Today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants explores the latest developments relevant to the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping India’s socio-political and economic landscape. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.

Contents
- 1 Role of DBT in empowering women
- 2 Typhoon Yagi
- 3 DPIIT to launch BHASKAR Initiative
- 4 ITU Releases Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024
- 5 Neelakurinji plants
- 6 Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile
- 7 Nidhi Companies
- 8 Gopalpur Port
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 9.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 9.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 9.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 9.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 10 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Role of DBT in empowering women

Tags: GS-2 – Vulnerable Sections – Women
Why in the news?
- 53 ministries under the Union government running 315 DBT schemes, 13 of which are related to the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- The ministry has a poor track record in implementing these schemes and ranks 31st in the DBT Performance Rankings.
The scenario of women in India:
- Labour Force Participation: India’s female labour force participation rate is 28%. One out of 3 young people is not engaged in education, employment or training, with women making up 95% of this group.
- Women at top positions: Only one is a woman for every five men in managerial positions.
- Domestic violence: Three out of 10 women in the age group of 18-49 years have experienced violence from their spouses, as per a survey by Niti Aayog.
- Gaps in political representation: There are 74 (2024) women MPs in the 16th Lok Sabha out of 543 members (13.6% of the total MPs).
- Financial Gap: About 32% of Women-owned bank accounts in India are inactive (Findex Survey 2021).
Challenges to women’s financial independence:
- Limited physical access to banking services: Limited physical access to banking services is hindered by “mobility constraints” that prevent women from travelling alone, along with ‘time poverty’ and the financial burden of transportation costs to and from banking outlets.
- Limited access to ICT: Gender norms around purity for marriage, subservience, patrilocal exogamy, and caregiving present a significant barrier to women’s mobile engagement.
- Digital Literacy Gap: Subtle gender biases, such as unfriendly or dismissive behaviour from bank staff, compounded by information asymmetry, discourage women from using banking services.
- High social costs: Women face social barriers to accessing financial services, such as feeling embarrassed about depositing small amounts. As a result, they store cash at home until they accumulate a larger sum.
Role of DBT in women’s empowerment
- Enhanced mobility: Transferring funds through direct deposits to women’s accounts or mobile payments gives women more control over the use of financial resources.
- Enhanced bargaining power: Financial independence boosts women’s household bargaining power, shifting traditional power dynamics and enabling women.
- Ripple effect: It has a positive impact on women’s employment, health, and education
Way Forward:
- Moving beyond gender-neutral to gender-intentional policies: Gender-intelligent regulatory frameworks, recognising alternative identification documents, and introducing a vulnerability lens in consumer-protection regulations to bridge the divide in financial inclusion.
- Appoint more women Business Correspondents: The BC model circumvents women’s challenges with mobility and literacy.
- Collect gender-disaggregated data: This will allow a better understanding of the underlying causes of gender disparity in financial inclusion and aid in formulating effective policies.
- Gender-inclusive design for infrastructure and encourage collaboration among financial service providers to enhance interoperability.
- Facilitation of contextual training for women: Deploying female staff to troubleshoot issues such as downloading the app, linking it with their bank accounts, and types of transactions to ensure the absorption of information.
Source: IE
Typhoon Yagi
Tags:GS-1, Geography- Geographical Phenomena – Cyclone GS- 3, Disaster Management
Why in the news?
- Recently, Typhoon Yagi, the strongest tropical cyclone in Asia this year and second only to Hurricane Beryl globally, has caused widespread devastation across Southeast Asia.
About cyclones:
- Cyclones that develop in the regions between the Tropics of Capricorn and Cancer are called tropical cyclones.
- The World Meteorological Organization uses the term ‘tropical cyclone’ to cover weather systems where winds exceed ‘hurricane force’ (at least 34 knots or 63 km/h).
- Tropical storms are progeny of the sea and atmosphere, and are driven by heat from the sea.
- They are driven by easterly industry, strong westerly winds, strong planetary winds, and their own strong energies.
Formation of cyclones:
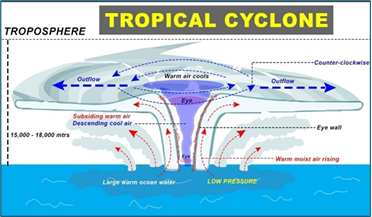
Tropical cyclones are known by different names in various regions:
- Hurricanes – In the West Indian islands in the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean.
- Tornados – In the Guinea lands of West Africa and southern USA
- Typhoons – In the Northwest Pacific Ocean, particularly affecting East and Southeast Asia (e.g., Japan, Philippines, China, Taiwan).
- Cyclones – In the Southwest Indian Ocean (off the coast of Africa, Madagascar), the Southeast Indian Ocean, and the Southwest Pacific Ocean.
- Willy-Willies – An informal term used for tropical cyclones in Australia.
Reasons behind Typhoon Yagi becoming the strongest storm in Asia:
- Warm Waters of the South China Sea:
- Typhoon Yagi began as a tropical storm in the western Philippine Sea.
- After weakening post-landfall in the Philippines, it intensified again due to the unusually warm waters in the South China Sea.
- It eventually reached Category 5 status, with peak winds of 260 kmph.
- Yagi is one of only four Category 5 storms recorded in the region, alongside Pamela (1954), Rammasun (2014), and Rai (2021).
- Although later downgraded to a tropical depression, it caused severe flooding in countries like Myanmar.
- Role of Climate Change:
- While scientists continue to debate the exact role of climate change in tropical cyclones, there is a consensus that rising global temperatures are making storms more intense.
- Research shows that cyclones in Southeast Asia are forming closer to coastlines, intensifying more rapidly, and staying longer over land.
- This trend is linked to warmer sea surface temperatures, which have risen by nearly 0.9°C since 1850.
- Warmer oceans increased storm intensity by fueling them with more heat and moisture, leading to stronger winds and heavier rainfall.
Operation Sadbhav by India:
India launched Operation Sadbhav to provide $1 million in flood relief to Vietnam and $100,000 to Laos, aiding recovery efforts in Laos, Myanmar, and Vietnam.
This operation aligns with India’s Act East Policy and emphasises its role as a first responder in ASEAN disaster relief efforts.
DPIIT to launch BHASKAR Initiative
Tags: GS-3, Economy- Fiscal policy- govt. Scheme & Incentive
Why in the news?
- Recently, The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, is set to launch the Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry (BHASKAR).
About:
- It aims to strengthen India’s startup ecosystem by centralising resources and fostering collaboration among startups, investors, mentors, service providers, and government bodies.
- To qualify as a startup under this initiative, an entity must be a private limited company, LLP, or partnership firm under 10 years old, with an annual turnover of no more than ₹100 crore.
Key feature of Bhaskar Initiative:
- Communication: To bridge the gap between startups and other stakeholders, and for easy communication across sectors.
- Centralised Access to Resources: Start-ups can provide immediate access to needed tools and expertise More effective decision making and scale.
- Building personal identity: Each participant will Bhaskar was not given a unique ID, ensure individuality, Interactive seminars and tailored experiences.
- Increased visibility: With powerful analytical tools, Users can easily find the right resources, colleagues, ensuring opportunities, decision making and speed of action.
- Support India’s global brand: It will promote India’s global brand Reputation as a hub for innovation, crossing borders a much easier conversation for startup investors alike.
India’ Startup Ecosystem:
- India has the 3rd largest startup ecosystem in the world and has over 1,46,000 DPIIT-recognized startups.
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) recognizes business as a startup.
- The adoption of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and data analytics.
Other Initiatives taken for Startups:
- The Startup India initiative, launched in 2016 to build a strong ecosystem for startups and innovation in India.
- Atal Incubation Centers by NITI Aayog as part of the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) launched in 2016
- MAARG portal (Mentorship, Advisory, Assistance, Resilience and Growth) of Startup India by DPIIT in 2023.
- Union Cabinet approved Fund of Funds for Startups (2016) with a corpus of ₹10,000 crore to be managed with SIDBI.
Source: PIB
ITU Releases Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- IT & Computer- Cybersecurity
Why in the news?
- Recently, India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024.
- This recognition by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) reflects India’s growing strength in protecting digital information and improving online safety.

International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- About: On 17 May 1865, the first International Telegraph Convention signed in Paris established the International Telegraph Union (the first incarnation of ITU).
- Members: 193 Member States (including India), other members include companies, universities, etc.
- Flagship reports: Global Connectivity Report, Global e-waste Monitor HQ Geneva, Switzerland ITU is the UN’s oldest specialised agency .
- Functions:
- It promotes the shared global use of the radio spectrum.
- It facilitates international cooperation in assigning satellite orbits.
- It assists in developing and coordinating worldwide technical standards.
- It works to improve telecommunication infrastructure in the developing world.
Key Highlights of the report :
- Model countries: India earned an impressive score of 98.49, placing it among the top 47 countries in the world with the best cybersecurity practices.
- Global Trends in Cybersecurity: Progress by region and Africa from 2021 (latest GCI publication) made great strides in cybersecurity
- Expansion of digital services:
- Most countries are either “establishing” (Tier 3) or “evolving” (Tier 4).
- These countries have largely expanded digital services and connectivity but must integrate cybersecurity measures.
India’s Score in each pillar: Legal Measures – 20, Technical Measures – 20, Organisational Measures – 18.49, Capacity Development – 20, Cooperation – 20
Challenges for India:
- Demands continuous vigilance and adaptation
- Ransomware attacks, cyber breaches affecting core industries, costly system outages.
- Limits in skills, personnel, equipment, and funding.
- Continuous improvement in legal frameworks
- Investment in cutting-edge technology
Suggestions:
- Develop and regularly update a comprehensive national cybersecurity strategy.
- Empowering cybersecurity professionals, youth and vulnerable groups.
- Promote domestic and international cooperation in information sharing, training opportunities and more.
Source: ET
Neelakurinji plants
Tags: GS-3, Ecology & Environment- Biodiversity- Species
Why in the news?
- The Chokramudi Hills, near Munnar, are facing significant destruction of Neelakurinji plants due to illegal constructions and land encroachments.
Neelakurinji (Strobilanthes kunthiana):
- Common Names: Kurinji, Neelakurinji in Tamil and Malayalam, and Gurige in Kannada.
- Unique Blooming Cycle: The plant blooms once every 12 years (most recent in 2018).
- Habitat: Thrives in the Shola forests of the Western Ghats, particularly Munnar in Kerala, where it grows at elevations between 1,300 to 2,400 meters.
- Physical Characteristics: The plant grows 30 to 60 cm tall and produces purple-blue flowers, with peak blooming from August to October.
- Ecological Role: Key indicator of ecosystem health and biodiversity in the Western Ghats and attracts wildlife, including the endangered Nilgiri Tahr.
- Conservation Status: VU.
- Threats: Due to agricultural expansion, particularly tea and coffee plantations, tourism.
Source: (TH)
Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- Defence technology
Why in the news?
- Recently, India successfully test-fired a Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile (VLSRSAM) from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
About Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile:
- It is a cruise weapon designed to neutralise a variety of short-range air threats, including naval installations.
- During the mid-flight, the missile uses a fiber-optic gyroscope-based passive guidance system, while the end stage uses active radar homing.
- The Indian Navy and DRDO jointly conducted a test of a land-based anti-aircraft missile against high-speed and low-flying aircraft.
features:
- It is designed to respond to a variety of long-range airborne threats, including aircraft, helicopters, drones and incoming missiles.
- It is equipped with an advanced guidance system and state-of-the-art technology that provides improved agility and accuracy in targeting.
- It weighs about 170 pounds and uses a solid propellant. At a top speed of Mach 4.5, the weapon system has a range of 16 km.
- The successful demonstration of this strategy further strengthens India’s air defence capabilities in maritime operations.
Source: IT
Nidhi Companies
Tags: GS-3, Economy- Growth & Development- Industry
Why in the news?
- Recently,the Registrar of Companies (RoC) under the corporate affairs ministry has penalised over two dozen Nidhi companies in about a fortnight for alleged violations of Companies Act provisions.
About Nidhi Companies:
- Legal Recognition: A NIDHI Company is recognised under Section 406 of the Companies Act 2013 and typically operates in the Non-Banking Financing Sector of India.
- Objective: It is formed to borrow and lend money to its members. It inculcates the habit of saving among its members and works on the principle of mutual benefit.
- Regulatory Requirements: It is not required to receive the licence from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), as these are registered with the Companies Act.
- Members: A minimum of seven members is required to start a Nidhi Company out of which three members must be the directors of the company.
Prohibited Activities:
- It can’t deal with chit funds, hire-purchase finance, leasing finance, insurance or securities business.
- It is strictly prohibited from accepting deposits from or lending funds to, any other person except members.
- Nidhi companies should not issue preference shares, debentures or any other debt instrument in any manner, name or form.
- Nidhi companies should not open current accounts with their members.
Source: ET
Gopalpur Port
Tags: GS-3, Economy- Growth & Development- Infrastructure – Port
Why in the news?
- Recently, The Odisha government approved a proposal to transfer 95 percent of the equity shares of Gopalpur Port to Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ).
About Gopalpur Port:
- Location: A deep-draft, multi-cargo port on the east coast of India in Odisha, positioned between Paradip Port (north) and Visakhapatnam Port (south).
- Strategic Hinterland: The hinterland of the port is the states of Odisha, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh, thus providing access to a mix of minerals, steel, aluminium, cement and power plants.
- Coal Reserves: The coal fields of IB and Talcher, which account for approximately 25% of India’s coal reserves, form part of the hinterland of the port.
Connectivity:
- Rail: The broad-gauge Howrah-Visakhapatnam-Chennai east coast trunk route, which runs parallel to the east coastline, is just 6 km away from the Gopalpur port site.
- Road: Close proximity to NH5 (Kolkata-Chennai) provides excellent road connectivity to and from Gopalpur.
Source: TP
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

