
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Caste-based violence
- 1.1 In News:
- 1.2 How Widespread are Caste-Based Crimes in India?
- 1.3 Regional Disparities in Crime Rates and Charge Sheets
- 1.4 Causes Behind Caste-Based Crimes in India
- 1.5 Ramifications of Caste-Based Crimes
- 1.6 Safeguards Against Caste-Based Discrimination in India
- 1.7 Possible Solutions to Address Caste-Based Crimes in India
- 2 AI regulation in India
- 3 India Infrastructure Report 2023
- 4 Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
- 5 ‘Group of Companies’ Doctrine
- 6 Pulsars
- 7 Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus
- 8 Megamouth Shark
- 9 Solar Orbiter
- 10 Multiple Sclerosis
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Caste-based violence
Tag: GS-2 Polity, Vulnerable Sections in India.
In News:
In a village in Banda, Uttar Pradesh, the dismembered body of a 40-year-old Dalit woman was discovered on the floor of an atta chakki. While the family alleges gang rape and murder by upper-caste men, the police contend it was an accident.

How Widespread are Caste-Based Crimes in India?
- Caste-based crimes encompass a range of offenses such as physical assault, murder, rape, sexual harassment, torture, arson, social boycott, economic exploitation, land grabbing, forced displacement, and various forms of humiliation and violence.
- As per the Annual Crime in India Report 2019 from the National Crimes Records Bureau, crimes against Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) saw an increase of over 7% and 26%, respectively, in 2019.
- The report also highlights that India records 88 rape cases daily, some of which are linked to caste-based crimes.
Regional Disparities in Crime Rates and Charge Sheets
- Caste-based crimes are influenced by regional variations and diverse strategies employed by different states to combat them.
- For instance, Madhya Pradesh (MP) had the highest crime rate against SCs in 2021, maintaining its position from 2020 and ranking second in 2019, behind Rajasthan.
- However, data indicates that MP exhibited a higher rate of filing charge sheets compared to most other states.
- Contrastingly, Rajasthan lagged significantly in this aspect, underscoring the need for enhanced efforts by state police.
Causes Behind Caste-Based Crimes in India
Caste System and Hierarchical Structure
- The ancient caste system, based on descent and occupation, establishes a rigid hierarchical structure.
- This structure fosters a sense of superiority among upper castes and generates feelings of inferiority among lower castes, resulting in discrimination and violence.
Influence of Social Norms and Cultural Beliefs
- Social norms and cultural beliefs, often transmitted across generations, perpetuate the notion of caste-based superiority and inferiority.
- These ingrained norms normalize discriminatory attitudes, making it difficult to eradicate caste-based violence.
Economic Exploitation as a Motivating Factor
- Caste-based violence can be fuelled by economic motives, with lower caste individuals often subjected to exploitation, forced labour, and economic oppression by dominant caste groups.
- This economic disparity can lead to conflicts and acts of violence.
Challenges Arising from Inter-Caste Marriages
- Inter-caste marriages, challenging traditional caste boundaries, may face hostility and violence from conservative segments of society aiming to preserve caste purity.
Inadequate Implementation of Laws
- Lack of enforcement contributes to a culture of impunity for perpetrators.
Ramifications of Caste-Based Crimes
Violation of Human Rights
- Caste-based violence leads to egregious human rights violations, infringing upon the right to life, dignity, equality, and liberty.
Social Fragmentation
- Caste-based violence exacerbates social divisions, fostering animosity among different caste groups.
Fear and Insecurity
- The prevalence of caste-based violence instils fear and insecurity within marginalized communities.
- This fear can lead to self-censorship and curtail the freedom of expression and movement for those affected.
Impediments to Development and Empowerment
- Caste-based violence poses obstacles to the development and empowerment of marginalized communities, limiting their access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
Erosion of Trust in Institutions
- Caste-based violence erodes trust in state institutions, law enforcement agencies, and the justice system.
Impact on International Reputation
- The persistence of caste-based violence adversely affects India’s international standing as a democratic and progressive nation.
Safeguards Against Caste-Based Discrimination in India
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 15, Article 16, Article 335, Article 330 and Article 332
Constitutional Bodies
- National Commission for Scheduled Castes
- National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
Statutory Provision
- Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Amendment Act, 2018
Possible Solutions to Address Caste-Based Crimes in India
- Strengthening Legal Implementation
- Emphasize the rigorous enforcement of existing laws such as the SC/ST Act, 1989; Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955; and Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013.
Promoting Awareness and Sensitization
- Conduct widespread awareness and sensitization campaigns involving all stakeholders, including upper castes, lower castes, civil society organizations, media, academia, religious leaders, and political parties.
Empowering SCs and STs
- Implement measures to empower Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) through initiatives in education, employment, land rights, political representation, social mobilization, legal aid, and counselling services.
Fostering Dialogue and Reconciliation
- Encourage open dialogue to build trust and solidarity among different communities. Challenge stereotypes and prejudices while promoting respect for diversity and human dignity.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Mains (2020) Q1. Has caste lost its relevance in understanding the multi-cultural Indian Society? Elaborate your answer with illustrations. Mains (2018) Q2. “Caste system is assuming new identities and associational forms. Hence caste system cannot be eradicated in India.” Comment. |
Source: TH
AI regulation in India
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
In the past month, a video showcasing actor Rashmika Mandanna went viral on social media, eliciting a mix of surprise and dismay among netizens.
[Text Wrapping Break]
Importance of Regulating Artificial Intelligence
Addressing Uncertainty and Risks
- As artificial intelligence (AI) usage proliferates, the associated risks and uncertainties escalate.
- The advancement of technology, enabling AI to perform diverse tasks, raises concerns that necessitate effective regulation.
Transparency Challenges
- Certain AI tools function as “black boxes,” with their complexity surpassing full comprehension even by their creators.
- This opacity raises questions about transparency, as the decision-making processes of these tools remain elusive, akin to a secret box generating outputs.
Inherent Inaccuracy and Biases
- AI tools, exemplified by facial recognition software and language models like GPT-3 and GPT-4, have led to issues such as mistaken arrests and biased treatment.
- Chatbots, while capable of producing high-quality content resembling human writing, may inadvertently generate inaccurate information or incorporate copyrighted material without authorization.
Unpredictable Future Behaviour
- AI introduces a unique challenge due to the uncertainty surrounding its behaviour.
- Unlike traditional engineering systems with predictable functionality, AI systems, particularly in domains like self-driving cars, pose challenges in anticipating their responses to novel situations.
- Engineers cannot guarantee how these systems will perform in unforeseen circumstances.
Global Approaches to AI Governance: A Comparative Analysis
India
NITI Aayog
- India’s policy think tank, has released key documents addressing AI issues, including the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence and the Responsible AI for All report.
- These emphasize social and economic inclusion, innovation, and trustworthiness.
United Kingdom
- The UK has adopted a light-touch approach, urging regulators in various sectors to apply existing regulations to AI.
- It published a white paper outlining five principles for companies: safety, security, and robustness; transparency and explain ability; fairness; accountability and governance; and contestability and redress.
United States
- The US introduced a Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights (AIBoR) highlighting the economic and civil rights harms associated with AI.
- It lays down five principles to mitigate these harms.
- Unlike the EU’s horizontal approach, the US endorses a sector-specific governance strategy, allowing individual sectors such as health, labour, and education to develop their plans.
China
- In 2022, China implemented some of the world’s initial nationally binding regulations targeting specific types of algorithms and AI.
- It enacted a law to regulate recommendation algorithms, focusing on their information dissemination.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2020) Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units Create meaningful short stories and songs Disease diagnosis Text-to-Speech Conversion Wireless transmission of electrical energy Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (b) Prelims (2018) Q2. Consider the following pairs: Terms sometimes seen in news Context/Topic 1. Belle II experiment Artificial Intelligence 2. Blockchain technology Digital/Cryptocurrency 3. CRISPR–Cas9 Particle Physics Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
Source: TH
India Infrastructure Report 2023
Tag: GS-2 Government Policies & Interventions, Infrastructure
In News:
The India Infrastructure Report (IIR) 2023 on Urban Planning and Development has been recently unveiled.
Key Highlights from the India Infrastructure Report
Thematic Emphasis on Urban Challenges
- The IIR systematically addresses crucial themes central to India’s urban challenges.
- This includes planning and governance, smart initiatives, public-private partnerships (PPPs) and financing, housing and migration, public service delivery, integrating infrastructure, and urban redevelopment.
Critique of Planning Mechanisms
- The report criticizes existing planning mechanisms, particularly constraints on building construction, for rendering cities “unliveable” and contributing to the emergence of slums.
- It underscores poor planning as a significant factor in urban challenges.
Low Floor Space Indices (FSIs) and Urban Sprawl
- Highlighting the impact of low floor space indices (FSIs) or floor area ratios (FARs) on high-density development and urban sprawl, the report links low FSI to the creation of slums.
- It advocates for a redevelopment policy to recover land, offering higher FSIs and improved road connectivity.
Financial Management of Urban Local Bodies
- The report emphasizes the analysis of the financial management of urban local bodies, stressing the urgent need for financial sustainability.
- It advocates for the use of PPPs and municipal bonds as crucial tools for financing urban development projects.
- Despite India’s leadership in PPPs, particularly in roads, ports, airports, and energy, the report notes the limited occurrence of PPPs in the urban sector.
The Present Urban Landscape in India
- India stands as one of the world’s fastest-growing economies, with urban centres serving as key drivers of this growth.
- Cities presently contribute 66% to the national GDP, and this figure is anticipated to climb to 80% by 2050.
- Despite India’s rapid economic expansion, the process of urbanization has been relatively gradual, with the proportion of the population residing in officially classified urban settlements increasing at a rate slightly exceeding 1.15% per year from 2001 to 2011.
- The seven most significant metropolitan areas in India include Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, Kolkata, Chennai, Hyderabad, and Ahmedabad.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Mains (2016) Q. The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods, highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. |
Source: PIB
Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
Tag: GS-2 Government Policies & Interventions GS-3 Growth & Development, Industrial Growth
In News:
The Ministry of Cooperation has recently highlighted the “Cooperative Sector’s Plan for the World’s Largest Grain Storage.”

Grain Storage Initiative in the Cooperative Sector: Empowering Agriculture
Holistic Infrastructure Development
- This initiative involves establishing diverse agricultural infrastructures at the Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies (PACS) level.
- These include warehouses, custom hiring centres, processing units, Fair Price Shops, and more.
Strategic Scheme Convergence
- The project strategically integrates various existing schemes of the Government of India (GoI), such as the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI), Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), and others.
- This approach ensures a comprehensive development plan.
Implementation Partners and Progress
- Implemented by the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) with support from institutions like the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) and the Food Corporation of India (FCI).
- Construction has commenced in 13 PACS in 13 States/ UTs, with 1,711 PACS identified for inclusion in the pilot project.
Oversight Committees for Effective Implementation
- The Ministry of Cooperation has established an Inter-Ministerial Committee (IMC) and a National Level Coordination Committee (NLCC) to provide guidelines, methodologies, and oversight.
- State and District Cooperative Development Committees (SCDC and DCDC) ensure coordination at the state and district levels.
Empowering Farmers
- PACS, equipped with godowns, enable farmers to store produce and access bridge finance for subsequent crop cycles.
- The initiative allows farmers to sell produce at their preferred time or to PACS at Minimum Support Price (MSP), preventing distress sales.
- Decentralized storage minimizes post-harvest losses, maximizing farmers’ earnings and contributing to national food security.
Ministry of Agriculture Initiatives to Tackle Food Grain Shortage
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- The AIF focuses on creating post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets by providing incentives and financial support.
- It includes a 3% interest subvention for loans up to Rs. 2 Crore per project location for 7 years and reimbursement of credit guarantee fees under the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) Scheme.
Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay SanraksHan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA)
- PM-AASHA aims to provide Minimum Support Price (MSP) to farmers for specified oilseeds, pulses, and copra.
- It comprises the Price Support Scheme (PSS), Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS), and Private Procurement and Stockist Scheme (PPSS).
- Price Support Scheme (PSS): Implemented at the request of the State Government, exempting procured produce from mandi tax. Central agencies undertake procurement directly from pre-registered farmers at MSP when market prices fall below MSP.
- Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS): Involves direct payment of the difference between MSP and the selling/model price. Pre-registered farmers benefit through a transparent auction process in notified market yards.
- Private Procurement and Stockist Scheme (PPSS): States can implement PPSS for oilseed procurement. Pilot procurement is conducted from pre-registered farmers in selected districts or APMC(s).
Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
- MIS involves the procurement of perishable agricultural and horticultural commodities for which MSP is not announced.
- This protects growers from distress sales during bumper crops when prices fall below economic levels.
Bhartiya Beej Sahakari Samiti Limited (BBSSL)
- Established under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002, BBSSL acts as an umbrella organization for the cultivation, production, and distribution of improved seeds under a single brand.
- The society enhances seed availability, boosts crop productivity, and increases farmers’ income.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2020) Q. Consider the following statements: In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks. One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) Prelims (2021) Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments. They can issue equity shares and preference shares. They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) Mains (2014) Q. In the villages itself no form of credit organisation will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural finance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? |
Source: PIB
‘Group of Companies’ Doctrine
Tag: GS-2 Polity and Governance
In News:
A Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court has recently affirmed that under the “group of companies” doctrine, an arbitration agreement can be binding on non-signatories.

Understanding the ‘Group of Companies’ Doctrine
Overview
- The “group of companies” doctrine posits that a non-signatory company to an arbitration agreement can be bound by the agreement if it belongs to the same group of companies as the signatory.
- The doctrine implies a mutual intent of the parties for the non-signatory’s inclusion.
Arbitration Mechanism
- Arbitration, a dispute resolution method, involves appointing a neutral party to adjudicate without court intervention.
- The arbitrator’s judgment holds legal enforceability.
International Arbitration Basis
- Unlike other non-signatory theories rooted in domestic law principles, the “group of companies” concept finds its basis in international arbitration jurisprudence.
Indian Recognition and Application
- The Indian Supreme Court acknowledged the doctrine in Chloro Controls India Private Limited v. Severn Trent Water Purification Inc. (2013).
- Subsequently, Indian courts applied it to bind group companies of signatories to arbitration agreements.
Factors Considered by the Courts
- In ONGC Ltd. vs. Discovery Enterprises (P) Ltd., the Supreme Court outlined factors for applying the doctrine:
- Mutual intent of the parties
- Relationship of the non-signatory to a signatory
- Commonality of subject matter
- Composite nature of the transaction
- Performance of the contract
Objective of Introducing the Doctrine in India
- The doctrine aims to prevent dispute fragmentation in composite transactions involving multiple parties and contracts.
Recent Supreme Court Ruling
- The Court clarified that signatories are not the sole entities bound by the arbitration agreement.
- A written agreement isn’t limited to signatories, and non-signatories can be bound if there’s a defined legal relationship and an intended commitment demonstrated through conduct.
- Non-signatories, due to their relationship and commercial involvement, aren’t strangers to the arbitration agreement.
Source: LL
Pulsars
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech.
In News:
A new pulsar, designated as PSR J1032−5804, has been recently identified by astronomers using the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP).
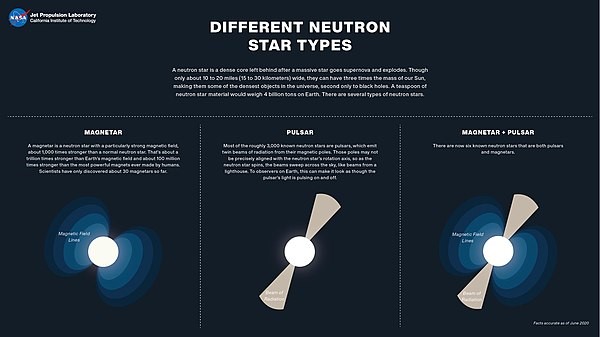
Exploring Pulsars: Marvels of Cosmic Regularity
Pulsars Defined
- Pulsars, captivating astronomical phenomena, are rotating neutron stars emitting rhythmic pulses of radiation at remarkably consistent intervals, ranging from milliseconds to seconds.
Energetic Light Beams
- Characterized by potent magnetic fields, pulsars generate particle jets along their magnetic poles.
- These accelerated particles produce intense beams of light.
- The magnetic field orientation often differs from the spin axis, causing the beams to sweep as the star rotates.
Pulsar Illumination
- As these beams cross our line of sight, pulsars manifest as intermittent pulses—essentially turning on and off—as the beams sweep across Earth.
Pulsar Masses
- Pulsar masses span between 1.18 and 1.97 times that of the Sun, with a prevalent mass of approximately 1.35 times that of the Sun.
Understanding Neutron Stars: Celestial Densities Unleashed
Formation Process
- Neutron stars emerge from the dramatic collapse of a massive star that exhausts its fuel, succumbing to gravitational forces.
- The core, imploding under immense gravity, compels every proton and electron into neutrons.
Critical Mass Range
- For cores with masses between 1 and 3 solar masses, the newly-formed neutrons resist complete collapse, resulting in the formation of a neutron star.
- Stellar masses exceeding this range continue collapsing into stellar-mass black holes.
Widespread Galactic Presence
- Originating from stellar remnants, neutron stars are dispersed across the galaxy, inhabiting regions akin to where stars are found.
- Similar to stars, they exist either in solitary arrangements or within binary systems alongside a celestial companion.
Source: PO
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), located in Izatnagar, Bareilly, has recently determined the prevalence of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus subtypes (EEHV) among the Asian elephant population in India.

Understanding Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)
Viral Classification
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus categorized within the Herpesviridae family.
Targeted Species and Severity
- This virus instigates acute and often fatal haemorrhagic disease primarily affecting both wild and captive juvenile Asian and African elephants.
- The disease is particularly lethal for elephants aged between one and twelve, exhibiting a rapid course of 28-35 hours.
Mode of Transmission
- The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids from infected elephants, encompassing saliva, shedding from skin lesions, and more.
Manifestation of Symptoms
- Infected elephants may display symptoms such as diminished appetite, nasal discharge, and swollen glands.
Treatment Approaches
- While there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses due to their ability to go latent, treatment strategies for EEHV involve a comprehensive approach.
- This includes a combination of antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid administration to counteract haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C, E, as well as anti-pyretic and analgesics to alleviate fever.
Challenges in Addressing Herpesviruses
- Both in animals and humans, true cures for herpesviruses remain elusive due to their ability to enter a latent state.
- As a result, managing the symptoms and mitigating the impact of the virus pose significant challenges.
Source: PIB
Megamouth Shark
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, a pregnant megamouth shark, a rare and enigmatic deepwater species, was found stranded on a beach in the Philippines.

The Enigmatic Megamouth Shark Unveiled
Species Identification
- The megamouth shark, scientifically known as Megachasma pelagios, stands out as an exceedingly rare and peculiar deep-water shark species.
Geographical Distribution
- These sharks are believed to inhabit the expansive region between latitudes 40°N and 40°S, spanning the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans.
Preferred Habitat
- Megamouth sharks thrive in the depths of warm oceanic waters, adding to their elusive nature.
Elusive Nature
- Encounters with this species in the wild are exceptionally rare, with scientists having documented and captured fewer than 60 individuals.
Distinctive Features
- Considerable Size: These sharks can reach impressive weights of up to 2700 pounds (1215 kg).
- Length Variation: Typically ranging from 425 to 515 cm, with females generally larger than males.
- Unique Head Structure: Characterized by an expansive, soft head and a large mouth positioned at the forefront.
- Coloration: Varies from grey to blueish-black on the upper side and pale grey below, often with white tips on fins.
- Teeth Configuration: Sporting small, hooked teeth along both upper and lower jaws.
Feeding Behaviour
- Megamouth sharks employ a filter-feeding strategy, swimming with their mouths perpetually open to filter their preferred planktonic prey.
- The inside of their mouths features light-producing organs, potentially used to attract pelagic crustaceans and other prey.
Conservation Status
- Listed as “Least Concern” on the IUCN Red List, the megamouth shark, despite its rarity, currently faces no imminent threats that warrant higher conservation concern.
Source: WION
Solar Orbiter
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The Solar Orbiter from the European Space Agency recently obtained the most detailed image to date of the complete disk of the Sun and its outer atmosphere, known as the corona.

Unveiling Solar Orbiter: A Sun-Centric Observatory
Scientific Marvel
- Solar Orbiter stands as a sun-observing satellite equipped with 10 specialized science instruments, collectively engineered to unravel the intricacies of solar workings.
Mission Objectives
- Conceived for an in-depth exploration of the Sun and the inner heliosphere, Solar Orbiter aims to venture into the uncharted realms of our Solar System’s innermost regions.
Collaborative Initiative
- This groundbreaking mission is a collaborative endeavour between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, representing an international commitment to solar exploration.
Unprecedented Complexity
- Distinguished as the most intricate scientific laboratory dispatched to the Sun, Solar Orbiter is poised to capture images from unprecedented proximity and venture into the unexplored polar regions of our solar luminary.
Mission Timeline
- Launched on February 10, 2020, Solar Orbiter unveiled its initial images in June of the same year. Commencing full-scale scientific operations in December 2021, the mission underwent multiple gravitational assist manoeuvres at Earth and Venus.
Orbital Dynamics
- Traversing an elliptical orbit around the sun, Solar Orbiter reaches its closest point, the perihelion, at approximately 25 million miles (40 million kilometres), a proximity surpassing even the orbit of Mercury.
Instrumentation
- The satellite carries six remote-sensing instruments for scrutinizing the Sun and its corona, complemented by four in-situ instruments dedicated to measuring the solar wind, energetic particles, and electromagnetic fields.
Extended Mission Duration
- Scheduled to endure until at least 2027, Solar Orbiter promises an extended mission lifespan, offering a prolonged window into the Sun’s mysteries.
Source: IT
Multiple Sclerosis
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Researchers report that individuals diagnosed with multiple sclerosis in the years preceding the diagnosis were more prone to experiencing depression, constipation, urinary tract infections, and sexual problems.
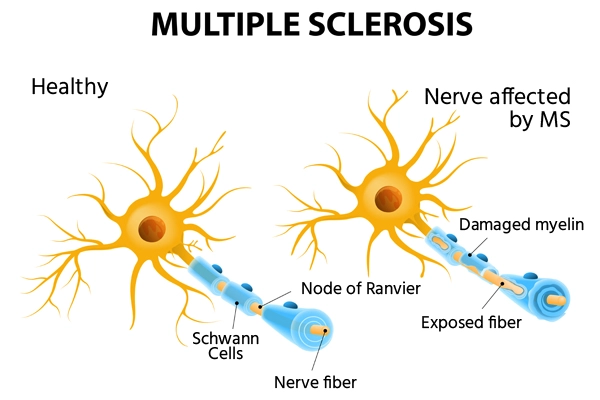
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Nature of the Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic ailment affecting the central nervous system, characterized by persistent and enduring symptoms.
Immune System Involvement
- In individuals with MS, the immune system targets cells in the myelin—a protective covering enveloping nerves in the brain and spinal cord.
Consequences of Myelin Damage
- The impairment to the myelin sheath disrupts the transmission of nerve signals from the brain to various parts of the body, manifesting symptoms that impact the brain, spinal cord, and eyes.
Progression and Permanent Damage
- Over time, the disease can lead to permanent damage or deterioration of nerve fibres, exacerbating the severity of symptoms.
Demographic Impact
- Prevalent among women, MS is most frequently diagnosed in individuals aged 20 to 40, although it can manifest at any age.
Diverse Causes
- Multiple factors contribute to the onset of MS, encompassing autoimmune disorders, infectious agents like viruses, environmental influences, and genetic predispositions.
Varied Signs and Symptoms
- The manifestation of MS symptoms varies widely among individuals, contingent on the location and intensity of nerve fibre damage in the central nervous system.
- Symptoms can range from mild, such as blurred vision and limb numbness, to severe cases involving paralysis, vision loss, and mobility challenges.
Treatment Approach
- While a definitive cure remains elusive, various treatments aim to expedite recovery from attacks, modify the disease’s progression, and manage symptoms effectively.
- These interventions contribute to enhancing the quality of life for individuals grappling with MS.
Source: MNT
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

