
India, a diverse and vibrant nation, is a tapestry woven with myriad cultural threads, each contributing to the rich and intricate fabric of its heritage. The cultural landscape of India is not homogenous but rather a mosaic of distinct regions, each characterized by unique traditions, customs, and artistic expressions. These cultural regions are demarcated by geographical, historical, and sociocultural factors, giving rise to a fascinating tapestry of diversity. From the northern Himalayan foothills to the southern coastal plains, and the arid deserts of the west to the fertile Gangetic plains in the east, India’s cultural regions showcase a kaleidoscope of customs, languages, cuisines, and artistic forms that reflect the depth and complexity of its cultural heritage. In this exploration, we delve into the cultural attributes that define and distinguish various regions of India, unraveling the captivating stories embedded in its traditions.
Contents
Answer
India is a multi-lingual, multi-ethnic, and multi-religious country (5 major religions, 118+ languages, 500+ dialects, 10 major dance forms, and a multitude of kitchen arts) Hence, although challenging, cultural regionalization in India can be made based on the linguistic, ethnic, and religious diversity of the country.
Cultural Regions of India:
Based on language, Religion and Culture:
There are 10 cultural regions:
- The Kashmiri – Muslim Cultural Region
- Stretches from the valley of Kashmir to southern parts of Ladakh (Kargil) divisions.
- Predominantly Muslim-dominated region
- Kashmiri language
- Presence of Hindus and Sikhs as minorities, Kashmiri speaking.
- The Ladakhi – Buddhist Cultural Region
- Dominance of Buddhism
- Ladakhi language
- Presence of Gompas and Monasteries in this region.
- Cultural centers- Leh and Dhramshala
- The Kinnauri – Dev – Bhumi Cultural Region:
- Himachal and Uttarakhand called the Dev – Bhumi due to presence of many religious shrines (Kedarnath, Badrinath, Haridwar, etc.).
- Himachal region- Kinnauri is the dominant language
- Uttarakhand- Hindi is the dominant language
- The Sikh – Gurumukhi Cultural Region:
- Punjab-Chandigarh region
- Dominance of Sikhs
- Punjabi language
- Hindus as minorities
- Presence of Gurudwaras in every village and town.
- Pilgrimage Center- Golden Temple, Amritsar
- The Hindu – Hindi Cultural Region
- Bihar, Haryana, MP, Rajasthan, southern parts of Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Hindi heartland
- Dominance of the Hindu religion.
- Western UP and Urban centres- Muslims constitute a significant minority
- Sikhs and Christians also sprinkled in the urban areas like Delhi, Kanpur, Lucknow, Varanasi, Meerut, Agra, and Allahabad.
- The Mixed Cultural Region of North East India
- Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura region of mixed culture. Eg. Kuki, Maiteyi, Garo, Khasi dominance of Hindus, Christians, Muslims and Tribal religion.
- Great diversity in the languages, religions, customs, folk-dances, music, and folk medicine.
- The Bengali Cultural Region
- West Bengal and the adjacent regions of Jharkhand and Bihar.
- Dominance of Bengali language.
- Dominant Religion-Hinduism
- Muslims constitute a significant minority in isolated pockets.
- The Tribo – Hindu Cultural Region
- Chotanagpur Plateau region
- Hindu dominant religion, while Christians also significant in number
- Majority Hindi speaking region
- The Marathi Hindu Cultural Region
- Maharashtra, parts of Gujarat, Goa, adjacent regions of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
- Dominance of the Marathi language and Hindu population.
- Concentration of Muslims and Buddhists is in isolated pockets.
- The Dravido Cultural Region
- People belong to the Palaeo – Mediterranean race Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
- People belong to the Palaeo – Mediterranean race
- Dravidian language. Eg. Tamil, Malayalam, Telgu, and Kannada.
Ministry of Culture’s Cultural Regions:
To promote and preserve the cultural heritage of various regions of India, the Ministry of Culture has defined seven overlapping cultural zones as follows:

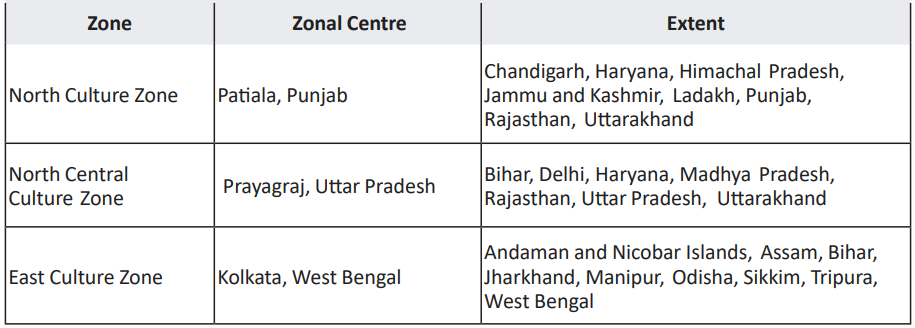
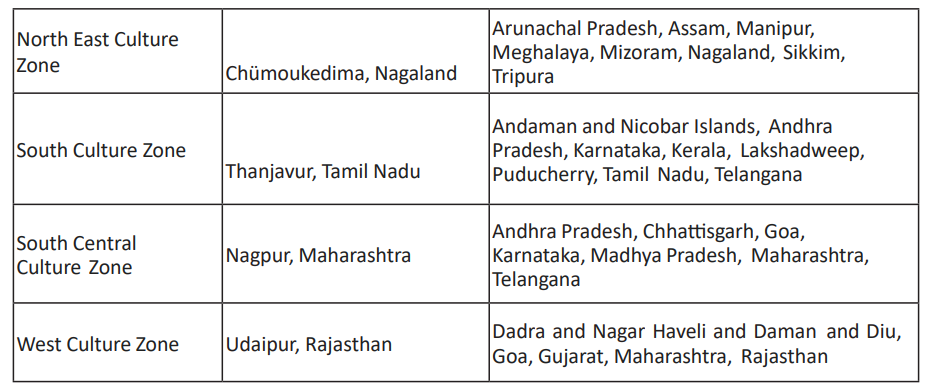
The cultural regions of India are an important aspect of the country’s identity, reflecting the influence of geography, history, and religion on its cultural practices and these cultural zones contribute to the country’s vibrant and varied heritage.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

