
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Concerns about Using Aadhaar in Welfare Schemes
- 2 India Ageing Report 2023
- 3 Palm-Oil Production
- 4 Aadhaar Linkage with the Electoral Roll is Voluntary
- 5 Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana
- 6 Pangolin
- 7 Policy Initiatives for Pharma Med Tech Sector
- 8 Surety Bonds
- 9 Sarna Code
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 10.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 10.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 10.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 10.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 11 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Concerns about Using Aadhaar in Welfare Schemes
Tag: GS-2 E-Governance, Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections, Digital Public Infrastructure
In News:
A recent Moody’s report, ‘Decentralised Finance and Digital Assets’, highlights the security and privacy vulnerabilities of centralized biometric systems based identities like Aadhaar and advocates for decentralized digital identity systems instead of centralized biometric systems.
About Aadhaar:
- Aadhaar is a unique identification number given to all Indian residents by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI).
- It serves as proof of identity and address (not citizenship) and is linked to an individual’s biometric and demographic information.
- Aadhaar enrolment involves the collection of demographic details of individuals along with their biometric fingerprints and iris scans, as they are considered to be unique identifiers of individuals. These details are stored in the Aadhaar database.
Rationale for Aadhaar:
- The objectives of UIDAI were to ensure that all residents have a unique ID and to curb corruption in accessing welfare programs by eliminating “ghost” and “fake” individuals.
- An individual is called a ‘ghost’ if they access rations in the name of a dead person, and a ‘fake’ if they access rations even though they are not officially entitled to it.
- The government favours Aadhaar for several other government-to-citizen cash transfer programmes and claims that it leads to substantial savings in welfare schemes, as it removes ghosts and duplicates.
Utility of Aadhaar:
- Aadhaar as financial address of individual: Aadhaar acts as the financial address of the individual and after linking it with their job card and bank account payments for various services like MNREGA wages, subsidies, etc. can be directly remitted to the account of the individual.
- Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS): Individuals can withdraw money from their Aadhaar-linked bank account through AePS. Cash can be withdrawn through private banking kiosks or private banking correspondents who use their point of sale machines to authenticate individuals using their biometrics
- Seeding of Aadhaar in the MGNREGS database: Seeding has been done without requiring the worker to authenticate using their biometrics. Payment to workers under the scheme is also made by directly crediting money in their account without requiring authentication of their biometrics.
- Improved targeting: Aadhaar can help to ensure that government benefits are targeted to the intended beneficiaries and that leakages and duplication are reduced.
Concerns regarding the use of Aadhaar in welfare schemes:
- Failure in curbing quantity frauds: several organizations have pointed towards quantity fraud being the main type of corruption. Aadhaar has no role in either detecting or preventing this fraud.
- Biometric authentication failure: Rural areas witness frequent authentication failure due to lack of reliable internet, fading fingerprints among daily wage workers, lack of phone connectivity to get an OTP, etc. leading to denials.
- People have to make multiple trips to ration shops, to authenticate with no guarantee that the authentication will work.
- Older women, people with disabilities, etc. are more prone to hardships and exclusions due to such stringent biometric authentication requirements.
- Payment failures: In Aadhaar-based payments, errors in any step result in payment failures. Different spellings in the job card and in the Aadhaar database can result in authentication failures.
- Diversion of wages: Lack of awareness and coercion by financial institutions to link Aadhaar to bank accounts without consent results in wages getting diverted to some other account without the worker’s knowledge. For example, Aadhaar payments of people got redirected to Airtel wallets.
- Misdirected payments: Misdirected payments through Aadhaar are difficult to detect and are nearly impossible to resolve. These happen when one person’s Aadhaar number gets linked to somebody else’s bank account.
- Exclusions as constitutional violation: Exclusions from social welfare services resulting from accessibility issues due to Aadhaar are often considered as constitutional violations.
- Security concerns: Banking correspondents using the AePS operate without any accountability framework.
- Multiple biometric authentication: Some banking correspondents ask individuals to biometrically authenticate multiple times. Each authentication gives access to the banking correspondents to operate the individual’s bank account. Using AePS, money from workers’ accounts have been withdrawn or that they have been signed up for government insurance programmes without their knowledge.
- Scams: Aadhaar related scams like those witnessed in Rs10 crore scholarship scam in Jharkhand is also witnessed.
- Deletion of MNREGA job cards: Job cards of several alive and active rural workers have been deleted on grounds that they are dead or “ghosts.”
- Linking Aadhaar with other services: The government has pushed for Aadhaar in other matters such as linking voter IDs with Aadhaar. However, critics are apprehensive that this might not be beneficial based on their prior experiences.
India Ageing Report 2023
Tags: GS – 1: Indian Society (Population), GS – 2: Social Justice (Welfare schemes for Vulnerable sections)
Why in News:
Recently, the United Nations Population Fund (UNPF), India, has released the “2023 India Ageing Report”, highlighting the rapidly growing elderly population in India.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Elderly Population Growth:
- With the decadal growth rate of the elderly population of India currently estimated to be at 41%.
- The percentage of the elderly population in the country is projected to double to over 20% of the total population by 2050.
- The elderly population will have surpassed the population of children (aged 0 to 15 years) in the country by 2046.
- Impact of Poverty:
- More than 40% of the elderly in India are in the poorest wealth quintile. Poverty among the elderly is a concern, affecting their quality of life and healthcare utilization.
- About 18.7% of them are living without an income.
- Life Expectancy of Women: In comparison to males, women have a higher life expectancy between the ages of 60 and 80, which varies across the states and union territories.
- Sex Ratio:
- Poverty is inherently gendered in old age when older women are more likely to be widowed, living alone, with no income and with fewer assets of their own, and fully dependent on family for support.
- Between 2011 and 2021, the sex ratio increased in India as a whole and across all regions, barring the Union Territories and western India.
- Regional Variations:
- There are significant inter-State variations in the elderly population and their growth rates.
- Most States in the southern region and select northern States such as Himachal Pradesh and Punjab reported a higher share of the elderly population than the national average in 2021.
Recommendations of the Report:
- By integrating pertinent questions in data collecting activities such as the National Sample Survey, the National Family Health Survey, and the Census of India, the absence of reliable data on a variety of topics relating to the elderly can be addressed.
- Increase awareness about the elderly initiatives already in place and bring all Old Age Homes under regulatory scrutiny. Promote the formation and operation of elderly self-help groups.
- Be sure to emphasise the value of elders residing in multigenerational homes. Promote legislation that makes this way of life easier and more comfortable.
- Encourage in situ (at home) ageing as much as possible by creating short-term care facilities like creches or day-care facilities.
Palm-Oil Production
Tags: GS – 2: International Relations (Effect of Policies and Politics of countries on India’s Interest), GS – 3: Indian Economy (International Trade)
Why in News:
Recently, Malaysia signed a deal to double palm oil exports to China annually is a move to offset potential revenue losses from the EU’s ban on commodities that are linked to deforestation.
Background of the Deal:
- The European Union (EU) intends to phase out imports of palm oil-based biofuel by 2030. The EU Deforestation-Free Regulation (EUDR) adopted in Brussels earlier this year will impose considerable non-tariff barriers on palm oil exporters to the EU countries.
- The two largest producers of palm oil in the world, Malaysia and Indonesia, have responded strongly to what they view as European protectionism.
- The regulation requires firms to ensure that the product exported to the EU has been grown on land that has not been deforested after December 31, 2020.
- The regulation is not WTO (World Trade Organization) compliant and is a non-tariff barrier.
Malaysia’s Response:
- Malaysia signed a deal with China earlier this month at the China-ASEAN Expo regarding the investment of €3.9 billion ($4.1 billion).
- Because much of Indonesia’s palm oil sector is under Malaysian ownership, a shift by Malaysia towards Chinese markets would also likely affect palm oil producers in Indonesia.
- The European Union remains a major consumer of palm oil globally. Considering the EU’s vast consumer base and its affluent middle class, it’s anticipated that this market will remain attractive to exporters
Palm Oil Production:
- It is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms.
- It is used as cooking oil, and in everything from cosmetics, processed foods, cakes, chocolates, spreads, soaps, shampoo, and cleaning products to biofuel.
- The use of crude palm oil in making biodiesel is being branded as ‘green diesel’.
- Indonesia and Malaysia together account for almost 90% of the global palm oil production.
- India is the biggest importer of palm oil, which makes up 40% of its vegetable oil consumption. India meets half of its annual need for 8.3 MT of palm oil from Indonesia.
- In 2021, India unveiled the National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm to boost India’s domestic palm oil production.
Aadhaar Linkage with the Electoral Roll is Voluntary
Tags: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, the Election Commission (EC) has told the Supreme Court that it is not mandatory to provide Aadhaar numbers for linking with the electoral roll.
About:
- SC’s Decision: SC recorded that the submission of Aadhaar numbers is not mandatory according to Rule 26-B of the Registration of Electors (Amendment) Rules 2022.
- Rule 26B, dealing with “special provision for providing Aadhaar number by existing electors”, states that “every person whose name is listed in the roll may intimate his Aadhaar number to the registration officer in Form 6B in accordance with sub-section (5) of Section 23 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950.
- Form 6B is a letter of information that contains a person’s Aadhaar number for the purpose of electoral roll authentication.
- ECI’s Response: The EC is considering making appropriate clarificatory changes to the forms related to the Aadhaar linkage, indicating its intent to clarify the voluntary nature of the Aadhaar submission.
- This practice violated Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution and could lead to the misuse of voters’ personal data.
- The poll body informed the Bench that “nearly 66.23 crore Aadhaar numbers have already been uploaded in the process of finalizing electoral rolls”.
Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana
Tags: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
In an endeavor for empowering persons with disabilities and senior citizens of the country the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India organized ‘Samajik Adhikarita Shivirs’ across 72 locations simultaneously across the country.
About:
- These camps aim to distribute various types of aid and assistive devices to over 12000 persons with disabilities and senior citizens under the Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana.
Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana:
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana is scheme for providing Physical Aids and Assisted-living Devices for Senior citizens belonging to BPL category.
- It was launched in 2017 by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- This is a Central Sector Scheme, fully funded by the Central Government.
- The expenditure for implementation of the scheme is being met from the “Senior Citizens’ Welfare Fund”.
- The Scheme is being implemented by the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation (ALIMCO), a PSU under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Features:
- The scheme works by distributing free of cost devices, commensurate with the extent of disability or infirmity that is manifested among the eligible senior citizens.
- The devices supported under the scheme are: Walking sticks, Elbow crutches, Walkers/Crutches, Hearing Aids, Wheelchairs, Artificial Dentures and Spectacles.
- The scheme is expected to benefit over 5 lakh Senior Citizens across the country.
Pangolin
Tags: GS – 3 Environment, Conservation
Why in news?
Recently, Scientists discovered a new pangolin species named Manis Mysteria.
About:

- There are eight previously known species of pangolin — four found in Asia and four in Africa.
- This discovery marks the ninth known species of pangolin.
- Pangolins are among the most trafficked wild mammals globally.
- Pangolins have been poached for bushmeat, but in the last decade, their skins, scales, and whole bodies have been in high demand in countries like Vietnam, China, and the US. This has led to a decline in their populations.
- Pangolins are nocturnal and have the ability to swim.
- Pangolins feed mainly on termites but also eat ants and other insects.
- India is home to two species:
- Indian Pangolin (EN), found across the subcontinent.
- Chinese Pangolin (CR) is found across a larger area in south Asia.
- Both species are Listed in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- IUCN status:
- All eight pangolin species are protected under national and international laws.
- Critically Endangered – Philippine Pangolin, Sunda Pangolin, Chinese Pangolin.
- Vulnerable – Temminck’s Pangolin.
- Endangered – Indian Pangolin, White-bellied Pangolin.
- Ecological Importance: They play a vital role in ecosystem management, mostly in aerating and adding moisture to the soil as well as the succession of plant communities through burrowing.
Manis Mysteria:
- This species bears similarities to the Asian branch of the pangolin family, known as Manis.
- The researchers gave it the name Manis Mysteria, in reference to its enigmatic nature.
- Origin – Most of the Asian pangolins are thought to have originated in South-East Asia.

Policy Initiatives for Pharma Med Tech Sector
Tags: GS –2 Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Relating to Development
Why in news?
Recently, Union Minister of Chemicals and Fertilisers and Minister of Health & Family Welfare launched the National Policy on Research and Development and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector in India and Scheme for promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma MedTech Sector (PRIP).
About:
National Policy on Research and Development and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector:
- This policy aims to transform India’s pharmaceutical and medical technology industries from being cost-based to becoming value-based and innovation-driven.
- The policy aims to encourage R&D in pharmaceuticals, including traditional medicines & phytopharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- The policy acknowledged the need for greater emphasis on encouraging R&D, through indigenously developed cutting-edge products and technologies upon three focus areas, namely, strengthening the regulatory framework, incentivizing investments in innovation, and creating a facilitatory ecosystem for Innovation.
- The event will see active participation from other dignitaries, including policymakers, and experts from the healthcare sector along with representatives from academia, think tanks, industry, and media.
Scheme for Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector (PRIP):
- The PRIP scheme focuses on fostering innovation and transforming the MedTech sector into an innovation-driven powerhouse.
- It emphasizes high-quality research and innovation, aiming to shift the sector towards value and innovation-based approaches.
Components
- Component A – Strengthening the research infrastructure by establishment of seven centres of excellence at the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER).
- Component B – Promoting research in Pharma’s 6 priority areas (like New Chemical Entities, Complex generics including biosimilars, medical devices, stem cell therapy, orphan drugs, Anti-microbial resistance, etc.), wherein financial assistance will be provided for both in-house and academic research.
Surety Bonds
Tags: GS – 3 Economy
Why in news?
The ambitious plan of the government to launch the Surety Insurance Bonds market – an alternative to bank guarantees in infrastructure projects — has failed to take off in the last three years due to technical and financial impediments.
About:
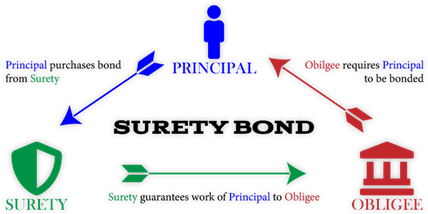
- Surety Bonds are a type of insurance policy protecting parties involved in a transaction or contract from potential financial losses due to a breach of contract or other types of non-performance.
- Aim: Surety bonds are mainly aimed at infrastructure development, mainly to reduce indirect cost for suppliers and work contractors thereby diversifying their options and acting as a substitute for bank guarantee.
- The issuing insurer provides guarantee, for a premium, in the case of a default in execution of a project.
- It is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement. The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal – The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety – The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee – The party who requires, and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organization.
- Surety bond is provided by the insurance company on behalf of the contractor to the entity that is awarding the project.
- Benefits:
- They serve as a risk mitigation tool for maintaining integrity, quality, and adherence to contractual terms, ultimately contributing to the smooth functioning of projects especially in infrastructure sector and fostering a healthy business environment.
- It will help contractors to have financial closure of their projects without depending upon only bank guarantees.
Sarna Code
Tags: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, Jharkhand Chief Minister wrote a letter to Prime Minister, requesting the recognition of the Sarna religious code for tribals.
About:

- The Sarna religion is a nature-worshipping faith that is also known as “Sarna Dharma” or “Religion of the Holy Woods”.
- Followers of the Sarna religion pray to trees and hills and believe in protecting forest areas.
- Their holy grail is “Jal (water), Jungle (forest), Zameen (land)”.
- Believers of Sarna faith do not practice idol worship, nor do they adhere to the concept of the Varna system, heaven-hell, etc.
- The Sarna religion is practised by a majority of the tribal community in Jharkhand.
- The tribal community celebrates the Sarhul festival, which is the New Year festival, as part of the Sarna religion.
- The followers are largely concentrated in the tribal belt states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
More Information:
- Sarna followers are demanding to include ‘Sarna’ as a separate religion for indigenous people in the next census.
- Significance: Recognition as a separate religious community will enable better protection of their language and history.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

