The edible oil scenario in India is a complex and evolving landscape. India is one of the largest consumers of edible oils globally, with oils like palm, soybean, and mustard being staples in Indian households. However, the country relies heavily on imports to meet its growing demand, as domestic production falls short. This dependency on imports makes India vulnerable to global price fluctuations and supply disruptions. In recent years, the government has been promoting initiatives to boost domestic production and reduce reliance on imports. Still, challenges like limited agricultural land and fluctuating crop yields continue to impact the edible oil industry.

Tags:GS-3,Economy-Growth&Development- Production- Government Policies & Interventions
Contents
- 0.1 Why in the news?
- 0.2 Edible Oil Scenario in India:
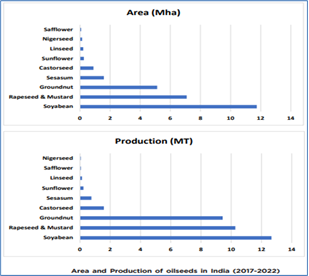
- 0.3 Area and production of oil seeds in India:
- 0.4 Report on ‘ Edible Oils Towards Atmanirbharta’:
- 0.5 Government Initiatives:
- 1 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
- 2 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Why in the news?
- The Ministry of Finance recently increased the import duty on edible oils from 0% to 20%, bringing the total effective duty, after including other components, to 27.5%.
- The Centre also announced soybean procurement at Minimum Support Price (MSP) in four states—Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Telangana.
Edible Oil Scenario in India:
- About Edible Oils:
- Edible oils are primarily vegetable oils that undergo several refining processes to remove impurities.
- These oils are generally considered healthier alternatives to animal fats due to their higher content of unsaturated fatty acids.
- Current Edible Oil Availability
- India contributes 5-6% to the global oilseeds production, with 41.35 million tons (MT) of nine cultivated oilseeds produced in 2022-23.
- Exports of oil meals, oilseeds, and minor oils amounted to 3.46 MT in FY 2022-23, valued at ₹14,609 crores.
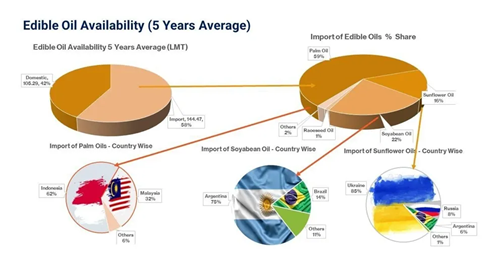
- India is the world’s second-largest consumer and the top importer of vegetable oil, meeting 55-60% of its demand through imports due to a production shortfall.
- Palm oil accounts for 62% of edible oil imports, mainly from Indonesia and Malaysia.
- Soybean oil (22%) is sourced from Argentina and Brazil, and sunflower oil (15%) comes from Ukraine and Russia.
- Overall scenario of edible oil availability in India:
Area and production of oil seeds in India:
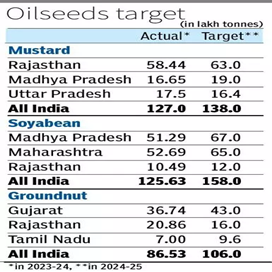
Report on ‘ Edible Oils Towards Atmanirbharta’:
- About the Report
- Released by NITI Aayog, this report examines the edible oil sector’s current state and potential for self-sufficiency.
- Key Highlights:
- Per capita edible oil consumption has risen to 19.7 kg/year.
- Despite increasing demand, domestic production only meets 40-45% of the total requirement, leading India to import 16.5 MT of edible oils in 2022-23.
- Roadmap for Self-Sufficiency:
- Supply growth projections: India’s edible oil supply is projected to reach 16 MT by 2030 and 26.7 MT by 2047 under a Business-As-Usual (BAU) scenario.
- Strategic Interventions:
- Crop retention and diversification.
- Horizontal expansion: Bringing more land under oilseed cultivation.
- Vertical expansion: Enhancing yields through better seeds, farming practices, and technology.
- Dynamic trade policies for balanced growth.
- Expanding the scope of the National Mission on Edible Oils to support self-reliance.
Government Initiatives:
- National Mission on Edible Oils-Oil Palm:
- Launched to increase domestic oil production, focusing on northeast regions and Andaman & Nicobar Islands, with a goal of expanding 6.5 lakh hectares for palm oil by 2025-26.
- Data Management:
- The Directorate of Sugar & Vegetable Oils has created a web-based platform (evegoils.nic.in) for better data management and tracking of oil production.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The quantity of imported edible oils is more than the domestic production of edible oils in the last five years.
- The Government does not impose any customs duty on all the imported edible oils as a special case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q2. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: C
Q3. Bollgard I and Bollgard II technologies are mentioned in the context of (2021)
- clonal propagation of crop plants
- developing genetically modified crop plants
- production of plant growth substances
- production of biofertilizers
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q:1 How can biotechnology help to improve the living standards of farmers? (2019)
Source: ET
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

