In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 The Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
- 2 Questioning in Parliament
- 3 SIM Cards
- 4 Marine Cloud Brightening
- 5 QR code in Food labelling
- 6 National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL)
- 7 Nano Di-Ammonia Phosphate (DAP) liquid
- 8 Benin
- 9 Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Tribunal
- 10 Exercise Harimau Shakti-2023
- 11 FAQs
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
The Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
Tag: GS-2 Polity, Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
A parliamentary committee has recently examined the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) 2023 Bill, which includes significant changes to India’s Criminal Justice System.
The parliamentary committee reviewing the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) 2023 Bill has made several noteworthy recommendations:
- The committee suggests including a gender-neutral provision to criminalize adultery, aiming to protect the institution of marriage without gender bias.
- They are considering criminalizing non-consensual sex and acts of bestiality, addressing a range of sexual offenses.
- The committee proposes improved definitions for terms like “community service” and “life imprisonment” within the bill.
- The new draft code removes Section 124A (Sedition) and provides provisions for prosecuting offenses committed in foreign countries, reflecting significant improvements in the criminal justice system.
Arguments in Favor of legalizing and criminalizing adultery can be summarized as follows:
Legalizing Adultery:
- The Supreme Court’s 2018 judgment in Joseph Shine vs. The Union of India highlighted the importance of individual autonomy and the right to privacy.
- Legalizing adultery acknowledges adults’ right to make personal relationship decisions, while the 158-year-old Section 497 of the IPC was deemed unconstitutional as it violated Article 21 and Article 14 of the Indian Constitution.
- Section 497 was rooted in the Doctrine of Coverture, which is incompatible with the Constitution and denies women their fundamental rights.
- The Supreme Court emphasized that marriage does not mean surrendering one’s autonomy. Allowing individuals to make sexual choices is a crucial aspect of human liberty.
Criminalizing Adultery:
- Criminalizing adultery is seen as a means to protect the institution of marriage, preventing its harm, broken families, and emotional trauma.
- Some argue that criminalizing adultery protects women from unfaithful spouses who might otherwise abandon them, leaving them economically vulnerable.
- The adultery law is viewed as upholding traditional moral and societal values important to many in Indian society.
- Criminalizing adultery is seen as a way to preserve the family structure, a fundamental building block of society.
The Path Ahead
- Encouraging awareness about adultery’s impact on families and relationships can empower individuals to make informed choices in their personal lives.
- Promoting marriage counselling and mediation as proactive solutions for marital issues, and enhancing their accessibility, is crucial.
- Additionally, there’s a necessity to promote alternative dispute resolution methods like arbitration and mediation to address infidelity and marital discord outside the legal system.
Source: HT
Questioning in Parliament
Tag: GS-2 Polity, Indian Constitution
In News:
In a recent development, a Member of Parliament (MP) is under scrutiny by both the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and the Lok Sabha Ethics Committee due to her suspected role in ‘cash for query’ accusations.
Procedure for Raising and Admitting Questions in Lok Sabha:
- The process adheres to Rules 32 to 54 of the “Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha” and Directions 10 to 18 set by the Lok Sabha Speaker.
- MPs must submit a notice to the Lok Sabha Secretary-General, including the question’s text, the designated Minister, the desired answer date, and preference order if multiple questions are tabled for the same day.
- MPs can submit up to five notices for questions (both oral and written) on a single day, with additional notices considered for subsequent days within the same session.
- A standard notice period of at least 15 days is required for questions.
- MPs can submit notices through the online ‘Member’s Portal’ or printed forms from the Parliamentary Notice Office.
- The Speaker of Lok Sabha reviews the notices for admissibility based on established criteria.
Conditions for Question Admissibility:
- Questions must be concise, under 150 words, and avoid arguments, defamatory statements, or references to personal conduct, except in an official or public context.
- Questions about broad policy issues are not admissible due to their complexity.
- Questions cannot pertain to matters under judicial consideration or before parliamentary committees and should not seek information that might undermine national unity and integrity.
Types of Questions in Parliament:
- Starred Question: MPs ask a starred question and receive an oral response from the Minister-in-charge. Each MP can ask one starred question per day, and supplementary questions can follow the oral answer.
- Unstarred Question: MPs seek a written answer from a minister, and the answer is laid on the table of the House. Supplementary questions are not allowed for unstarred questions.
- Short Notice Question: These are for urgent matters of public importance, requiring an oral answer. They have a notice period of less than 10 days.
- Question to Private Member: Questions addressed to private members are permitted under specific parliamentary rules (Rule 40 in Lok Sabha and Rule 48 in Rajya Sabha). They should relate to a matter for which the member is responsible, such as a Bill, resolution, or other issues.
The Importance of Raising Questions:
- Questioning is an essential and unimpeded parliamentary privilege for MPs, serving as a means for legislative oversight of executive actions.
- This process enables MPs to gather information about government operations, scrutinize policies, expose governmental deficiencies, and encourage ministers to take actions that benefit the public.
- Questions offer valuable insights to the government about public opinion regarding policies and governance. They can lead to the establishment of parliamentary investigations, inquiries, or the introduction of new laws.
Way Ahead
- The Question Hour in parliament is a constitutional right under Article 75, representing a form of direct democracy.
- MPs, as representatives of the people, directly question the government on governance matters, and the government is obligated to respond in the House.
- In cases where a question is disallowed, officials should provide a valid reason, which is not accessible through RTIs due to parliamentary privilege.
- Challenging such decisions in court can be challenging due to the privilege of the House.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2017) Q. The Parliament of India exercises control over the functions of the Council of Ministers through Adjournment motion Question hour Supplementary questions Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (d) Adjournment motion is introduced in the Parliament to draw attention of the House to a definite matter of urgent public importance. It interrupts the normal business of the House, thereby making it a device of censure against the government. Hence, 1 is correct. Question Hour is a tool of “Parliamentary Oversight” over the administration or executive. During Question Hour, the government is answerable for all its acts of omission and commission to the Parliament. There are four types of questions: Starred Questions, Unstarred Questions, Short Notice Question and Question to Private Member. Hence, 2 is correct. Under the Starred Question, an oral answer is required from the minister and the members are allowed to ask the supplementary questions. Hence, 3 is correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer. |
Source: IE
SIM Cards
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, Department of Telecommunication (DoT) gives telcos time till Dec 1 to comply with new SIM card rules.
About a SIM card
- A SIM card, or Subscriber Identity Module card, is a tiny integrated circuit that serves as an individual’s ID card within a cellular network.
- It carries a unique identification number (IMSI) for locating and confirming a subscriber’s identity.
- A SIM card is essential for connecting a mobile phone to a GSM-based cellular network, and it stores a special authentication key (SAK) for secure access.
- In addition to network access, SIM cards can store data like location information, preferred networks for roaming, and sometimes even emergency contact numbers, contacts, and SMS messages.
- They are crucial for the functionality and security of mobile communication.
Working of SIM cards
- A SIM card operates according to the ISO/IEC 7816 international standard, with metal contacts segmented into pins, each serving a specific function.
- The SIM card plays a vital role in authenticating a subscriber’s data on the cellular network, using an authentication key.
- When a call is made, the SIM card verifies the recipient’s identity, directing the call through the network if the recipient is connected to the same exchange.
Evolution of SIM cards over time
- The evolution of smart cards, including SIM cards, began in the late 1960s, driven by technological advancements described by Moore’s law.
- The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) played a significant role in standardizing SIM cards.
- With the transition to 3G networks, the term ‘SIM’ was separated into hardware (UICC) and software, and eSIMs emerged.
- eSIMs are software-based and permanently integrated into a mobile device during manufacturing, eliminating the need for physical SIM cards.
- Notable devices like Google Pixel and iPhone 14 support eSIMs. Benefits of eSIM technology include environmental friendliness, enhanced security, and remote reprogramming by network operators.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2010) Q. Which among the following do/does not belong/ belongs to the GSM family of wireless technologies? (a) EDGE (b) LTE (c) DSL (d) Both EDGE and LTE Answer: (c) Prelims (2019) Q. With reference to communication technologies, what is/are the difference/differences between LTE (Long Term Evolution) and VoLTE (Voice over Long-Term Evolution)? (2019) LTE is commonly marketed as 3G and VoLTE is commonly marketed as advanced 3G. LTE is data-only technology and VoLTE is voice only technology. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: (d) |
Source: TH
Marine Cloud Brightening
Tag: GS-3 Environment, Science and technology.
In News:
Marine cloud brightening is gaining attention as a method to combat extreme ocean heat, reduce coral bleaching, and protect marine ecosystems.
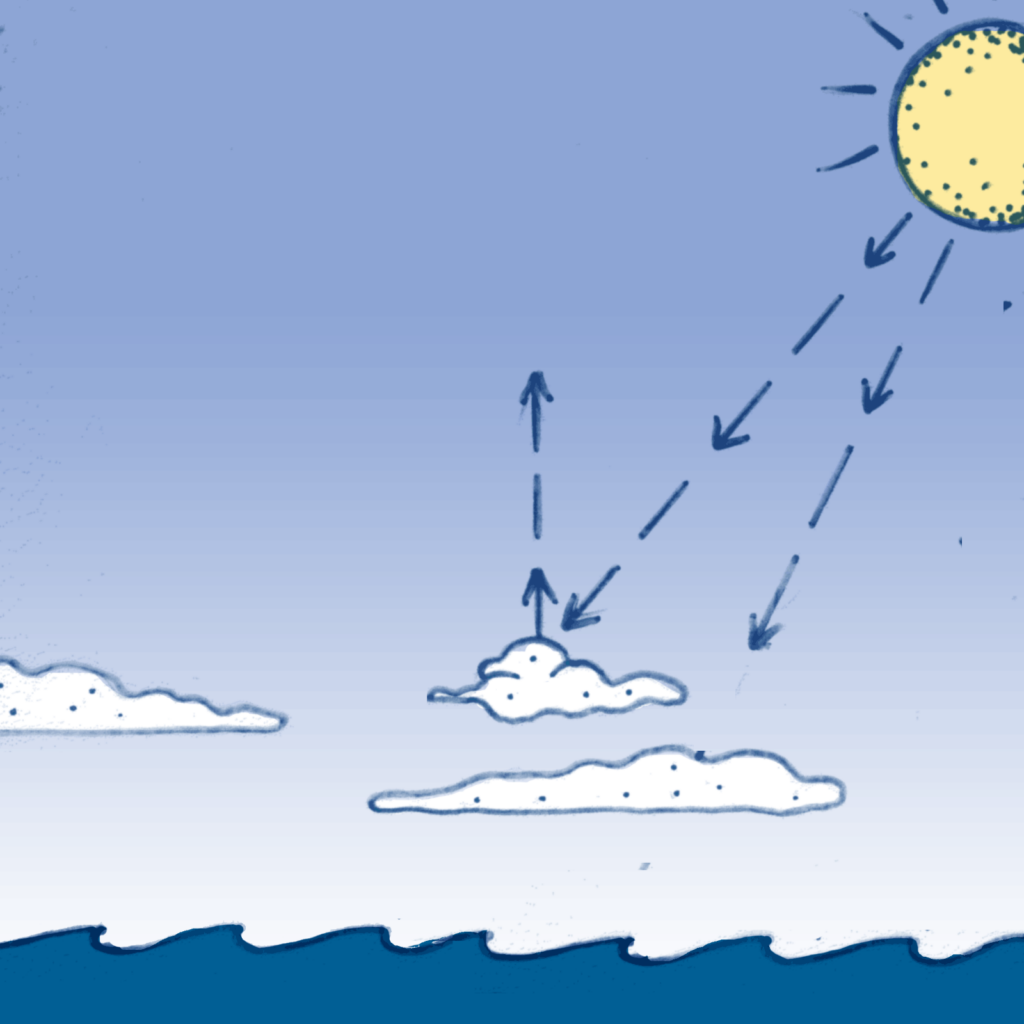
Marine Cloud Brightening What and How?
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB) is a concept introduced by British cloud physicist John Latham in 1990 to address global warming.
- It aims to enhance the reflectivity of marine clouds by releasing sea water droplets into the atmosphere, which, when evaporated, leave behind salt particles that create denser and brighter clouds.
- This process can help counteract the warming effects of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide over vulnerable ocean areas.
Pros and Cons of Marine Cloud Brightening:
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB) offers potential benefits by reducing sea surface temperatures, potentially lessening coral bleaching events and aiding coral recovery.
- It’s being explored for the Great Barrier Reef.
- However, there are technical challenges, environmental impacts like altered climate patterns, ethical dilemmas concerning human intervention, and a moral hazard of reduced commitment to greenhouse gas emissions reduction.
Conclusion:
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB) is being explored to combat ocean heat and reduce coral bleaching.
- It involves making clouds whiter by releasing fine sea water droplets into the atmosphere.
- MCB has potential benefits for coral reefs and is being studied for the Great Barrier Reef.
- However, it faces technical, environmental, ethical, and moral challenges. Coral bleaching, caused by elevated sea temperatures, weakens and can kill corals.
- MCB is a complementary measure for short-term coral reef protection, alongside conservation, restoration, adaptation, and innovation to address climate change impacts.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2016) Q.”Biorock technology” is talked about in which one of the following situations? (a) Restoration of damaged coral reefs (b) Development of building materials using plant residue (c) Identification of areas for exploration/extraction of shale gas (d) Providing salt licks for wild animals in forests/protected areas Answer: (a) Prelims (2018) Q.2Consider the following statements: Most of the world’s coral reefs are in tropical waters. More than one-third of the world’s coral reefs are located in the territories of Australia, Indonesia and Philippines. Coral reefs host far more number of animal phyla than those hosted by tropical rainforests. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (d) Prelims (2014) Q.3 Which of the following have coral reefs? Andaman and Nicobar Islands Gulf of Kachchh Gulf of Mannar Sundarbans Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 2 and 4 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 Answer: (a) Mains (2019) Q. Assess the impact of global warming on the coral life system with examples. |
Source: TH
QR code in Food labelling
Tag: GS-3 Economy and GS-2 Polity and Governance
In News:
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has suggested the utilization of Quick Response (QR) codes on food items.
The Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, 2020
- The Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, 2020, provides detailed guidelines for the information that must be displayed on food product labels.
- This includes essential details like the product name, shelf life, nutrition facts, vegetarian/non-vegetarian logos, ingredient lists, allergen warnings, and specific labelling requirements.
- The primary objective is to empower consumers with the information they need to make informed choices when purchasing food products.
Need for QR codes
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act 2016 acknowledges the rights and requirements of people with disabilities, with a focus on accessibility and promoting their health.
- To enhance this accessibility, one practical approach is to include QR codes on food product labels.
- These QR codes would contain extensive information about the product, such as its ingredients, nutritional facts, allergens, and manufacturing date.
Source: TH
National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL)
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News:
In response to an export ban, the government has chosen to facilitate the sale of 12 lakh metric tonnes (LMT) of non-basmati white rice to 11 countries through the National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL).
About National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL)
- The National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL), established to oversee cooperative sector exports, has achieved remarkable success, securing orders worth Rs 7,000 crore.
- The Union Minister of Cooperation highlighted that around 50% of export profits will directly benefit farmers through NCEL.
- NCEL is a registered umbrella organization under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, 2002, operating in the cooperative sector with six key objectives, including increasing exports, supporting farmers, diversifying crops, accessing global markets for organic products, positioning India in the global biofuel market, and strengthening the cooperative sector.
Utility of National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL)
- The establishment of the National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL) aims to boost the demand for Indian cooperative products and services worldwide, while ensuring the best possible prices.
- It promotes exports through various activities such as procurement, storage, processing, marketing, branding, packaging, and more, covering goods and services produced by cooperative societies.
- The society assists with financing, technical guidance, training, capacity building, market intelligence, and the implementation of government schemes to enhance exports from the cooperative sector.
- This initiative supports “Make in India” and contributes to ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat.’
- It aligns with the goal of “Sahakar-se-Samriddhi” through an inclusive growth model for cooperatives, facilitating their access to export-related schemes and policies through a comprehensive government approach.
Source: TH
Nano Di-Ammonia Phosphate (DAP) liquid
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently Home Minister inaugurated India’s first nano DAP plant in Gujarat on Vijaya Dashami
About DAP and its potential benefits
- Nano-DAP is a highly concentrated phosphate-based fertilizer designed to provide phosphorous nutrition throughout the crop growth cycle.
- It is a collaborative effort between the Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO) and a private player, Coromandel.
- This innovative fertilizer, priced at Rs 600 for a 500 ml bottle, is equivalent to one bag of conventional DAP, which costs Rs 1,350.
- The introduction of Nano-DAP is expected to have significant benefits, particularly for India’s fertilizer sector.
- DAP is the second most consumed fertilizer in the country, and the majority of it is imported due to insufficient local production.
- Nano-DAP aims to reduce India’s reliance on fertilizer imports, ultimately lowering the annual subsidy on non-urea fertilizers.
Source: MC
Benin
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) shareholders approve Benin, Ivory Coast to join as members.
About
- Benin officially the Republic of Benin and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa.
- It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east.
- The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the Bight of Benin, part of the Gulf of Guinea in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean.
- The capital is Porto-Novo, and the seat of government is in Cotonou, the most populous city and economic capital.
Source: REUTERS
Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Tribunal
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Centre constitutes Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Tribunal to declare JKDFP as unlawful association
About UAPA and it’s major provisions
- The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) in India aims to prevent unlawful activities.
- Particularly those threatening the nation’s integrity and sovereignty.
- It is often referred to as the Anti-terror law.
- The UAPA grants substantial powers to the central government and allows for severe penalties, including death penalty and life imprisonment.
- Key provisions include
- Designating individuals/organizations involved in terrorism
- Special procedures for property seizures related to terrorism
- Empowering officers of the National Investigation Agency (NIA).
- The process of declaring an association unlawful involves gazette notifications
- Tribunals to investigate
- Confirming the decision through official gazette publications.
What is UAPA Tribunal?
- The UAPA establishes a tribunal headed by a retired or sitting High Court judge to give legal validity to the government’s bans.
- When the Centre notifies the tribunal, the association in question has 30 days to present reasons why it should not be declared unlawful.
- Following a hearing and possible inquiry, the tribunal, within 6 months, determines whether there is enough evidence to declare the association unlawful.
- The government’s notification does not take effect until the tribunal confirms it through an official order.
Source: AIR News
Exercise Harimau Shakti-2023
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News:
Exercise Harimau Shakti 2023, a joint bilateral training exercise between India and Malaysia, has commenced at Umroi Cantonment.
About Exercise Harimau Shakti 2023
- This exercise focuses on setting up a Joint Command Post, an integrated surveillance grid, and a Joint Surveillance Centre.
- It emphasizes the deployment of joint forces in diverse environments, intelligence operations, the utilization of drones and helicopters, casualty management, and logistics.
- The exercise highlights the enhancement of defines cooperation between the Indian and Malaysian armies, reinforcing the bilateral relations between the two countries.
Source: PIB
FAQs
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


