In large and diverse countries like India, persistent disparities in development and incomes between regions remain a significant challenge. The multifaceted nature of this issue can be attributed to a complex interplay of historical, social, economic, and political factors. Regional imbalances often arise from uneven distribution of resources, varying levels of infrastructure development, and disparities in access to education and healthcare. However, recent initiatives, such as the Area Development Plans (ADP), have been introduced to specifically address these disparities. The ADP aims to strategically allocate resources, implement targeted policies, and foster inclusive growth to bridge the developmental gaps among regions. This plan signifies a concerted effort to tackle the root causes of regional disparities and pave the way for more equitable and balanced development across the diverse landscapes of the country.
Contents
Answer
As per AE Smailes, the regional imbalance is the phenomenon where certain areas are well-developed while others are not. For a country as vast and diverse as India regional disparities are very natural.
Disparities in development and incomes between regions in large countries like India are due to:
- Uneven resource distribution
- Uneven Industrialization and Infrastructure development
- Variations in Access to Markets
- Physiographic variations
- Shape of the country
- Political heterogeneity of the country
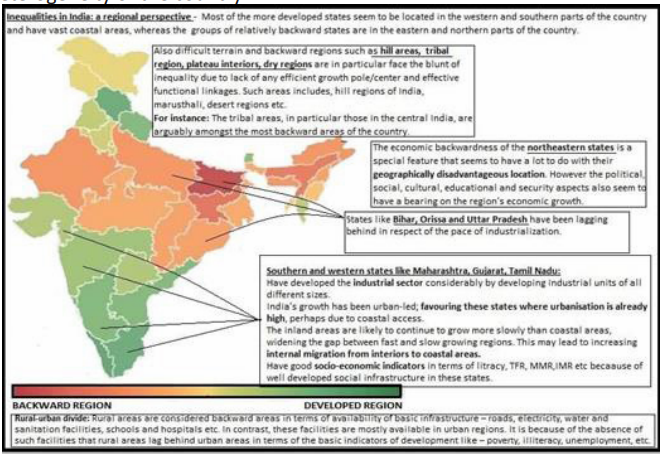
- Uneven resource distribution and resource curse
- Regions with abundant natural resources may experience faster economic growth compared to resource-poor regions.
- For e.g., Gujrat’s rich natural resources, including a strategic coastline and mineral reservesHigh per capita income (PCI in 2022-23:250100 Rupees) and rapid economic development.
- In contrast, Bihar’s resource limitations, marked by water and soil issues-lower per capita income (PCI in 2022-23:49470 Rupees) and greater poverty rates
- Uneven Industrialization and Infrastructure development (Higher levels of primacy)
- Investments in industrialization and infrastructure development tend to be concentrated in certain areas, leading to disparities in economic activity and job opportunities.
- This regional bias is partly result of colonial legacy which resulted in development of few primate cities like Delhi, Kolkata at cost of others
- Physiographic variations
- Differences in terrain, climate, and geographical features, have contributed to significant regional disparities in economic development
- For e.g. The Himalayan region-rugged terrain, less suitable for agriculture and industrial development.
- While the Indo-Gangetic Plains, known for fertile alluvial soil and flat landscapes, more conducive to farming, higher agricultural productivity and greater population density.
- Shape of the country
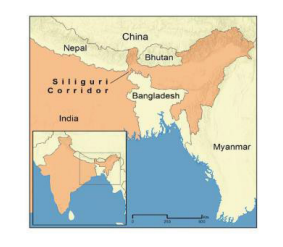

- India’s prorupted shape, characterized by the presence of a narrow corridor of land connecting the main territory to the northeastern states, has contributed to regional disparities due to Connectivity Challenges, Isolation, Limited Trade Opportunities etc.
- Political heterogeneity of the country
- Political heterogeneity in large countries can result in variations in policy decisions and resource allocation, leading to regional disparities based on differing political ideologies, priorities, and interests.
- For e.g., Kerala’s left-wing policies have prioritized social welfare, leading to high literacy and strong healthcare
- Gujarat’s right-wing focus on industrial growth has attracted investment, driving economic development.
The Aspirational District Program (ADP) is a specific initiative launched by the Government of India to address regional disparities Here’s how the Aspirational District Program addresses the issue of regional disparities:
- Identification of Underdeveloped Districts
- The program relies on data-driven analysis to identify specific challenges and areas that require intervention.
- A baseline ranking is established for these districts to measure progress over time.
- The ADP introduces a competitive element among districts.
- It encourages districts to compete with each other for better rankings, which can result in more focused efforts to improve development indicators.

- The program encourages the sharing of best practices and innovative solutions among districts.
- This enables districts to learn from each other’s successes and adapt effective strategies.
National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM), North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS), Special Assistance for States with Hilly and Difficult Terrain, North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS) Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) are steps in the right direction to overcome regional and income inequalities in India.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here