethanol by using yeast (saccharomyces cerevisiae).
- Molasses already contain sucrose, glucose and fructose.
- Some leading sugar companies, including Triveni Engineering & Industries Ltd, DCM Shriram and Dhampur Sugar Mills, have installed distilleries with the flexibility to operate on multiple feedstocks and, hence, round the year.
- The flexibility and incentive for mills/distilleries to use multiple feedstocks has largely come from the government’s policy of differential pricing.
- Till 2017-18, the OMCs were paying a uniform price for ethanol produced from any feedstocks.
- From 2018-19, the government began fixing higher prices for ethanol produced from B-heavy molasses and whole sugarcane juice/syrup.
- The idea was to compensate mills for revenues foregone from reduced/nil production of sugar.
- Uttar Pradesh is a major sugarcane grower, just as Bihar is in maize. If their farmers were to supply rice, barley and millets as well to distilleries, these two states could well “fuel India” the way Punjab, Haryana or Madhya Pradesh “feed India”.
- The domestic availability or stocks of cereals and sugar might get affected from El Niño-induced monsoon uncertainties.
- While the government has already banned exports of wheat, sugar and non-parboiled non-basmati rice, it hasn’t put any brakes so far on the ethanol blending programme.
Byproduct benefits
- The new molasses-based distilleries have MEE (multi effect evaporator) units, where the spent wash is concentrated to about 60% solids.
- The concentrated wash is used as a boiler fuel along with bagasse in 70:30 ratio.
- The resultant ash coming out from the incineration boiler in dry form contains up to 28% potash, which can be used as fertiliser.
- DDGS or distillers’ dried grain with solubles, is sold as animal feed.
Source: Indian Express
FAO Strategy on Climate Change 2022-2031
Tag: GS Paper-2: Important international institutions
In News:
The new FAO Strategy on Climate Change 2022-2031 rests on our vision of climate-resilient agriculture to transform agri-food systems to be more efficient, more inclusive, more resilient and more sustainable, accelerating the achievement of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
About the FAO Strategy on Climate Change 2022-2031
VISION
- FAO envisions the future state brought about by its climate action.
- Agri-food systems are sustainable, inclusive, resilient and adaptive to climate change and its impacts and contribute to low-emission economies while providing sufficient, safe and nutritious foods for healthy diets, as well as other agricultural products and services, for present and future generations, leaving no one behind.
GUIDING PRINCIPLES
- Take an agri-food systems approach.
- Put farmers, livestock keepers, fishers, aquaculturists and forest-dependent people at the centre.
- Embrace good practices and innovations.
- Build on science-based evidence, including open science and data.
- Promote country-driven climate action for sustainable results.
- Deliver through strategic partnerships.
- Mainstream gender equality, youth engagement, Indigenous People’s participation and social inclusiveness.
- Support inclusive multi-stakeholder approaches.
- Scale up support.
- Adopt a “no-one-size-fits-all” approach.
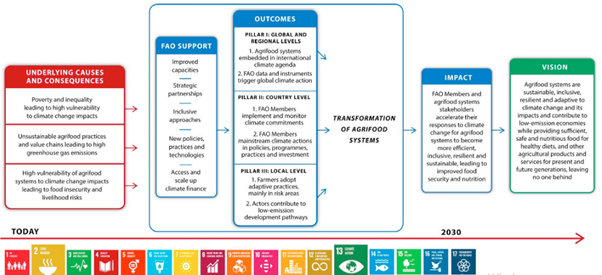
- Theory of Change
Source: FAO
WTO: Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies
Tags: GS-II: IR
In News:
Civil society and Trade experts call on India to refrain from ratifying WTO’s Fisheries Subsidies Agreement
About WTO: Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies:
- The World Trade Organisation (WTO) has reached an agreement on fisheries subsidies in Geneva which was part of the ‘Geneva Package’ secured in 2022.
- The goal of the agreement is to curb harmful fishing subsidies that contribute to overfishing and depletion of marine resources.
- As per the proposal the developed countries engaged in distant water fishing will be prohibited from providing subsidies for illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing activities.
- Ratification requires acceptance from two-thirds of the 164 WTO members and for now only 10 countries have ratified the agreement excluding India.
- Trade experts and certain members of civil society are urging India not to ratify the current agreement and instead advocate for a comprehensive pact.
- Developing countries have sought restrictions on non-specific fuel subsidies used by developed countries to subsidize their fishing fleets however the demand was rejected in negotiations.
- Overall, there is a need to ensure a fairer distribution of subsidies, supporting sustainable small-scale fishing activities, and addressing the imbalance caused by industrial fishing fleets from developed nations.
Source: Economic Times
Silvopasture systems
Tags: GS-III: Environment
In News:
Research findings suggest the potential of harnessing Silvopasture Systems for Local Climate Resilience
About Silvopasture Systems:
- Silvopasture is an ancient and proven land management practice that integrates trees, forage, and livestock on the same piece of land.
- It is a sustainable agroforestry system that offers numerous environmental and economic benefits besides helping to combat deforestation and promote sustainable land use.
- Important features:
- The combination of trees and pasture enhances biodiversity, providing habitat for wildlife and contributes to carbon sequestration and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions.
- These systems have been found to sequester significantly more carbon than traditional pastures without trees as trees act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- It reduces soil erosion and improves soil health by enhancing nutrient cycling and organic matter content.
- It creates a favourable microclimate for livestock which experiences improved welfare due to the provision of shade and wind protection reducing heat stress during hot weather.
- It promotes better water management, as tree roots help increase soil water infiltration and storage capacity.
- This agroforestry system also provides economic benefits to farmers by diversifying income streams through timber, forage, and livestock products.
- Silvopasture practices can be tailored to specific ecological and socio-economic contexts, making it adaptable to different regions and farming systems.
- Overall, Governments and agricultural policymakers can promote and incentivize the adoption of silvopasture systems to foster sustainable agriculture and combat climate change.
Source: Down to Earth
‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign
Tag: GS-1
In News:
Centre plans nationwide events under the ‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign in August.
About
- ‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign as part of the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’ celebration of India’s 75 years of Independence.
- It aims to develop a garden called Amrit Vatika along the Kartavya Path in Delhi using soil collected from different parts of the country in August.
- It includes events at the panchayat, village, block, urban local body, state, and national levels.
- The agenda involves installing a memorial plaque bearing the names of those who made the supreme sacrifice, including freedom fighters and defence personnel.
Source: The Hindu
PM-WANI
Tag: GS-3 Infra development
In News:
Wi-fi hotspot pouches: Internet from a sachet Distributed through PMWANI, it can be a game changer in digital connectivity.
About
- The Digital India program has outlined three key vision areas: digital connectivity, software and services on demand, and the digital empowerment of citizens. To effectively achieve these goals, the concept of PM-WANI (Wi-Fi Access Network Interface) was introduced.
- PM-WANI aims to establish interoperable public Wi-Fi hotspots, particularly in rural and underserved regions, to make affordable Internet access readily available to the general public.
- This initiative operates through Public Data Offices (PDOs), which act as last-mile distributors of broadband services. They offer internet packages at very affordable rates, as low as Rs 5 to 10, known as “sachet-sized” packages.
- The beauty of this framework lies in the opportunity it presents for aggregators, known as PDOAs, to establish Wi-Fi hotspots without the burden of additional licensing fees. This, in turn, encourages the growth of local nano-entrepreneurs who can set up Wi-Fi hotspots and provide internet access to users.
- PM-WANI’s affordability and reliability make it a highly beneficial solution for areas that have been traditionally underserved.
- Expansion of internet connectivity benefits Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and Telecommunication Companies (Telcos) by enabling them to reach a larger customer base and foster further growth in the digital landscape.

Source: Indian Express
Fluorochemicals
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
A team of chemists has developed an entirely new method for generating critically important fluorochemicals that bypasses the hazardous product hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas.
About
- Fluorochemicals play a crucial role in diverse industries such as polymers, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and lithium-ion batteries, owing to their exceptional properties like high thermal stability and chemical resistance.
- The conventional method of producing fluorochemicals involves an energy-intensive process that relies on hazardous hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas. This gas is generated by reacting the mineral fluorspar (CaF2) with sulfuric acid under harsh conditions, leading to safety risks and environmental issues, particularly due to the potential for HF spills.
- The new approach has the potential to enhance safety and environmental impact, streamline the supply chain, and reduce energy demands in the rapidly expanding global fluorochemical industry.
Source: PHYS
Hygroelectricity
Tag: GS-3 Infrastructure Project
In News:
Harvesting electricity from humid air could one day power our devices.
About
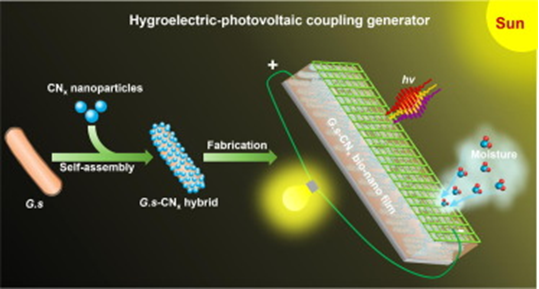
- Hygroelectricity is the generation of electricity from the humidity of the air. It is a type of renewable energy that has the potential to be a major source of power in the future.
- Hygroelectricity, as described, utilizes a tiny device with nanopores to generate electricity from the water molecules present in the air.
- The interaction between the water molecules and the nanopores leads to an electric charge imbalance, effectively creating a miniature battery that can continuously generate electricity.
Source: BBC News
Argentina
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
India and Argentina have agreed for a bilateral exchange of young researchers and Startups, particularly in the field of Biotechnology and Agriculture.
About
- Argentina, the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, is situated between the Andes Mountains and Chile to the west. The country’s interior is characterized by vast, fertile grasslands known as the Pampas, extending eastward.
- The eastern boundary of Argentina is defined by the Atlantic Ocean, while Bolivia lies to the northwest and Paraguay to the north.
- Lithium Triangle’ is an area of South America located in Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile.
- Argentina is famous for livestock ranching in the world. Argentina’s world-famous ranchers are culling their breeding cows at the fastest rate in 30 years.
- Agriculture in Argentina is relatively capital intensive, employing around 7% of the workforce and accounting for less than a third of all labor even during its heyday around 1900.
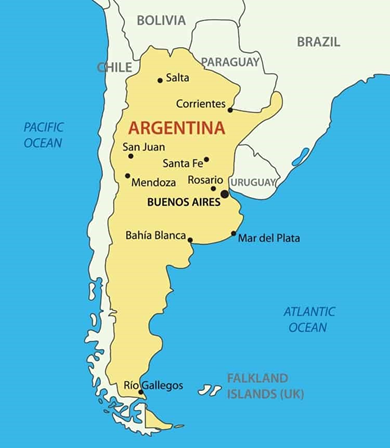
Source: PIB GOV.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

