
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Palliative Care in India
- 2 The problem with battery electric vehicles
- 3 Chandrayaan-3 mission
- 4 Variable Rate Reverse Repo Auctions (VRRRs)
- 5 Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) air pollution
- 6 Sangam-age stud, bead unearthed in Tamil Nadu
- 7 Lambani Art
- 8 Majorana zero modes
- 9 ISRO to transfer SSLV to the private sector.
- 10 Global Peace Index 2023
- 11 Cluster Bomb
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Palliative Care in India
Tag: GS-2 Health, Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
A new set of operational guidelines for National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD) has been issued by the government, which limits the focus of palliative care in India to people with cancer.
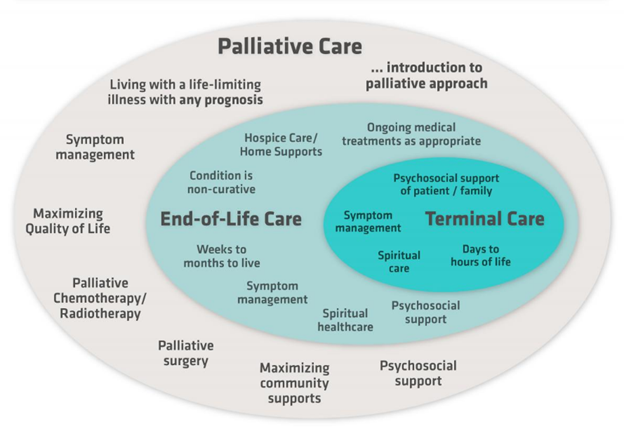
About Palliative Care:
- Palliative care is the branch of medicine focusing on improving the quality of life and preventing suffering among those with life-limiting illnesses. It aims to identify patients at risk of over-medicalization at the expense of quality of life and financial burden on the family.
- It is often misinterpreted as end-of-life care, however, palliative care aims to improve the quality of life by addressing the physical, psychological, spiritual, and social domains of the health of people suffering from life-limiting diseases like heart failure, kidney failure, certain neurological diseases, cancer, etc.
- A palliative care team supports the affected families in a way that focuses on the person as a whole, not just the disease. “Palliative care also includes bereavement support for the caregivers in case of the death of the patient,
Status of Palliative Care in India
- With the steep rise of lifestyle-related non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, respiratory diseases etc. and around 1.4 million people being diagnosed with cancer every year, India is in acute need for palliative care.
- Due to this skewed availability of palliative care services limited to urban areas, it is accessible to only 1-2% of the estimated 7-10 million people who require it in the country.
- Over-medicalization plays a significant role in this financial burden. Around, 55 million people in India are pushed below the poverty line yearly due to health-related expenditures.
- National Programme for Prevention & Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS), launched in 2010, now renamed as National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD), includes chronic diseases whose treatment contributes the most to health-related expenses and require palliative care more than curative care.
Concerns regarding the new guidelines:
- Limits Palliative care for Cancer patients: According to Global Atlas of Palliative Care, need for palliative care was higher for non-cancer illnesses. However, the revised NP-NCD operational guidelines mention palliative care for cancer only.
- This is a step back from the previous operational guideline (2013-2017), in which chronic and debilitating conditions also fell under the ambit of palliative care.
- No mention of Home Based Care: Unlike previous programme guidelines which mentioned support for home-based palliative care services, the new guidelines provide palliative care services which start from the district hospital.
- Lack of dedicated budget: The lack of dedicated funding and resources for palliative care programs hinders their implementation and expansion. NPCC launched in 2012 still lacks a dedicated budget.
- Poor awareness among health professionals: Medical officers at primary health centres are not aware of the existence of the National Programme for Palliative Care (NPCC). Furthermore healthcare professionals like doctors, nurses, and other caregivers, often lack adequate training in palliative care.
- Neglect of Paediatric palliative care: Around 98% of children facing moderate to severe suffering during their end of life due to diseases like cancer, birth defects, neurological conditions, reside in lower and middle-income countries like India.
- Inaccurate assessment metrics: Access to palliative care will be assessed by estimating morphine-equivalent consumption of strong opioid analgesics per death from cancer. However an indicator focusing only on cancer patients can lead to inaccurate assessment of coverage of services.
Source: The Hindu
The problem with battery electric vehicles
Tags: GS – 3: Environment (Pollution), Science and Technology (Developments and effects in everyday life)
Why in News:
Recently, Rowan Atkinson, known for his love of cars, expressed his scepticism about the push for electric vehicles (EVs). In a Guardian article, he raised concerns about the environmental impact of manufacturing EVs and the state support for them. He believes this focus on EVs could be problematic if replicated in India.
Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- These are vehicles that are powered by electricity, instead of traditional fuel sources like gasoline or diesel.
- They utilize an electric motor for propulsion, and the electricity that powers them is stored in rechargeable batteries.
- Types of EVs:
- Hybrid EVs (HEVs): These are the vehicles which combine a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an electric propulsion system. Example – Toyota Hyryder in India.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): They run on a fully electric drivetrain powered by rechargeable batteries. They have no ICE or fuel tank. Example – Tata Nexon in India.
- Plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs): A hybrid drivetrain uses both an ICE and electric power for motive power, backed by rechargeable batteries that can be plugged into a power source. Example – Chevrolet Volt.
- Fuel cell vehicles (FCVs): They combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, which runs the motor, and the only residue of the chemical process is water. Example – Honda Clarity.
Issues with BEVs:
- Government subsidies benefited by few: The problem is that much of the subsidy or tax breaks end up in the hands of the middle or upper middle classes, who are typically the buyers of battery electric four-wheelers.
- Lack of charging network: Only about 2,000 public charging stations are currently operational across the country.
- Different charging demands based on different vehicles and models.
- Non-renewable electricity source: In India, the supply to the grid is mostly by coal fired thermal power plants.
- Supply chain issue: India relies heavily on imports for the lithium required to produce Li-ion batteries for BEVs.
Way Forward:
- According to the World Bank, investment in charging infrastructure is 4 – 7 times more effective in EV than providing upfront purchase subsidies.
- Other alternatives should be explored such as Flex fuel vehicles (mixture of fuels like petrol and ethanol), Hydrogen Fuel cell vehicles (practically zero emission), etc.
Source: Indian Express
Chandrayaan-3 mission
Tags: GS – 3: Science and Technology (Space)
Why in News:
ISRO has scheduled to launch Chandrayaan – 3 (India’s upcoming lunar mission) on 14th July, 2023.
Chandrayaan – 3 Mission:
- Chandrayaan-3 is India’s third moon mission and is a follow-up of Chandrayaan-2 (2019) which aimed to land a rover on the lunar South Pole.
- It aims to be the world’s first mission to soft-land near the lunar south pole.
- The Mission will have three major modules:
- Propulsion module: It will carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit.
- Lander module: It has capability to soft land and deploy Rover.
- Rover: It will carry out in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface.
- Budget for the mission is Rs 615 million.
- Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3) (earlier known as GSLV-MK III) is a three-stage launch vehicle. It consists of two solid propellants S200 strap-ons and one core stage L110 liquid stage and C25 cryogenic stage.
Importance of South Pole of the Moon:
- It contains larger shadowed areas than the northern pole and can provide a preserved record of the Moon’s history and the early Solar System.
- The scientists believe that the moon have formed from debris generated by a giant impact between a Mars-sized object and the early Earth. By studying the lunar south pole, scientists can gain insights into the materials and conditions that existed during the formation of the Earth-Moon system.
- The south pole region is believed to have water molecules in substantial amounts, possibly trapped as ice in the permanently shadowed craters.
- ISRO can develop and demonstrate innovative technologies for soft landing, navigation, resource utilization, and long-duration operations that can be applied in future space missions.
Comparison of Lunar Missions of ISRO:
| Missions | Chandrayaan – 1 | Chandrayaan – 2 | Chandrayaan – 3 |
| Launch Year | 2008 | 2019 | 2023 |
| Objectives | Study lunar surface | Study lunar surface and land rover on the lunar south pole | Soft landing on the lunar south pole |
| Launch Vehicle | PSLV | GSLV – Mk 3 | LVM3 |
| Components | Orbiter, Moon Impact Probe | Orbiter, Lander (Vikram), Rover (Pragyan) | Propulsion Module, Lander, Rover |
Source: Indian Express
Variable Rate Reverse Repo Auctions (VRRRs)
Tags: GS-III: Economy
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is employing variable rate reverse repo auctions (VRRRs) to eliminate excess liquidity from the banking system.
About variable rate reverse repo auctions (VRRRs):
- VRRRs are a monetary policy tool used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to manage liquidity in the banking system.
- The purpose of VRRRs is to absorb excess liquidity from the banking system by offering banks the option to park their surplus funds with the RBI.
- Important features:
- These auctions are conducted on a variable rate basis, where banks submit bids specifying the rate at which they are willing to lend funds to the RBI.
- The RBI sets a minimum bid rate, known as the cut-off rate, below which it will not accept bids.
- Banks participate by submitting their bids electronically through the RBI’s auction platform.
- The cut-off rate in VRRRs helps the RBI control the overnight call money rate and keep it close to the desired target rate.
- These auctions are conducted daily or as per the prevailing liquidity conditions to address the surplus liquidity caused by factors like government spending and return of ₹2,000 banknotes.
- The amount of funds absorbed through VRRRs can vary depending on the liquidity requirements and market conditions.
- Overall, VRRRs are an important tool for the RBI to manage liquidity and maintain stability in the banking system.
Source: Hindu Business
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) air pollution
Tags: GS-III: Health
In News:
A science review commissioned by the Health and Environment Alliance (HEAL) highlights the significant health effects of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) air pollution.
About Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Air Pollution:
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is an air pollutant that forms primarily from the burning of fossil fuels, particularly in vehicles and power plants.
- It is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent odour, and it is a major component of urban air pollution.
- Sources of NO2 emissions include road traffic, diesel engines, power generation, industrial processes, and residential heating.
- It contributes to the formation of smog and acid rain, and it is a significant component of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution.
- Exposure to NO2 can have adverse effects on human health, particularly on the respiratory system.
- Children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory conditions are more susceptible to the health effects of NO2.
- Short-term exposure to high levels of NO2 can cause respiratory symptoms, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Long-term exposure to NO2 has been linked to the development and exacerbation of respiratory conditions, including asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory infections.
- NO2 also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, which has harmful effects on plants, crops, and ecosystems.
- Overall, steps including stricter vehicle emission standards, promotion of clean energy sources, and improved industrial and urban planning practices etc., can help reducing NO2 emissions in long run.
Source: ENV health
Sangam-age stud, bead unearthed in Tamil Nadu
Tags: General Studies –1 Art and Culture
Why in news?
Recently, A gold stud, a bone point and a carnelian bead have been unearthed by archaeologists at Porpanaikottai in Pudukottai district of Tamil Nadu.
About:

Key findings:
- Gold Stud has a six-petal flower pattern.
- It is reported to have been used as a nose stud and weighs 0.26 grammes.
- Bone Point has carved pointy tips on both sides.

- probably employed in weaving
- The carnelian bead, a round-shaped red stone, was also discovered at the site.
- Similar beads have been found in other parts of Tamil Nadu, indicating a system of domestic trade.
- Carnelian beads were commonly sourced from Gujarat.

- In addition to these artefacts, the excavation has revealed a three-course brick structure and over 150 other antiquities, such as potsherds, hopscotches, spouts, pieces of glass bangles and beads, a terracotta lamp, a coin, a spindle whorl and rubbing stone.
- A Sangam-age fort is believed to have existed at the site.
Sangam Age
- Sangam Age refers to the period of the history of ancient Tamil Nadu, Kerala spanning from the 6th century BCE to 3rd century CE.
Source: The Hindu
Lambani Art
Tags: General Studies –1 Art and Culture
Why in news?
Recently, PM has praised the Guinness World Record achieved for the “largest display of Lambani items,” totalling 1755 items, during the 3rd G20 Culture Working Group Meeting held in Hampi, Karnataka
About:

- It is an intricate embroidery art done on a piece of cloth, practised by the Lambani community, also known as the Banjara community in Karnataka.
- It is characterized by its vibrant colours, intricate embroidery, and mirror work.
- It has quilting stitches with borders of “Kangura” patchwork.
- Lambani art includes a wide range of products, such as clothing, textiles, accessories, home decor items, and jewellery.
- It received the status of Geographic Indication (GI) tag in 2010 from Karnataka.
Banjara or Lambanis
- These are nomadic tribes that are spread across India.
- They are considered to be the descendants of the Romanis of Europe.
- Came from the Ghor province of Afghanistan and then settled in Rajasthan, Gujarat and then migrated down south.
- These tribal communities of Banjara or Lambani mainly reside in Sanduru, Bellary and Bijapur in Karnataka, and Hyderabad in Andhra Pradesh.
- Banjaras now live in several states and are known by different names like
- Lambada or Lambadi in Andhra Pradesh
- Lambani in Karnataka
- Gwar or Gwaraiya in Rajasthan
- The language of Banjara is known as “Gorboli” “Gor mati Boli” or “Brinjari” an independent dialect (under the category of Indo-Aryan language)
Source: PIB Gov.
Majorana zero modes
Tags: General Studies – 3 IT & Computers
Why in news?
Recently, Microsoft researchers announced a significant breakthrough in the creation of Majorana Zero Modes, a type of particle with potential implications for revolutionizing quantum computing.
About:
- Majorana zero modes are unique particles that could make quantum computers less fragile and more computationally powerful.
- The particles, also known as Majorana fermions, were first proposed by Italian physicist Ettore Majorana in 1937.
- They possess special properties that make them their own antiparticles, which is advantageous for building quantum computers.
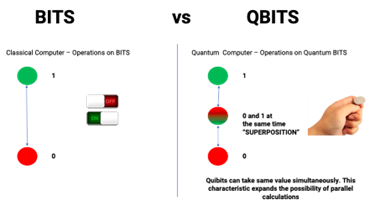
- Majorana zero modes can be used as qubits, the fundamental units of information in quantum computing, and have the potential to protect encoded information from decoherence, a major challenge in quantum computing.
- A quantum computer stores information in the form of quantum bits (qubits) that can take on various combinations of zero and one.
- These particles could enable topological quantum computing, which offers computational advantages and additional degrees of freedom for algorithms.
Source: The Hindu
ISRO to transfer SSLV to the private sector.
Tags: General Studies –3 Science & Technology
Why in news?
Recently, The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is planning to transfer its Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) to the private sector after conducting two successful flights of the rocket.

About:
- Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a three-stage launch vehicle configured with three Solid Propulsion Stages and a liquid-propulsion based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) as a terminal stage.
- The SSLV is designed to provide on-demand services for launching satellites weighing up to 500 kg into low-Earth orbit.
- Small rockets like the SSLV are specifically designed for nano and micro-satellites, offering dedicated launch services without the need for larger rockets.
Key Features of SSLV
- Low cost
- Low turn-around time
- Flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites
- Launch demand feasibility
- Minimum launch infrastructure required.
More Information:
- The SSLV was the sixth launch vehicle developed by the ISRO after the Satellite Launch Vehicle-3 (SLV-3), Advanced Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV), Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) and Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM-3). The SLV-3 and the ASLV have since been retired.
- The SSLV injected the ISRO’s EOS-07 satellite, US-based firm Antaris’ Janus-1 and Chennai-based space start-up Space Kidz’s AzaadiSAT-2 satellites into a 450-km circular orbit.
- The commercial satellite launch services sector in India is projected to contribute $13 billion to the economy by 2025, with the SSLV transfer expected to accelerate its growth.
Source: The Hindu
Global Peace Index 2023
Tags: General Studies – 2 Important International Institutions
Why in news?
The 2023 Global Peace Index (GPI) recently released its annual ranking of the most peaceful countries in the world.
About:
- It is released annually by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP).
- 2023 Global Peace Index (GPI) ranked 163 independent states and territories according to their level of peacefulness.
- It measures the state of peace across three domains:
- Societal safety and security;
- Ongoing domestic and international conflict;
- Militarization;
Key findings:
- Most Peaceful: Iceland retaining its position as the most peaceful country, followed by Denmark, Ireland, New Zealand, and Austria.
- Least Peaceful: Afghanistan remains the least peaceful country, followed by Yemen, Syria, South Sudan, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- India: India has occupied the 126th spot in the rankings, two higher than its previous position.
- The report stated that India experienced an improvement of 3.5 per cent in overall peacefulness over the past year, owing to improvements in violent crime, neighbouring countries’ relations, and political instability.
- An overall deterioration in global peacefulness: Over the past fifteen years, the global average score of peacefulness has declined by five percent, indicating a decline in peace worldwide.
- Prominent Countries: Nepal, China, Sri Lanka, USA, and Pakistan have been ranked 79, 80, 107, 131, and 146, respectively.
Source: Visit of Humanity
Cluster Bomb
Tags: General Studies – 3, General Studies – 2 International Treaties & Agreements
Why in news?
Recently, the decision by the United States to supply Ukraine with cluster bombs has caused concern among key US allies.
About:

- Cluster bomb is a type of weapon that is designed to disperse smaller bombs over a large area.
- They are also known as cluster munitions, with the smaller bombs referred to as submunitions or bomblets.
- They can be dropped from air or fired from ground/sea, dispersing dozens or hundreds of bomblets across a large area.
- These explosions pose a grave threat to anyone in the vicinity, causing death or severe injuries.
- Some bomblets fail to detonate immediately, leaving behind unexploded ordnance that can harm or kill people for years to come.
Convention on Cluster Munitions:
- The Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM) prohibits the use, stockpiling, production, and transfer of cluster munitions.
- However, major countries like the U.S., Russia, China, India, Israel, Pakistan, and Ukraine, along with several NATO countries, are not party to the convention.
- Convention on Cluster Munitions was adopted in Dublin on 30 May 2008 and opened for signature in Oslo on 3 December the same year.
- The Convention became binding international law when it entered into force on 1 August 2010.
- Till date a total of 123 States have joined the Convention – 111 States Parties and 12 Signatories.
More Information:
- According to Cluster Munition Monitor 2022, sixteen countries that have refused to sign the convention and who produce cluster munitions included Brazil, China, Egypt, Greece, Iran, Israel, India, North Korea, Pakistan, Poland, Romania, Russia, Singapore, South Korea, the United States and Turkey.
Source: The Hindu
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

