
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Regulating Misleading Advertisements in India
- 2 Regulation of Advertisements in India
- 3 Potential Prosecution of Political Party for Money Laundering
- 4 Criminalisation of Politics
- 5 India’s Toy Industry
- 6 About Sariska Tiger Reserve
- 7 Strait of Gibraltar
- 8 Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre
- 9 The Great Pyramid of Giza
- 10 Geomagnetic Storms and Solar Wind
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Regulating Misleading Advertisements in India
Tag: GS – 2 Transparency & Accountability, Government Policies & Interventions GS – 4
In News:
To protect consumers from deceptive advertising, the Supreme Court of India has mandated that advertisers must provide self-declarations prior to promoting products through the media.

Regulation of Advertisements in India
Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)
- The CCPA, operating under the Department of Consumer Affairs, regulates matters concerning consumer rights violations and unfair trade practices.
- Established under section 10 of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, it aims to prevent false or misleading advertisements and safeguard consumer rights.
Enforcement Guidelines
- The CCPA enforces the ‘Guidelines for Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements, 2022’, empowered by the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- These guidelines aim to protect consumer rights by ensuring advertisements refrain from unsubstantiated claims, exaggerated promises, and misinformation.
Objective and Provisions
- The guidelines define various forms of misleading advertisements and lay down provisions to protect consumers’ rights to information, choice, and safety.
- They outline duties of manufacturers, service providers, advertisers, and advertising agencies to ensure transparency and clarity in advertisements, enabling informed consumer decisions.
Penalties for Violations
- The CCPA can impose penalties of up to 10 lakh rupees for manufacturers, advertisers, and endorsers for misleading advertisements.
- Subsequent violations may attract penalties of up to 50 lakh rupees.
- Endorsers of misleading advertisements can face prohibition from making endorsements for up to 1 year, extendable to 3 years for subsequent violations.
Regulation by Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Deceptive advertising falls under Section-53 of the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, making it punishable.
- FSSAI mandates truthful, unambiguous, and scientifically substantiated advertisements through the Food Safety and Standards (Advertisements & Claims) Regulations, 2018.
Legislations Governing Advertising
- Advertisement Standard Council of India (ASCI): A nonstatutory tribunal enforcing advertising ethics through the ASCI code, applicable to advertisements seen in India.
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986: Grants consumers rights to information and redressal against misleading advertisements.
- Cable Television Network Act and Amendment Act: Regulates television advertisements to ensure compliance with prescribed codes.
- Restrictions on Tobacco Advertisement: Prohibits tobacco advertisements in all forms of media under the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act, 2003.
- Drug and Magic Remedies Act, 1954 & Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940: Regulates drug advertisements to prevent misuse and false claims.
- Regulation of Prenatal Diagnostic Techniques Act, 1994: Prohibits advertisements related to prenatal sex determination.
- Criminality of Advertisements under Indian Penal Code (IPC): Prohibits obscene, defamatory, or inciteful advertisements, with offenses punishable under IPC provisions.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2012) Q. With reference to ‘consumers’ rights/privileges under the provisions of law in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. Consumers are empowered to take samples for food testing. 2. When a consumer files a complaint in any consumer forum, no fee is required to be paid. 3. In case of death of consumer, his/her legal heir can file a complaint in the consumer forum on his/ her behalf. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (c) Mains (2013) Q. What are social networking sites and what security implications do these sites present? |
Source: TH
Potential Prosecution of Political Party for Money Laundering
Tag: GS-2 Polity GS-3 Money laundering
In News:
The Enforcement Directorate (ED) has notified the Delhi High Court of its intention to designate the Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) as an accused in the ongoing money laundering probe linked to purported irregularities within the Delhi excise policy scam.

Overview of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002
- Enactment and Objectives
- The PMLA, enacted in January 2003, aims to combat money laundering in India with three main objectives:
- Prevent and control money laundering
- Confiscate and seize property obtained from laundered money
- Address any other issues related to money laundering in the country.
- Definition of Offence
- Section 3 of the Act defines the offence of money laundering as any attempt, assistance, or involvement in activities related to proceeds of crime to present them as untainted property.
- Amendments
- The PMLA has been amended multiple times, including through the Finance Acts of 2015, 2018, and 2019.
Political Parties and Money Laundering
- Section 70 of the PMLA deals with offences by companies, holding individuals in charge liable for contraventions.
- While political parties are not companies under the Companies Act 2013, the Act’s explanation broadens the definition of “company” to include associations of individuals, potentially encompassing political parties.
Potential Prosecution
- If a political party were directly accused in a money laundering case, it would be a first instance.
- Political parties have previously faced investigations under the Income Tax Act.
Challenges for the Election Commission
- Suspension or Withdrawal of Recognition: The EC can suspend or withdraw a party’s recognition under specific grounds outlined in The Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, primarily related to violations of the Model Code of Conduct.
- De-registration: While the EC can register parties under the Representation of the People Act, it has limited grounds for de-registration, mainly if a party obtained registration through fraud, renounces allegiance to the Constitution, or is declared unlawful by the Union Government under specific laws.
- However, if a political party were implicated in money laundering, the Representation of the People Act lacks provisions to address such situations.
Source: IE
Terms
Criminalisation of Politics
Tag: GS – 2 GS – 4 Transparency & Accountability, Representation of People’s Act, Executive, Judgements & Cases, Ethics and Human Interface, Ethics in Human Actions, Ethics in Private & Public Relationships
In News:
Recent cases of alleged sexual harassment involving MPs, MLAs, and government employees shed light on a troubling aspect of the criminalisation of politics. These incidents highlight ethical issues like moral responsibility and failure to uphold professional ethics.

Understanding the Concept of Criminalisation of Politics
Definition and Impact
- Criminalisation of politics occurs when individuals with criminal backgrounds or charges become politicians and secure elected positions.
- It poses a threat to democratic principles, including fair elections, accountability, and adherence to the law.
Statistics Highlighting the Issue
- Data from the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) indicates a steady increase in the number of elected representatives with criminal charges since 2004.
- In the 2019 Lok Sabha, 43% of members faced criminal charges, with 21% facing serious allegations such as rape and murder.
Root Causes of Criminalisation
- Nexus between politicians and criminal elements, leveraging money and muscle power for electoral success.
- Weak law enforcement and judicial systems, leading to low conviction rates for politicians with criminal backgrounds.
- Lack of internal party democracy, allowing leaders to prioritize electability over integrity.
- Voter apathy and limited political awareness, particularly in rural areas, where immediate benefits may outweigh long-term governance concerns.
Ethical Concerns Associated with Criminalisation
- Lack of non-partisanship and accountability, evidenced by the defence of politicians facing serious criminal charges.
- Absence of democratic accountability through public outrage, highlighting the reactive nature of political responses to scandals.
- Culture of impunity and individual accountability, with women often bearing the burden of pursuing justice against powerful perpetrators.
- Women’s empowerment as a fallacy, with substantive progress on women’s issues remaining elusive despite rhetoric.
Ethical Implications of Criminalisation
- Societal erosion of moral fabric and reduced civic participation due to distrust in corrupt systems.
- Inequality and exclusion of marginalized communities from political representation.
- Focus on short-term gains over long-term societal development.
- Undermining democratic principles of integrity, fairness, and transparency.
Recommendations for Addressing the Issue
- Strengthening institutional mechanisms for accountability, including anti-corruption agencies and internal party disciplinary processes.
- Promoting a culture of ethical conduct through comprehensive codes of conduct and mandatory training programs.
- Empowering citizens and civil society through civic education and greater participation in the political process.
Conclusion
Restoring accountability and ethical standards within India’s political landscape requires a multifaceted approach that addresses institutional weaknesses, cultural norms, and societal engagement. While challenging, such efforts are essential for preserving the integrity of the democratic process and advancing equitable governance.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2021) Q. Consider the following statements: 1. In India, there is no law restricting the candidates from contesting in one Lok Sabha election from three constituencies. 2. In the 1991 Lok Sabha Election, Shri Devi Lal contested from three Lok Sabha constituencies. 3. As per the existing rules, if a candidate contests in one Lok Sabha election from many constituencies, his/her party should bear the cost of bye-elections to the constituencies vacated by him/her winning in all the constituencies. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 2 and 3 Ans: (b) Mains (2022) Q.1 Discuss the procedures to decide the disputes arising out of the election of a Member of the Parliament or State Legislature under The Representation of the People Act, 1951. What are the grounds on which the election of any returned candidate may be declared void? What remedy is available to the aggrieved party against the decision? Refer to the case laws. Mains (2013) Q.2 It is often said that ‘politics’ and ‘ethics’ do not go together. What is your opinion in this regard? Justify your answer with illustrations. |
Source: IE
India’s Toy Industry
Tag: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions GS -3 Industrial Growth
In News:
The Global Trade Research Initiative report has recently recommended a thorough strategy aimed at fostering the growth of India’s toy industry and boosting its exports.

Overview of India’s Toy Industry
Status
- India’s position in the global toy trade remains marginal, accounting for only 0.3% of exports and 0.1% of imports, according to the Global Trade Research Initiative report.
- Ranking 27th in global toy exports and 61st in toy imports, India shows diversity in manufacturing capabilities, particularly in electronic toys, plastic dolls, and non-electronic toys.
Potential
- The Indian toy industry is witnessing rapid growth, projected to reach USD 3 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12% between 2022-2028.
- There is an expansion in global presence, marked by increased high-value exports to Middle East and African countries.
Challenges Faced by India’s Toy Industry
- Lack of Technology
- Outdated technology and machinery hinder manufacturing quality and design of toys.
- High GST Rates
- Mechanical toys attract 12% GST, while electronic toys face an 18% tax, leading to classification complexities.
- Lack of Infrastructure
- Inadequate infrastructure, including testing labs, toy parks, clusters, and logistics support, poses challenges.
- Unorganized and Fragmented
- Approximately 90% of the market remains unorganized, making it difficult to harness maximum benefits.
- Other Challenges
- Factors like cost-effectiveness, product diversity, quality standards, and trade agreements significantly influence the industry.
Way Forward:
- Government Initiatives
- Support the industry through schemes like SFURTI and promote exports to bolster global presence.
- Encourage Global Brands
- Invite international toy manufacturers, such as Hasbro and Mattel, to consider setting up production facilities in India.
- Collaboration for Technology Transfer
- Partner with international entities for technology transfer and skill development to enhance competitiveness.
- Learning from China
- Study China’s success in becoming a major exporter and adapt strategies for market penetration.
- Localize Production
- Promote local manufacturing of key toy-making materials to reduce dependency on imports and enhance self-sufficiency.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2012) Q. What is/are the recent policy initiative(s) of Government of India to promote the growth of manufacturing sector? 1. Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones 2. Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’ 3. Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) Mains (2015) Q. “Success of ‘Make in India’ program depends on the success of ‘Skill India’ programme and radical labour reforms.” Discuss with logical arguments. |
Source: GTRI
About Sariska Tiger Reserve
Tag: GS-3 Environment and Conservation
In News:
Even after 46 years since its designation as a Tiger Reserve, Sariska, one of the initial 12 reserves in the country, still awaits proper land ownership acknowledgment in the state’s revenue records.
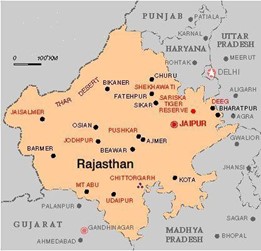
Exploring Sariska Tiger Reserve
- Location: Situated in the Alwar district of Rajasthan, Sariska Tiger Reserve spans across 800 square kilometers and is nestled within the Aravali Hills.
- Historical Background: Originally a hunting ground for the Maharaja of Alwar, Sariska was designated as a natural reserve in 1955 and later declared a national park in 1979.
- Conservation Milestone: Renowned as the first reserve globally to successfully relocate tigers, Sariska has played a pivotal role in tiger conservation efforts.
- Tourist Attractions: Besides its wildlife, Sariska is renowned for its historical and cultural landmarks, including Pandu Pol, Bhangarh Fort, Ajabgarh, Pratapgarh, Siliserh Lake, and Jai Samand Lake.
- Topography: The reserve boasts a diverse terrain comprising rocky landscapes, scrub thorn arid forests, grasslands, hilly cliffs, and semi-deciduous woodlands.
- Vegetation: Sariska’s vegetation primarily consists of Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests and Northern Tropical Thorn Forests, dominated by dhok trees covering approximately 90% of the sanctuary. Other species such as salar, kadaya, gol, ber, Banyan, gugal, bamboo, kair, and adusta are also found here.
- Fauna Diversity: In addition to tigers, Sariska Tiger Reserve is home to a rich variety of wildlife, including leopards, sambhar, chital, nilgai, four-horned antelope, wild boar, rhesus macaque, langur, hyena, and jungle cats.
Source: TOI
Strait of Gibraltar
Tag: GS-1 Physical Geography GS-2 IR
In News:
In Moroccan waters within the Strait of Gibraltar, a sailing yacht was sunk by a group of orcas after being rammed, with the exact number of orcas involved remaining unknown.
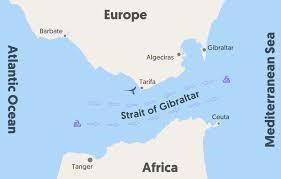
Exploring the Strait of Gibraltar
- Location: The Strait of Gibraltar is situated as a narrow waterway separating Europe from Africa, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean. Its narrowest point lies between Morocco’s Point Cires and Spain’s Point Marroquí.
- Geographical Features: With depths ranging from 300 to 900 meters, the strait forms a significant gap between the high plateau of Spain and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa.
- Formation: Geological studies have unveiled that the Strait was formed due to the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate.
- Water Flow Dynamics: Due to varying salinity levels, the highly saline waters from the Mediterranean Sea flow outward and underneath the currents from the Atlantic Ocean, while the less saline Atlantic waters flow inward and on top of the Mediterranean Sea current.
- Role as a Chokepoint: Serving as a chokepoint for ships entering or leaving the Mediterranean Sea, the Strait of Gibraltar is also a crucial shipping route for countries across northern Africa, southern Europe, and western Asia.
- Significant Port: A key port located along the Strait of Gibraltar is the Moroccan port of Tanger-Med, situated near Tangier.
Source: Reuters
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech., Cybersecurity
In News:
In partnership with Microsoft, the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) has successfully blocked over 1,000 Skype IDs engaged in activities such as blackmail, extortion, and impersonation of police and law enforcement officials, leading to “digital arrests” by cybercriminals.
Overview of the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), established under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), aims to address cybercrime nationwide in a coordinated and comprehensive manner.
- It operates from New Delhi and focuses on enhancing coordination among various Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) and stakeholders to combat cyber threats effectively.
Functions of I4C
- Serving as a pivotal point in combating cybercrime.
- Identifying research needs and collaborating with academia and research institutes to develop new technologies and forensic tools.
- Preventing the misuse of cyberspace by extremist and terrorist groups.
- Proposing amendments to cyber laws to align with evolving technologies and international cooperation.
- Coordinating the implementation of Mutual Legal Assistance Treaties (MLAT) with other countries regarding cybercrimes.
Components of I4C
- National Cybercrime Threat Analytics Unit (TAU) for regular threat reporting.
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) for citizens to report cybercrime complaints.
- National Cybercrime Training Centre (NCTC) for training government officials, especially state law enforcement agencies.
- National Cybercrime Research and Innovation Centre for indigenous tool development.
- Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Coordination Team for inter-state LEAs coordination.
- Cybercrime Ecosystem Management Unit for mass awareness on cyber hygiene.
- National Cybercrime Forensic Laboratory (Investigation) Ecosystem to aid LEAs in cyber forensics investigation.
Additional Initiatives
- Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System for immediate reporting of financial cyber frauds.
- Operation of the National Toll-free Helpline number ‘1930’ for citizen assistance in lodging online cyber complaints.
- Utilization of the CyberDost handle on various social media platforms to raise cyber awareness among citizens.
Source: TH
The Great Pyramid of Giza
Tag: GS-1 Cultural Heritage GS-2 IR
In News:
The recent unearthing of a mysterious structure concealed beneath the sands in close proximity to the renowned Great Pyramid of Giza has the potential to alter our understanding of these ancient monuments.

Overview of the Great Pyramid of Giza
- The Great Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Great Pyramid or Great Pyramid of Khufu, stands as an ancient Egyptian marvel and is the largest among the three Pyramids of Giza.
- Situated on the Giza plateau, approximately five miles west of the Nile River near Cairo, Egypt, it was constructed during the reign of Khufu (Cheops), the second king of Egypt’s 4th dynasty, around 2580-2560 BC.
- Until the completion of the Eiffel Tower in Paris, France, in 1889, the Great Pyramid held the title of the world’s tallest human-made structure for over 3,000 years.
- Excavated in 1880 by British archaeologist Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie, the pyramid originally stood about 481 feet tall, though erosion and the removal of its top piece have reduced its height to approximately 455 feet. Each side of its base measures around 755 feet.
- Comprising over two million stone blocks, each weighing more than 2000 pounds (907 kg), the pyramid features three main chambers: the King’s Chamber, the Queen’s Chamber, and the Grand Gallery, accessible through small tunnels and air shafts.
- Rising at an angle of 51.87°, the pyramid’s sides are accurately aligned with the four cardinal points of the compass.
- Constructed primarily of yellowish limestone blocks, with inner passages made of finer, light-colored limestone, the pyramid’s interior burial chamber consists of massive granite blocks.
- Additionally, the Great Pyramid is part of a trio of 4th-dynasty (c. 2575–c. 2465 BCE) pyramids on the Giza plateau, each built for a different pharaoh: Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure. They are collectively considered the last surviving wonders of the ancient world.
Source: TOI
Geomagnetic Storms and Solar Wind
Tag: GS-3
In News:
A recent powerful geomagnetic storm, the strongest in more than twenty years, struck Earth, resulting in radio disruptions and extending the appearance of the northern lights to as far south as the United States.
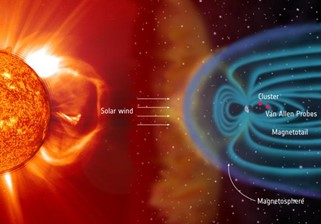
Understanding Geomagnetic Storms and Solar Wind
Geomagnetic Storms
- A geomagnetic storm is a significant disruption of Earth’s magnetosphere caused by the efficient transfer of energy from the solar wind into the space environment surrounding Earth.
- These storms occur due to fluctuations in the solar wind, leading to substantial changes in the currents, plasmas, and fields within Earth’s magnetosphere.
- Conditions conducive to geomagnetic storms include sustained periods of high-speed solar wind and a southward-directed solar wind magnetic field at the dayside of Earth’s magnetosphere.
- The most severe geomagnetic storms are linked to solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs), where massive amounts of plasma from the sun, along with its embedded magnetic field, reach Earth.
Effects of Geomagnetic Storms
- Geomagnetic storms induce intense currents in the magnetosphere, alterations in the radiation belts, and changes in the ionosphere, including heating the ionosphere and the thermosphere.
- These storms can cause spectacular auroras on Earth due to the heating of the ionosphere.
- Long-range radio communication reliant on sub-ionospheric reflection can be disrupted during geomagnetic storms.
- Ionospheric expansion during storms can increase satellite drag and challenge orbit control.
- Satellite electronics may suffer damage from static-electric charges buildup and discharge.
- Global navigation systems can experience disruptions during geomagnetic storms.
- Harmful geomagnetic-induced currents (GICs) may occur in power grids and pipelines.
Solar Wind
- Solar wind is a continuous flow of protons and electrons emitted from the sun’s outermost atmosphere, the corona.
- These charged particles travel through the solar system at speeds ranging from approximately 250 to 500 miles per second in a plasma state.
- The solar magnetic field is embedded in the plasma and extends outward with the solar wind.
- Different regions of the Sun produce solar wind with varying speeds and densities.
- Upon reaching Earth, the solar wind introduces charged particles into the magnetosphere and along Earth’s magnetic field lines, particularly towards the poles.
Source: Earth.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

