
Agro-climatic and land capability indicators play a pivotal role in the macro-agricultural regionalization of India, offering a systematic approach to understanding the diverse agricultural potential across different regions of the country. These indicators encompass a range of factors such as climate, soil types, topography, and water availability, providing crucial insights into the suitability of specific areas for various crops and agricultural practices. By integrating these indicators, policymakers and agricultural planners can develop comprehensive strategies tailored to the unique characteristics of each region, optimizing productivity and sustainability. This process is particularly significant in a country as diverse as India, where varying climatic and soil conditions necessitate a nuanced approach to agricultural planning. The utilization of appropriate maps further enhances the visual representation of agro-climatic zones and land capabilities, aiding in effective decision-making and resource allocation for sustainable agricultural development.
Contents
Answer
Agro-climatic and land capability indicators are essential tools for macro-agricultural regionalization in India, as they help in classifying and planning agricultural regions based on geographic concepts related to climate, soil, and terrain.
Agro-climatic and land capability indicators assist in the macro-agricultural regionalization of India in the following manner:
- Agro-climatic zones are geographical areas that are characterized by specific climate patterns and are used for agricultural planning and development. Some examples are as follows:
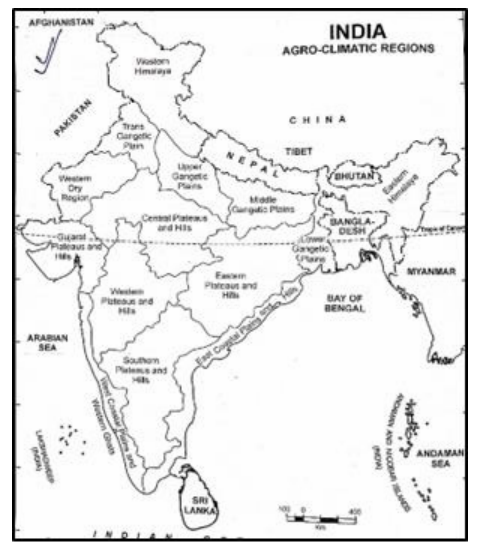
- Western Himalayan Region:
- Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Average annual temperature -20°C to 25°C and alpine regions with heavy snowfall during winter.
- Wheat, barley, apples, and saffron are commonly grown in this region due to its cold climate.
- Eastern Himalayan Region:
- Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and parts of Assam.
- Cool and temperate climate (Average annual temperature -5°C to 25°C) with high rainfall.
- Tea, cardamom, oranges, and ginger thrive in this region due to its favorable climate.
- Gangetic Plains:
- Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and parts of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Hot and humid climate (Average annual temperature -10°C to 40°C) with a distinct wet and dry season.
- Rice, wheat, sugarcane, and jute are major crops cultivated in this region due to its fertile alluvial soil.

- Western Coastal Region:
- Kerala, Karnataka, Goa, and parts of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Tropical, high humidity with an average annual temperature of 20°C to 35°C and heavy rainfall.
- Rubber, coconut, spices (like black pepper), and cashews are cultivated in this region due to its humid conditions.
- Western Desert Region:
- Rajasthan.
- Extremely arid with low rainfall and high temperatures (Average annual temperature 10°C to 50°C)
- Pearl millet (bajra) and drought-resistant crops are grown in this region due to its harsh desert climate.
- Land capability indicators consider factors like soil type, depth, and drainage.
- Soil suitability is a fundamental geographic concept that influences crop choice.
- For instance, alluvial soils in the Gangetic Plain are suitable for rice cultivation
- The red and laterite soils in regions like Odisha are suitable for crops like millets and oilseeds.
However, cropping patterns in India often do not adhere strictly to the traditional agro-climatic regions. Loss of Biodiversity, Market Price Volatility, Soil Degradation, and Water Stress are some of the problems that have surfaced due to this. National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA), Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY), Soil Health Card Scheme, and Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) are steps in the right direction.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

