Urban expansion poses both challenges and opportunities, influencing the dynamics of urban fringes in both developed and developing nations. As cities grow and populations increase, the urban fringe, the transitional zone between urban and rural areas, becomes a focal point for various issues. In developed nations, the problems may revolve around issues of sustainability, infrastructure strain, and potential loss of green spaces. Meanwhile, in developing nations, rapid urbanization may bring challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, informal settlements, and environmental degradation. However, amidst these challenges lie prospects for sustainable development, improved living conditions, and the creation of vibrant urban spaces. Analyzing the problems and prospects of urban expansion in the context of the urban fringe unveils the complex interplay of socio-economic, environmental, and infrastructural factors that shape the future of urban areas worldwide.
Contents
Answer
The term “urban fringe” refers to the transitional area at the outskirts of an urban area or city where urban and rural land uses mix. It is the zone where the city meets the surrounding countryside, and characteristics of both urban and rural environments coexist.
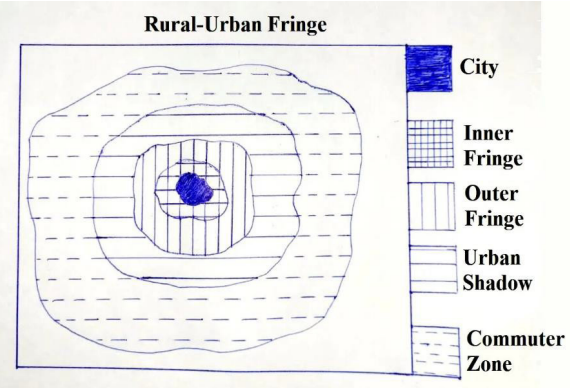
Problems of Urban Expansion in Urban Fringe
- Land Use Conflicts and Land Use Changes Due to Urban Expansion in Urban Fringe
- According to the bid-rent theory, competing demands for prime land in the urban fringe may result in conflicts between agricultural and urban land uses.
- The conflict between suburban residential development and preserving agricultural land exemplifies bid-rent dynamics, notably observed in developed nations like the United States.
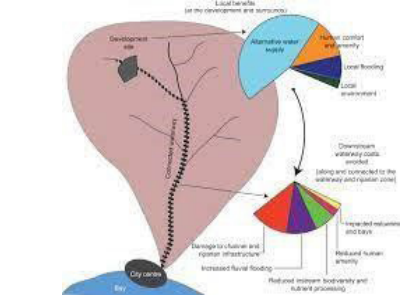

- Urban Sprawl Induced Environmental Degradation
- Urban sprawl, driven by factors like population growth and accessibility, contributes to environmental degradation as it encroaches upon natural habitats and ecosystems.
- Developing nations, such as India, witness ecological imbalances in the urban fringe due to unchecked urban sprawl affecting biodiversity and natural resources.
- Infrastructure Challenges due to Urban Expansion in Urban Fringe
- The peripheral model posits that urban expansion occurs along transportation routes, often creating challenges in providing adequate infrastructure to support the growing urban fringe.
- Both developed and developing nations experience infrastructure challenges as suburban areas expand along transportation corridors, leading to issues of congestion and insufficient services.
- Congestion induced due to Urban Expansion in Urban Fringe
- Transportation geography emphasizes the spatial aspects of movement.
- In urban fringe expansion, increased demand for transportation contributes to congestion issues.
- Developing nations may grapple with transportation problems in the urban fringe, where inadequate public transit systems result in increased congestion and commuting difficulties.
Prospects of Urban Expansion in Urban Fringe
- Central Place Theory and Economic Growth Opportunities
- Central place theory suggests that urban fringe areas can function as economic nodes (Growth Centres), providing growth opportunities for businesses and industries.
- Business parks strategically located in the urban fringe serve as economic centers, attracting companies seeking cost-effective locations, aligning with central place theory principles.
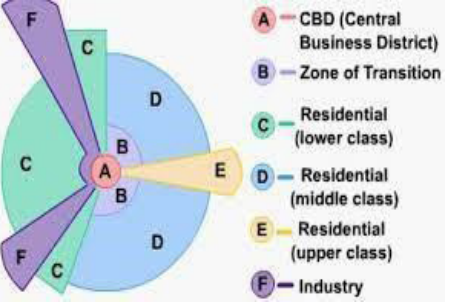
- Housing Development as a result of Urban Expansion in Urban Fringe
- The sector model posits that cities expand in sectors.
- Urban expansion in the fringe facilitates housing development to accommodate the growing population.
- Housing projects in the urban fringe of both developed and developing nations align with sector model dynamics, responding to the demand for residential spaces.
- Green Belts and Environmental Conservation
- Green belts, a planning strategy, aim to preserve natural features.
- The strategic urban expansion includes green spaces and recreational areas for environmental conservation.
- Developed nations often integrate green belts into urban fringe planning, exemplifying a deliberate effort to balance expansion with environmental preservation.
- Growth of Employment Opportunities
- Location theory emphasizes spatial considerations in economic activities.
- Urban expansion in the fringe can lead to the development of employment centers.
- Technology parks and industrial zones strategically located in the urban fringe provide job opportunities, illustrating location theory principles in both developed and developing nations.
- Sustainable Development and Integrated Planning
- Sustainable development principles advocate for a balanced approach.
- Integrated planning in the urban fringe seeks to balance economic growth with environmental and social considerations.
- Zoning regulations and green belts implemented in developed nations reflect an integrated planning approach to guide urban expansion while preserving natural features.
Hyper urbanization in contemporary times primarily in developing countries because of primacy (Primate City) is causing unsustainable urbanization, in such a scenario programs like Smart Cities Mission, AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation), National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM), Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY), Sustainable Urban Transport Project (SUTP) are a step in the right direction.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here