
India’s trade policy serves as a critical cornerstone in shaping the nation’s economic landscape, emphasizing both domestic development and international engagements. Characterized by a commitment to liberalization, globalization, and facilitation of trade, India has undertaken various reforms to enhance its competitiveness in the global market. Key features include the promotion of exports through initiatives like the ‘Make in India’ campaign, tariff rationalization, and efforts to ease business processes. However, amidst these endeavors, the bilateral trade relationship with China stands out as a significant aspect of India’s trade dynamics. The balance of trade between these two economic giants has drawn attention due to concerns about trade deficits and its impact on India’s economy. Analyzing the status of India’s balance of trade with China provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities that characterize this vital economic relationship.
Contents
Answer
India’s trade policy is formulated by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry under the foreign Trade Development and regulation act, of 1992. Since independence, it has undergone structural changes in line with the demands of the economy.
Some salient features are:
- Key approach based on 4 pillars:
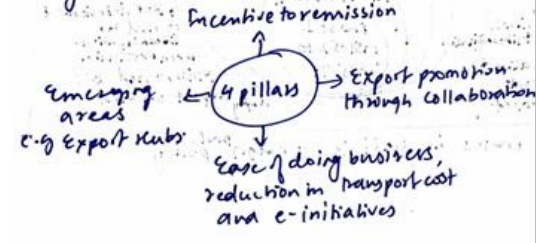
- Process re-engineering and automation:
● To facilitate ease of doing for exporters.
● FTP,2023 codifies implementation mechanisms in paperless online environments. - Town of Export Excellence (TEE):
● 4 new towns designated as TEE e.g. Faridabad, Moradabad, Mirzapur, Varanasi. - Recognition of exporters:
● 2-star and above exporters are encouraged to provide trade-related training to individuals.
Instrumental in building a skilled manpower pool to service a $5 trillion economy before
2030. - Promotion of districts as export hubs:
● to accelerate the development of a grassroots trade ecosystem via export action plans for
specific districts. - E-commerce export:
● has potential of $200-300 billion by 2030 for establishing e-commerce hubs. - Export promotion of capital goods (EPCG) scheme:
● Allows import of capital goods at zero customs duty for export production.
● Key changes are the exemption of the dairy sector from average export obligation.
● Green technology products e.g. green hydrogen included. - SCOMET policy:
Wider understanding and outreach of Special chemicals, organisms, materials, equipment, and technology. - Amnesty scheme: for reducing litigation and trust-based relationships to alleviate issues of
exporters.
India’s balance of trade with China:
Status of BoT:
India has a large trade-deficit with China which is still growing ( around $73 billion in 2021-22 expected to cross $100 billion in FY23.).
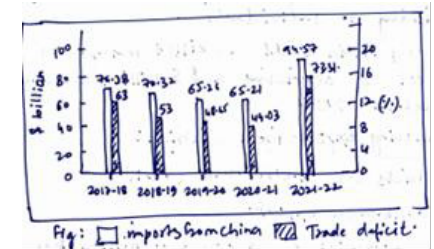
The trade deficit is due to the following factors:
- China’s manufacturing dominance:
● Accounts for 29% of global output due to cheap manufacturing and high technological
advancements. - India’s dependence on chinese goods: india dependence on china especially in: (imports in $million)
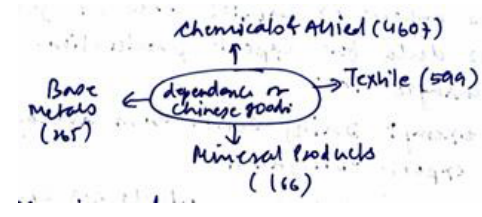
- Exchange rate difference: currency exchange rates i.e. $1=82 rupees and $1= 0.14 yuan along with non-tariff barriers make BoT wide.
Therefore to manage BoT with China, we need to diversify imports ( from Vietnam and Southeast Asia, boost exports, and review the FTA with China. Curbs on dumping are also required.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

