In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)
- 2 Standing Committee Report on “Judicial Process and their Reforms”
- 3 Keralam
- 4 Tidal energy potential
- 5 Belem Declaration
- 6 Indian Web Browser Development Challenge
- 7 First-ever 2D composite quantum material
- 8 Mission Indradhanush
- 9 Ghana
- 10 Kenya
- 11 Mali
- 12 SuSwagatam portal
- 13 Athidhi Portal
- 14 FAQs
- 14.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 14.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 14.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 14.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 14.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 15 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)
Tag: GS-3 Economy, Health
In News:
Recently, “Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana” completes five years of its implementation.
About
Ayushman Bharat, a prominent initiative by the Government of India, was introduced following the recommendations of the National Health Policy 2017. The primary objective was to realize the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) through two interconnected components: Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY).
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY):
- PM-JAY is the world’s largest government-funded health insurance scheme. Launched in February 2018, it offers a comprehensive coverage of up to Rs. 5 lakhs per family for both secondary care (non-super specialist) and tertiary care (super specialist) medical services.
- Beneficiaries of PM-JAY receive seamless access to cashless and paperless healthcare services directly at the hospital.
- The scheme encompasses various Health Benefits Packages, covering medical procedures, surgeries, daycare treatments, medication expenses, and diagnostic services.
- These packages are designed with all-inclusive rates, ensuring that beneficiaries are not charged separately for individual components. Once these rates are set, hospitals are not allowed to charge beneficiaries any additional amount.
Beneficiaries:
- PM-JAY operates on an entitlement-based approach, targeting individuals identified in the latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- Upon inclusion in the SECC database, beneficiaries become insured and can avail themselves of healthcare services at any empaneled hospital.
Funding:
- The funding structure for PM-JAY is shared between the central government and states/Union Territories (UTs).
- The distribution ratio is 60:40 for states/UTs with their own legislatures, 90:10 for Northeast states, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand, and 100% central funding for UTs without legislatures.
Nodal Agency:
- To ensure the effective implementation of PM-JAY in collaboration with state governments, the National Health Authority (NHA) was established as an independent entity under the Society Registration Act, 1860.
- State Health Agency (SHA), serves as the apex body within each state and is responsible for overseeing the execution of AB PM-JAY at the state level.
Impact of the Scheme:
- Reduced Out-of-Pocket Expenditure: Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) has provided vital support to more than 12 crore families, with the ambitious goal of covering 50% of India’s population. This substantial coverage has effectively curtailed out-of-pocket healthcare expenses and resulted in savings of over Rs. 1 lakh crore in medical treatment costs.
- Promotion of Gender Equality: The scheme has actively contributed to promoting gender equality in healthcare. Notably, 48% of the beneficiaries receiving treatments are women, demonstrating a commitment to ensuring unbiased access to healthcare services.
- Advancement towards Universal Health Coverage: AB-PMJAY aligns seamlessly with Sustainable Development Goal 3.8, which aims to achieve universal health coverage. By guaranteeing quality healthcare services irrespective of economic status, the scheme has moved India closer to fulfilling this global objective.
- Enhanced Accessibility: With a network of over 27,000 hospitals that honor the Ayushman Card for free medical treatment, AB-PMJAY has facilitated easy access to healthcare for patients across the country. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for migrants who may need medical assistance while in different states.
- Efficient Fraud Prevention: To ensure the integrity of the scheme, AB-PMJAY has implemented robust fraud prevention measures. This includes the establishment of the National Anti-Fraud Unit (NAFU) and state-level units, as well as the integration of Aadhaar-based authentication and cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to detect and deter fraudulent activities. The scheme has taken action against over 210 hospitals found in violation, resulting in their removal from the empanelled list.
- Establishment of Feedback Mechanism: AB-PMJAY has implemented a systematic feedback mechanism wherein patients receive follow-up calls after their treatments. This practice not only helps evaluate the quality of services provided but also enhances accountability within the healthcare system, ultimately leading to improvements in service delivery.
Source: Indian Express
Standing Committee Report on “Judicial Process and their Reforms”
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Judiciary)
Why in News:
Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice released its 133rd report on Judicial Process and their Reforms.
Parliamentary Standing Committee:
- A Standing Committee is a permanent and regular committee that is formed according to the provisions of an Act of Parliament or the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business from time to time.
- There are 24 department-related standing committees (DRSCs). The 24 standing committees have jurisdiction over all of the Central Government’s ministries and departments.
- Each standing committee is made up of 31 people (21 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha).
- The Speaker of the Lok Sabha nominates members from among the Lok Sabha’s members, just as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha nominates members from among the Rajya Sabha’s members.
Key issues highlighted by the report:
- Lack of Transparency in the Judiciary
- Huge pendency of cases
- Currently, only a few HCs release their annual report.
- Long Court Vacations
- Lack of Social Diversity in Judicial Appointments. Currently, only 15% of registered advocates are women.
Recommendations proposed by the Committee to fix these issues:
- Enact a law requiring judges of the Supreme Court and high courts to declare assets annually.
- Establish 4-5 regional benches of SC, wherein the regional benches may decide appellate matters.
- SC should direct HCs to publish Annual Reports in a unified format.
- Suggest doing away with long court vacations to address the perception of inconvenience to litigants. Vacations contribute to the pendency issue.
- Stress on appointing an adequate number of women and candidates from marginalized sections to high courts and the Supreme Court, promoting diversity and trust in the judiciary.
- Amend the Constitution to increase the retirement age of high court and Supreme Court judges and Reassess judges’ performance based on health, judgment quality, and quantity delivered. This can contribute to impartiality and quality in post-retirement assignments.
Source: Hindustan Times
Keralam
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Union & its territory)
Why in News:
Recently, State Legislative Assembly of Kerala passed a resolution urging the Central government to officially change the name of the state from ‘Kerala’ to ‘Keralam’.
Significance of the new name:
- The resolution aims to align the English and Malayalam names. The term ‘Kerala’ has its origins in ancient texts, and ‘Keralam’ is considered a closer reflection of the original Malayalam pronunciation. While the English version ‘Kerala’ was adopted for ease of pronunciation and writing.
- Scholars believe that the term ‘Keralam’ might have originated from the word ‘Cheram’ referring to the region between Gokarnam and Kanyakumari.
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 3 of the Constitution deals with the Parliament’s power to create new states or reorganize existing ones.
- This provision allows for the adaptation of state names to better represent the identity and heritage of the people residing within those states.
Procedure to be followed:
- The state government drafts a resolution expressing the desire to change the name of the state.
- Since changing the name of a state involves altering the Constitution, approval from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is required.
- The MHA seeks No Objection Certificates (NOCs) from various central government agencies such as the Ministry of Railways, Intelligence Bureau, Department of Posts, etc.
- If the MHA finds the proposal acceptable and all the necessary NOCs are obtained, a Constitutional amendment is initiated.
- The Bill goes through the usual legislative process in both the Lok Sabha (Lower House) and the Rajya Sabha (Upper House). The Bill requires a simple majority to be passed.
- Once the President gives his assent, the Bill becomes law and the name change becomes official and is implemented.
Source: Indian Express
Tidal energy potential
Tags: GS-III: Energy
In News:
Standing Committee submits inquiry report on Tidal Energy Potential assessment in India
About Tidal energy potential:
- The Standing Committee on Energy has recently released a report which focuses on assessing tidal, wave, and thermal energy potential in India.
- Tidal energy is generated from the gravitational forces between Earth, Moon, and Sun affecting ocean tides.
- These are of two types viz., Tidal stream systems (kinetic energy of moving water) and tidal range systems (potential energy from water level differences).
- Major highlights:
- The theoretical estimated potential of India is 12,455 MW for tidal power and 41,300 MW for wave power with the global energy potential estimated at 800 TWh/year.
- In India, coastal regions have potential for strong tidal currents such as Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Cambay, Sundarbans Delta.
- These are predictable and reliable as tides follow lunar cycles, providing consistent energy generation and tidal currents being denser than air, allows efficient power extraction.
- As there is no greenhouse gas emissions or pollution during energy production, these are environmentally friendly with minimal visual impact.
- However, tidal energy faces a range of challenges including high infrastructure costs, limited suitable locations, environmental impact, technological complexity etc,
- Overall, Tidal energy holds significant promise as a clean and renewable energy source and will go a long way to help fight global warming threat.
Major Tidal Energy projects:
- Gulf of Kutch, India: Proposed demonstration tidal power project.
- Durgaduani Creek, West Bengal: Tidal Energy Research and Demonstration Project.
- La Rance, France: One of the world’s first tidal power plants, operational since 1966.
- MeyGen, Scotland: Large-scale tidal stream array generating power since 2016.
Source: Down To Earth
Belem Declaration
Tags: GS-III: Conservation
In News:
Declaration released for advancing conservation and indigenous participation in Amazon region
About Belem Declaration:
- Belem declaration has been released during the Amazon Summit organized recently by the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO).
- The declaration highlights the critical aspects of biodiversity conservation and Indigenous engagement in the Amazon region.
- It aims to prevent deforestation, protect rich biodiversity, and ensure the well-being of Indigenous communities.
- Key features:
- It represents an effort to address environmental and Indigenous rights concerns in the Amazon region and encourages sustainable use of biodiversity resources in the Amazon.
- It emphasizes the significance of Indigenous knowledge for biodiversity conservation and calls for the full and effective participation of Indigenous Peoples in decision-making and policy formulation.
- It recognizes that Indigenous Peoples are under constant threats and stresses the importance of securing their land rights.
- It has been suggested that Brazil’s “Amazon fund” could potentially be expanded to cover the entire Amazon region.
- A working group will be established to discuss financial requirements and resource mobilization to address the concerns related to the implementation of the Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
- It also acknowledges the importance of financing conservation efforts and aligns with the GBF’s objective of protecting at least 30% of land and sea by 2030.
- The declaration highlights the need for multiple forest economy solutions to counter the dominance of agricultural commodity models in the region.
- Overall, the declaration demonstrates the commitment of Amazon countries to work together for the conservation of the vital ecosystem often referred as the “lung of earth”.
Source: Down To Earth
Indian Web Browser Development Challenge
Tag: GS-2 E-Governance, Government Policies and Interventions; GS-3 Cyber Security
In News:
The Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), launched the Indian Web Browser Development Challenge (IWBDC) in association with Controller of Certifying Authorities (CCA) and Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) Bangalore.
About the Indian Web Browser Development Challenge (IWBDC):
- The IWBDC is an Open Challenge Competition to inspire and empower technology enthusiasts, innovators, and developers from all corners of the country to create an indigenous web browser.
- Proposed browser would also focus on accessibility and user friendliness, ensuring built-in support for individuals with diverse abilities.
- Moreover, the browser envisions the ability to digitally sign documents using a crypto token, bolstering secure transactions and digital interactions.
Significance of IWBDC
- Stride towards Atmanirbhar Bharat: This challenge marks a significant stride towards an Aatmanirbhar Bharat, designed to strengthen India’s digital sovereignty through the development of the Indian Web Browser
- Enhanced security and data protection: The web browser brings in cutting edge functionalities, enhanced security & data privacy protection features through inbuilt trust store.
- Reduces dependence on SSL certificates issued by Roots of Foreign entities: India has been dependent on SSL certificates issued by Roots of Foreign entities. Initialising to develop its Own Browser with inbuilt India Root Certificate would help overcoming this challenge.
- Step towards Internet Resilience: India has moved a step ahead for making the country Internet Resilient which refers to a country’s ability to withstand and recover from various disruptions and threats that may impact its internet infrastructure and connectivity.
About Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Certificates:
- An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and enables an encrypted connection.
- It is a security protocol that creates an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser.
- SSL certificates are essential for a website as it secures online transactions and protects customer’s information privacy.
- While India has a legally valid root certifying authority called the Root Certifying Authority of India, established in 2000 under the CCA, the certificates issued by it are not widely recognised by popular web browsers.
- This has led to Indian government and private websites obtaining SSL certificates from foreign certifying authorities.
Source: PIB Gov.
First-ever 2D composite quantum material
In News:
2-D carbides or nitrides of transition metals were used by a team of scientists to develop a new composite quantum material using computer simulations, that exhibits an exotic quantum property called Rashba splitting, in colossal scale, in a metallic environment.
About the 2D composite quantum material
- 2-D materials are materials with confined geometry in one of the directions.
- Quantum materials are compounds with exotic physical properties that arise due to quantum effects like quantum fluctuations, quantum coherence, and quantum entanglement, having no counterpart in the classical world.
- They hold the promise of revolutionising quantum technology, such as quantum computing, communication, sensors, and memory devices.
- Composite 2-D quantum materials, are quantum materials exhibiting two apparently different quantum properties, but connected by the basic requirement of symmetries.
- This material can help interfacing with other substrates in spintronic devices like spin transistors, spin diodes, and spin filters.
About Spintronics and Rashba effect:
- Spintronics is a technology (used on next-generation nanoelectronic devices) that exploits the intrinsic spin of electrons alongside their charge for innovative electronic devices.
- An example is a spin transistor, where electron spin is used for information storage and processing, potentially leading to more energy-efficient and faster electronic devices.
- Rashba splitting is a quantum phenomenon in materials where spin-up and spin-down electrons separate due to interactions with an electric field.
- For instance, in a 2-D carbide material, Rashba splitting causes momentum-dependent separation of electron spin bands, enabling novel spintronic device applications.
About the research:
- The study has led to the first-ever discovery of a 2-D composite quantum material.
- In their study, by proper choice of materials ingredients, the scientists managed to demonstrate the existence of two distinct quantum phenomena Rashba effect and Nonlinear anomalous Hall effect.
- The team chose two dimensional carbides or nitrides of transition metals technically called MXenes and zeroed down on Mo2CO2.
- Starting with this parent material, they computationally designed a Janus structure Mo2COX, named after the two-faced Roman God.
- Even as Rashba splitting in the designed 2-D material was being computed for different X atoms in the Janus structure, the material under study was found to also have the ability to display another quantum property called the anomalous Hall Effect under the effect of longitudinal DC electric field along a particular direction.
Source: DST Gov.
Mission Indradhanush
Tags: GS – 3 Health
Why in news?
As per Health Management Information System (HMIS) 2022-23, 6 States/UTs have achieved 100% full immunization Coverage (FIC) whereas 17 States have achieved FIC of more than 90%
About:
- Mission Indradhanush was launched in 2014 as a special drive to expand full immunization coverage in India.
- The Mission Indradhanush (MI) initiative, operating under the Universal Immunization Program (UIP), focuses on low-immunization areas to vaccinate children and pregnant women who missed Routine Immunization.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW).
- In 2022, the Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) 4.0 was executed in 416 high-priority districts across India.
Universal Immunization Programme (UIP):
- India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) provides free vaccines against 12 life threatening diseases.
- It provides life-saving vaccines to all children across the country free of cost to protect them against Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, Hepatitis B, Pneumonia and Meningitis due to Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib), Measles, Rubella, Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and Rotavirus diarrhea. (Rubella, JE and Rotavirus vaccine in select states and districts).
Source: PIB Gov.
Ghana
Tags: GS – 1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, Ghana has approved a new policy to maximize benefits from mining green minerals, aligning with the global demand for clean energy resources.
About:
- Ghana is a country in West Africa, situated on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea.
- It is bordered to the northwest and north by Burkina Faso, to the east by Togo, to the south by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the west by Côte d’Ivoire.
- The capital is Accra. Ghana is the second-most populous country in West Africa, after Nigeria.
- Ghana has rich mineral resources such as gold, diamonds, manganese, limestone, bauxite, iron ore as well as various clays and granite deposits.
- Ghana is the second largest producer of gold in Africa.
Source: Down To Earth
Kenya
Tags: GS – 1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, Kenya’s Environment and Land Court has issued a 14-day stay on President Ruto’s decision to repeal a logging ban introduced in 2018 to protect forests.
About:
- Environmentalist has argued that lifting the ban could harm the environment, threaten communities reliant on forests, and lack proper scientific and participatory basis.
Kenya
- Kenya is in East Africa with a coastline on the Indian Ocean.
- It is bordered to the north by South Sudan and Ethiopia, to the east by Somalia and the Indian Ocean, to the south by Tanzania, and to the west by Lake Victoria and Uganda.
- The capital of Kenya is Nairobi.
- It encompasses the savannah, Lakelands, the dramatic Great Rift Valley and mountain highlands.
- From Nairobi, the capital, safaris visit the Maasai Mara Reserve, known for its annual wildebeest migrations, and Amboseli National Park, offering views of Tanzania’s 5,895m Mt. Kilimanjaro.
Source: Down To Earth
Mali
Tags: GS – 1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, France and Mali have suspended issuing visas to each other’s citizens in a heightening of a row between the former allies.
About:
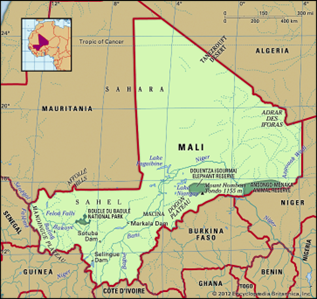
- Mali is a landlocked country of western Africa, with the Niger River flowing through its central region.
- It is bounded on the north by Algeria, on the east by Niger and Burkina Faso, on the south by Côte d’Ivoire and Guinea, and on the west by Senegal and Mauritania.
- It is the eighth-largest country in Africa.
- The climate is hot and dry in the north, and more humid in the south.
- The major ethnic groups in Mali are the Bambara, Malinke, Songhai, and Tuareg.
- The Desert covers about 65 per cent of Mali’s total area.
Source: The Hindu
SuSwagatam portal
Tags: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) announced the launch of the portal ‘SuSwagatam’, which would enable advocates, visitors, interns and others to register themselves online and get e-passes to enter the apex court.
About:
- Suswagatam’ is a web-based and mobile-friendly application that allows users to register themselves online and request for e-passes for various purposes such as attending court hearing, meeting advocates, etc.
- In July 2023, the portal underwent testing as a pilot project and received positive responses from its users.
Source: The Hindu
Athidhi Portal
Tags: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Kerala government is set to launch the ‘Athidhi Portal’, which aims to expedite the registration process for migrant workers in the state.
About:
- It is a user-friendly web portal to expedite the registration for migrant workers in Kerala.
- The goal is to ensure comprehensive registration and provide social security for all migrant workers.
Key Features:
- Contractors, who bring migrant workers to the state and employers can register the workers in the portal. It also allows workers to register themselves individually as well.
- The enrolling officer will examine the details entered in the portal and issue a unique ID to each worker.
- The portal will also ensure that they have social security.
Need of the portal:
- In light of recent incidents involving sexual crimes against children allegedly carried out by migrant workers, the government is taking measures to enhance the registration of “guest workers.”
- The exploitation of unregistered migrants by contractors and the lack of social security.
Source: The Economic Times
FAQs
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


