Urban flooding is becoming an increasingly serious crisis in cities around the world, including in India. As cities grow and expand, more natural landscapes are replaced with concrete, leaving little room for water to be absorbed into the ground. Heavy rains, combined with poor drainage systems and unplanned urbanization, lead to frequent waterlogging and floods in many cities. This not only disrupts daily life but also damages property, harms the economy, and poses serious health risks. Addressing urban flooding requires better infrastructure planning, effective water management systems, and stronger disaster preparedness efforts.

Tags: GS – 3, Disaster Management– Flooding
Contents
Context:
- Urban flooding is a major concern in India, with many states receiving 20% more rainfall than normal this monsoon.
- This rise in extreme weather events is linked to climate change, as 64% of Indian sub-districts have seen more heavy rainfall days in the past decade.
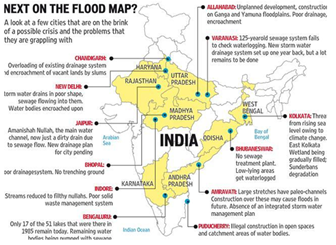
What is Urban Flooding?
- Urban flooding refers to flooding of land or property in densely populated areas due to excessive rainfall, overflowing rivers, poor drainage, or other water-related issues
- Unlike typical rural or natural flooding, urban flooding typically occurs in urban areas (such as roads, sidewalks, and buildings) that have impervious surfaces that do not water cannot penetrate the floor
- This leads to flooding, disruption of transportation, damage to infrastructure and health hazards for urban dwellers.
Cause of Urban flooding:
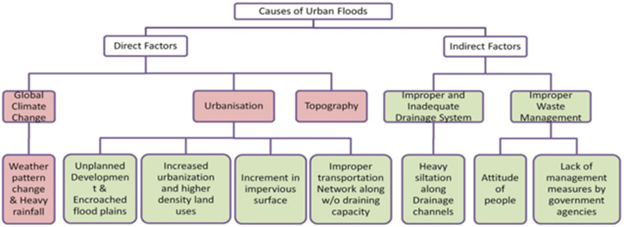
Major Impacts of Urban Flooding:
- Financial Devastation:
- The 2005 Mumbai floods caused USD 2 billion in damage, and the 2015 Chennai floods resulted in USD 3 billion in losses.
- Urban flooding can reduce foreign investment, tourism, and potentially cost USD 1 trillion annually by 2050, according to the World Bank.
- Public Health Crisis:
- In the 2019 Patna floods, outbreaks of malaria and diarrhea occurred, and the 2005 Mumbai floods led to a leptospirosis outbreak.
- Long-term health impacts include a 50% rise in gastrointestinal illnesses among children exposed to floodwaters.
- Urban Mobility Paralysis:
- During the 2022 Bengaluru floods, IT companies lost ₹225 crore daily due to disrupted work commutes.
- Disproportionate Impact on the Urban Poor:
- Slum dwellers and low-income communities, often living in flood-prone areas.
- In Mumbai, over 40% of residents live in slums, which were severely affected during the 2005 floods, perpetuating poverty and limiting access to education.
- Psychological Toll:
- Recurring floods lead to long-term mental health issues, with a 67% increase in cases among urban flood survivors.
- PTSD rates can reach 30-40% in affected areas, significantly impacting social cohesion, productivity, and quality of life.
- Cultural Heritage Damage:
- Urban floods threaten cultural heritage sites, which are key to a city’s identity and economy. The 2019 floods in Hampi, a UNESCO site, caused extensive damage, impacting tourism and urban identity.
Government Initiatives Related to Urban Flooding:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA):
- Launched in 2019, JSA is a water conservation campaign aimed at rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and watershed management.
- In 2023, over 700,000 water conservation structures were created under JSA to address both water scarcity and urban flooding.
- Amrit Sarovar Mission:
- Launched in 2022, the mission aims to develop and rejuvenate 75 water bodies in each district of India.
- By August 2023, over 60,000 Amrit Sarovars had been developed nationwide, helping to reduce urban flood risks through better water management.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABY):
- A central scheme launched in 2020, ABY promotes groundwater management in water-stressed regions.
- The scheme covers over 8,000 gram panchayats across seven states and has enhanced groundwater recharge in flood-prone regions.
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) 2.0:
- Launched in 2021, AMRUT 2.0 aims to make urban areas water-secure by focusing on water supply, sewage, and stormwater management.
- Over 4,700 urban local bodies and includes projects for integrated stormwater drainage to prevent flooding in cities.
Measures to Enhance the Flood Resilience of Indian Cities:
- Sponge City Revolution:
- The “Sponge City” concept mimics natural water absorption by creating permeable surfaces, rain gardens, bioswales and reducing flood risks by up to 50%, recharge groundwater, and improve biodiversity.
- Smart Stormwater Systems:
- IoT technology integrated into stormwater management & Smart sensors, like Singapore’s SWAN system, can reduce flood-prone areas and damage costs in Indian cities.
- Urban Wetland Revival:
- Wetlands can absorb up to 1 million gallons per acre and provide natural flood protection. Kolkata’s East Kolkata Wetlands protect the city from floods while treating wastewater.
- Skyscrapers as Green Flood Barriers:
- Buildings like Milan’s Bosco Verticale absorb rainwater and CO2, easing pressure on urban drainage systems. Such structures can be incorporated into urban planning to combat flooding.
- Flood-Resilient Architecture:
- Elevated and water-permeable designs, like New Orleans’ FLOAT House, can adapt new constructions in flood-prone areas to protect homes and save billions in reconstruction costs.
- Community-Led Micro-Interventions:
- Cities like Rotterdam use “water squares” to collect excess rainwater while serving as recreational spaces. In Maharashtra,Nagdarwadi successfully addressed water scarcity through community-driven rainwater harvesting.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Questions (PYQs)
Mains:
Q:1 The interlinking of rivers can provide viable solutions to the multi-dimensional inter-related problems of droughts, floods, and interrupted navigation. Critically examine. (2020)
Q:2 Account for the huge flooding of million cities in India including the smart ones like Hyderabad and Pune. Suggest lasting remedial measures. (2020)
Source: HT
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

