The Gondwana system of rocks in India holds a rich geological history that unfolds over millions of years, providing crucial insights into the Earth’s evolution. The origin of the Gondwana rocks dates back to the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, which occurred during the Mesozoic era, around 180 million years ago. This geological system encompasses a diverse range of sedimentary formations, including sandstones, shales, and coal beds, reflecting the dynamic environmental conditions prevailing at the time. The distribution of Gondwana rocks is widespread across the Indian subcontinent, prominently found in regions such as the Damodar Valley, the Satpura Range, and parts of central and southern India. The economic significance of the Gondwana system lies in its vast coal deposits, which have been a cornerstone of India’s energy resources. The coal-bearing strata of Gondwana rocks have fueled industrial development and played a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of the country. Additionally, the Gondwana system preserves a treasure trove of fossilized flora and fauna, offering valuable insights into prehistoric life and environmental conditions in ancient India.
Contents
Answer
The Gondwana system of rocks in India has a rich geological history, spanning from the late Precambrian to the early Cenozoic era.
Origin of Gondwana Rocks
- The Gondwana system originated as a result of the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, which began around 180 million years ago.
- They are deposits laid down in synclinal troughs on ancient plateau surfaces.
- The Indian subcontinent was part of Gondwana, and as it drifted northward, the sedimentary deposits formed the Gondwana rock system.
Distribution of Gondwana Rocks
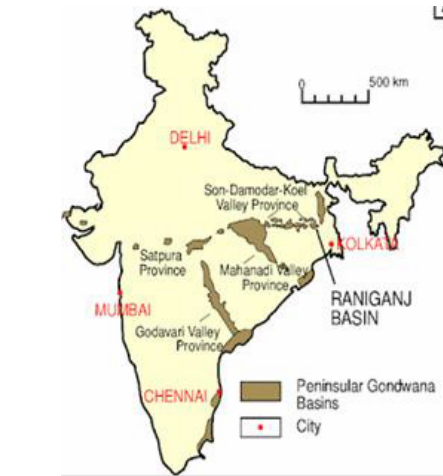

- Peninsular India
- Extensive deposits of Gondwana rocks are present in the peninsular region, covering states such as Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and parts of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Northern India
- Gondwana rocks are also found in the northern regions, including Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and parts of Uttarakhand.
- Northeastern India
- Gondwana rock formations extend into parts of Assam, Meghalaya, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Economic Significance of Gondwana Rocks
- Coal Deposits
- Gondwana rocks are renowned for hosting vast coal reserves.
- Gondwana rocks contain nearly 98 per cent of India’s coal reserves.
- However, Gondwana coal is much younger than the Carboniferous coal and hence its carbon content is low.
- E.g., The Damodar Valley Basin in Jharkhand and West Bengal is known for its extensive coal deposits, contributing significantly to India’s energy sector.
- Abundance of Minerals and Ores
- Gondwana rocks contain valuable minerals and ores, contributing to the mining industry.
- E.g., The Chhattisgarh region is rich in iron ore deposits found in Gondwana rocks, playing a crucial role in the iron and steel industry.
- Agricultural Fertility
- Gondwana rocks contribute to soil fertility as they are rich in nutrient content and also provide optimal PH to the soil thus enhancing its fertility.
- For, The Godavari and Mahanadi basins, where Gondwana rocks are prevalent, have fertile soils that support agriculture in states like Chhattisgarh and Odisha.
- Hydrocarbon Reservoirs
- Gondwana rocks can act as reservoirs for hydrocarbons due to geological processes that occurred over millions of years like Organic Material Accumulation, Burial and Diagenesis and Reservoir Formation.
- E.g., The Cambay Basin is an example of a sedimentary basin formed during the Gondwana breakup and subsequent geological processes. It is known for hydrocarbon deposits, including oil and natural gas.
Understanding the distribution and economic significance of the Gondwana system of rocks in India provides insights into the geological processes that shaped the subcontinent and highlights the importance of these in identifying potential Growth poles and growth centers.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here