The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Summit is a major international event where leaders from several countries come together to discuss and cooperate on important issues like security, economic development, and cultural exchange. The SCO, which includes countries like China, Russia, India, and Pakistan, aims to promote peace, stability, and mutual understanding among its members. The summit provides a platform for these nations to work together on common challenges, such as combating terrorism, enhancing trade, and addressing regional conflicts. By collaborating closely, the SCO hopes to create a more secure and prosperous future for all its member countries.

Tags: GS – 2, IR- Regional Groupings – Important International Institutions
Contents
- 0.1 Context:
- 0.2 Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- 0.3 Significance of SCO:
- 0.4 Relevance of SCO for India:
- 0.5 Criticism of SCO:
- 1 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 2 FAQs
- 3 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context:
- Indian External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar participated in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Summit in Astana, Kazakhstan’s capital.
- During the summit, he held talks with Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi.
- Additionally, he conducted bilateral meetings with counterparts from SCO members Tajikistan and Russia, along with the newest member Belarus.

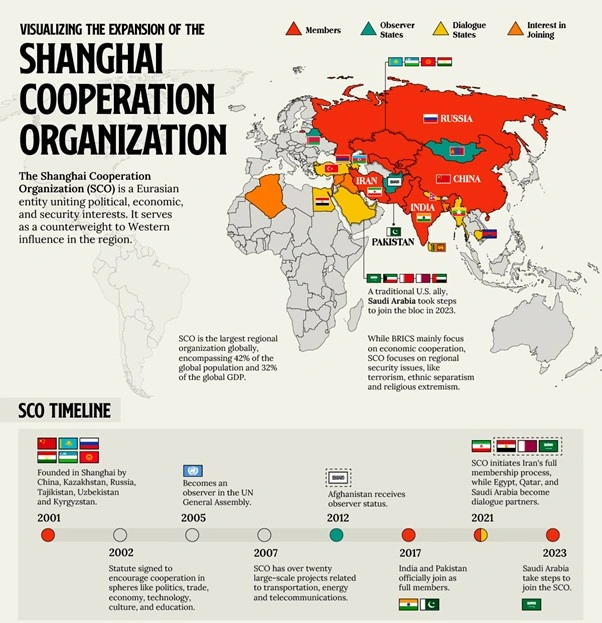
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- About SCO:
- The SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation established in June 2001 in Shanghai, China.
- Founding members include Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan.
- Originally formed in 1996 as the Shanghai Five, the group aimed to enhance regional security, reduce border troops, and combat terrorism in the post-Soviet era.
- In 2001, Uzbekistan joined, and the organisation was renamed SCO, promoting the Shanghai spirit of cooperation through its charter.
- The organisation represents approximately 42% of the world’s population, 22% of its land area, and 20% of its GDP.
- Official working languages are Chinese and Russian.
- SCO Secretariat is located in Beijing, China.
- Members, Observers, and Dialogue Partners:
- 10 member states: China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan, Iran, and Belarus.
- India and Pakistan became full members in 2017 at the Astana Heads of State Council meeting.
- Iran joined as the 9th member in 2023 during India’s chairmanship.
- Belarus became the 10th member during the 2024 summit.
- 2 Observer members: Afghanistan and Mongolia.
- 9 Dialogue Partners: Azerbaijan, Armenia, Egypt, Cambodia, Qatar, Nepal, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and Sri Lanka.
- In 2022, Bahrain, Kuwait, Maldives, Myanmar, and the United Arab Emirates initiated the process for Dialogue Partner status at the SCO Summit in Samarkand.
- Organisational Structure of SCO:
- The Heads of State Council (HSC) is the highest decision-making body, meeting annually.
- The Council of Heads of Government is the second-highest council.
- The Council of Foreign Ministers meets regularly to discuss international issues.
- The Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) in Tashkent combats terrorism, separatism, and extremism.
- India’s Association with SCO:
- India joined SCO as an observer in 2005 and became a full member in 2017.
- India introduced five pillars of cooperation in SCO: Startups and Innovation, Traditional Medicine, Digital Inclusion, Youth Empowerment, and Shared Buddhist Heritage.
- Two new mechanisms were established: Special Working Group on Startups and Innovation and Experts Working Group on Traditional Medicine.
- Kashi/Varanasi was designated as the SCO Tourist and Cultural Capital for 2022-23.
Significance of SCO:
- Security Focus: SCO is notable for addressing security issues and comprises primarily Asian members.
- Alternative Order: Russia and China advocate SCO as an alternative to Western-dominated international structures.
- Positioning Against US Influence: Alongside BRICS, Russia and China position SCO against US influence, evident amid tensions like the Russia-Ukraine War and US-China trade disputes.
- Expansion Influence: Iran’s 2023 inclusion enhances SCO’s influence, countering US diplomatic efforts.
Relevance of SCO for India:
- Cooperation Opportunity: SCO membership facilitates deeper ties with Central Asian nations, addressing mutual security concerns despite historical tensions since 1991.
- RATS Functionality: The Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) aids in counter-terrorism operations, intelligence sharing, and combating drug trafficking.
- Challenges: India’s strained relations with China and Pakistan impact SCO dynamics.
- Virtual Summit Stand: India’s virtual SCO summit during its presidency and non-endorsement of BRI in the New Delhi Declaration reflects concerns over CPEC’s passage through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
Criticism of SCO:
- Competition between Russia and China:
- Despite professed “limitless friendship,” competition for influence exists between Russia and China, particularly in Central Asia.
- Traditionally under Russia’s sphere, Central Asian nations have also seen significant Chinese investments through the Belt and Road Initiative.
- The inclusion of India and Pakistan in 2017 reflects this rivalry, with Russia supporting India and China backing Pakistan to maintain a balance of power.
- Chinese Hegemony:
- The West views SCO primarily as a platform to advance Chinese interests, raising concerns about Chinese hegemony in the organisation.
- Rivalries Among Members:
- SCO’s initiatives are criticised for their vagueness, allowing member countries to overlook rivalries rather than resolve them.
- Tensions between India and Pakistan, as well as between India and China, persist despite SCO membership.
- Broad SCO language enables nominal support for initiatives while prioritising national interests during conflicts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q:1 Consider the following: (2022)
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Missile Technology Control Regime
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
India is a member of which of the above?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q:1 Critically examine the aims and objectives of SCO. What importance does it hold for India? (2021)
Source: IE
FAQs
Q: What is the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)?
- Answer: The SCO is an international organization that promotes cooperation in areas like security, economics, and culture among its member countries. It includes countries like China, Russia, India, and several Central Asian nations.
Q: What happens at the SCO Summit?
- Answer: At the SCO Summit, leaders from the member countries meet to discuss important issues like regional security, economic cooperation, and cultural exchanges. They make decisions and sign agreements to work together on these matters.
Q: Why is the SCO Summit important?
- Answer: The SCO Summit is important because it helps strengthen relationships between member countries, addresses regional challenges, and promotes peace and stability in the region. It also opens up opportunities for economic and cultural cooperation.
Q: What are some recent topics discussed at the SCO Summit?
- Answer: Recent topics at the SCO Summit have included combating terrorism, enhancing trade and economic ties, dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic, and promoting cultural and educational exchanges among member countries.
Q: How does India benefit from being part of the SCO?
- Answer: India benefits from being part of the SCO by having a platform to discuss security and economic issues with neighboring countries, enhancing trade opportunities, and participating in joint efforts to combat terrorism and other regional threats. It also helps India build stronger diplomatic relationships in the region.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

