Major mountain ranges like the Rockies, Alps, and Himalayas influence local weather by blocking or redirecting prevailing winds, causing orographic effects. As air rises over mountains, it cools, leading to precipitation on the windward side and creating rain shadows on the leeward side. Examples include the wet western slopes of the Andes and the arid regions east of the Rockies.
UPSC Mains General Studies Paper – 1 Mains 2021
UPSC Mains Civil Services IAS Exam Question Paper – 2021
Contents
Approach
- Start with the Briefly intro of the keywords “mountain ranges” and its characteristics.
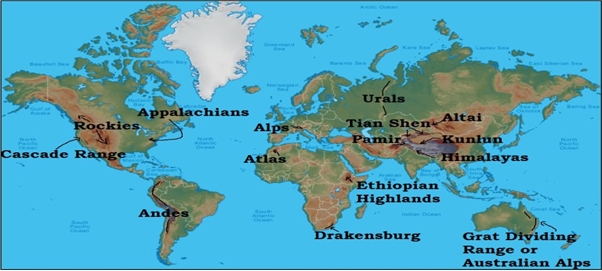
- Mentioning the alignment of mountain ranges of the world (Aspirants drawing a world map).
- Explain the ‘mountain ranges’ impact on local weather conditions, with examples.
- Conclusion accordingly.
Answer
Introduction
- Mountain ranges are majestic natural formations that span vast areas across the Earth’s surface. They are characterised by towering peaks, rugged terrain, and diverse ecosystems. These geological features are formed through tectonic activity, such as the collision of continental plates or volcanic eruptions, and have a significant impact on the environment and climate. Mountain ranges often serve as barriers that influence weather patterns, water distribution, and vegetation growth in their surrounding regions.
Body
Mention the alignment of mountain ranges of the world: Major mountain ranges span various regions around the world, each with its unique alignment. Some notable alignments mention :
1. North-South Alignment:
- Andes: The Andes act as a barrier to moisture-laden winds, resulting in a wetter climate on the eastern slopes and a drier climate on the western side. This influences the formation of the Amazon rainforest and the arid Atacama Desert.
- Rockies: The Rockies create a barrier to westward-moving moist air from the Pacific, leading to increased rainfall on the western slopes and drier conditions in regions to the east, such as the Great Plains.
2.East-West Alignment:
- Himalayas: The Himalayas block northward movement of cold air, resulting in a high-pressure system and the Indian Monsoon. Moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean bring heavy rainfall to the foothills and the Indian subcontinent.
- Alps: The Alps intercept moisture-bearing winds from the Atlantic, causing enhanced precipitation on the windward side and a rain shadow effect on the leeward side, creating drier conditions in areas like the Po Valley.

3. Circum-Pacific Alignment:
- Pacific Ring of Fire: This alignment includes the Andes, Rockies, Japan Alps, and Kamchatka Peninsula. Associated with intense volcanic and seismic activity, it can impact local weather conditions and lead to the formation of unique ecosystems.
4. Subtropical Alignment:
- Atlas Mountains: The Atlas Mountains influence weather patterns, resulting in a Mediterranean climate on the northern slopes and a more arid climate on the southern side in North Africa.
- Sierra Madre Oriental: With a similar subtropical alignment, the Sierra Madre Oriental affects local weather conditions in Mexico, contributing to the formation of distinct ecosystems and vegetation zones.
The ‘mountain ranges’ impact on local weather conditions: Mountain ranges have a significant impact on local weather conditions. Here are some key ways in which mountain ranges influence weather:
- Orographic Lifting: Air encounters a mountain range, rises, cools, and condenses, leading to cloud formation and enhanced precipitation on the windward side of the mountains.
- Rain Shadows: Mountains create areas of reduced precipitation on the leeward side as air descends, warms, and dries out, resulting in arid or semi-arid conditions.
- Temperature Gradients: Mountain slopes create temperature variations, with higher elevations experiencing cooler temperatures due to reduced atmospheric pressure and increased altitude.
- Microclimates: Mountain ranges contribute to the formation of unique microclimates within a larger region, influenced by factors like altitude, slope orientation, and topographic features.
- Precipitation Patterns: Mountains modify wind patterns, causing areas of increased rainfall on the windward side and decreased precipitation on the leeward side, leading to distinct differences in rainfall amounts over short distances.
Conclusion
- Hence, the alignment of major mountain ranges impacts local weather conditions by influencing wind patterns, precipitation distribution, and temperature variations. Mountains act as barriers to air movement, causing orographic lifting, creating rain shadows, and modifying wind and moisture patterns. These effects result in diverse climates, microclimates, and ecological systems in the regions surrounding these mountain ranges.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here