India is focusing on natural farming, which uses traditional techniques and organic materials to grow crops without chemical fertilizers or pesticides. This approach is seen as a way to promote sustainable agriculture, improve soil health, and produce healthier food. By focusing on natural farming, India aims to reduce the environmental impact of conventional farming, lower production costs for farmers, and ensure that the food reaching consumers is free from harmful chemicals. This shift is part of a larger effort to create a more eco-friendly and economically viable agricultural sector.

Tags: GS – 1, Geography- Agricultural Resources – Cropping Patterns
Contents
- 0.1 Context:
- 0.2 Objectives:
- 0.3 Key Components:
- 0.4 Implementation Strategy:
- 0.5 Benefits of Natural Farming:
- 0.6 Government Initiatives to Promote Natural Farming in India:
- 0.7 Union Budget 2024-25 Announcements regarding Natural Farming:
- 0.8 Way Forward:
- 1 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 2 FAQs
- 3 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context:
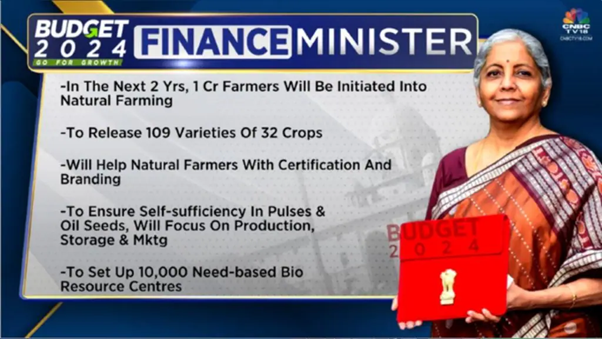
- Recently, Budget proposals for 2024-25, the Union Finance Minister announced that in the next two years, one crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming supported by certification and branding.
- The National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) is an initiative by the Government of India designed to promote chemical-free farming practices.
Objectives:
- Promote Natural Farming:
- Encourage farmers to adopt chemical-free, eco-friendly, and sustainable farming techniques.
- Reduce the use of synthetic fertilisers and pesticides, thereby decreasing the environmental footprint of agriculture.
- Improve Soil Health:
- Enhance the organic matter content of the soil through chemical-free practices.
- Restore soil fertility and structure, leading to increased agricultural productivity.
- Sustainable Agriculture:
- Promote the use of locally available natural resources.
- Reduce the cost of cultivation and improve the economic viability of farming.
- Increase Farmer Income:
- Reduce input costs and increase the profitability of farming through sustainable practices.
- Provide market linkages and support to farmers practising chemical-free farming.
Key Components:
- Training and Capacity Building:
- Conduct training programs and workshops for farmers, extension workers, and other stakeholders.
- Develop a cadre of master trainers and resource persons to support the dissemination of chemical-free farming techniques.
- Research and Development:
- Promote research on natural farming methods, including traditional knowledge and modern innovations.
- Develop and validate natural farming models suitable for different agro-climatic regions.
- Demonstration and Extension:
- Establish demonstration plots to showcase the benefits and techniques of natural farming.
- Use extension services to disseminate knowledge and practices to a wider audience.
- Policy Support:
- Formulate policies and guidelines to support natural farming initiatives.
- Provide incentives and subsidies to farmers adopting chemical-free farming practices.
Implementation Strategy:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Work in collaboration with state governments, agricultural universities, research institutions, and non-governmental organisations.
- Involve community-based organisations and farmer groups in the planning and implementation process.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Establish a robust monitoring and evaluation framework to track the progress and impact of the mission.
- Use data-driven approaches to assess the effectiveness of interventions and make necessary adjustments.
- Public Awareness and Education:
- Conduct awareness campaigns to educate the public about the benefits of chemical-free farming.
- Use various media channels to reach out to a larger audience and promote the mission’s objectives.
Benefits of Natural Farming:
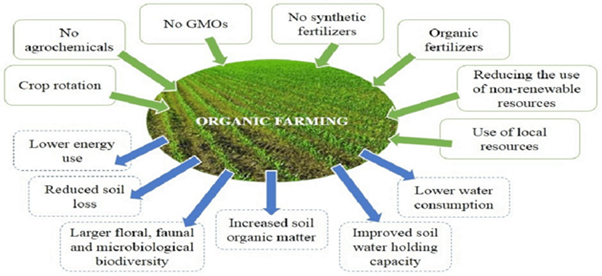
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Reduced Chemical Use: Minimise the use of synthetic fertilisers and pesticides, reducing soil and water pollution.
- Soil Health: Practices like crop rotation, use of organic compost, and green manuring improve soil fertility and structure, enhancing long-term agricultural productivity.
- Biodiversity: Encourage biodiversity by promoting the use of native seeds and supporting various species in the ecosystem.
- Health Benefits:
- Safe Food: Organic produce is free from harmful chemical residues, making it healthier for consumers.
- Reduced Health Risks for Farmers: Minimising exposure to toxic chemicals reduces health risks for farmers and agricultural workers.
- Economic Viability:
- Cost-Effective: Reduce dependence on expensive chemical inputs, lowering production costs in the long run.
- Market Demand: Growing consumer demand for organic products can open new markets and improve farmers’ income.
- Resilience to Climate Change:
- Climate-Resilient Crops: Practices like intercropping and agroforestry enhance resilience to climate change impacts, such as droughts and floods.
- Carbon Sequestration: Organic farming practices increase carbon sequestration in soils, helping mitigate climate change.
Challenges:
- Yield Reduction: The initial transition to natural farming may lead to a temporary reduction in crop yields.
- Knowledge and Training: Farmers need training and support to adopt new practices and manage the transition effectively.
- Certification: Obtaining organic certification can be challenging and expensive for small farmers.
- Supply Chains: Developing robust supply chains and ensuring market access for organic produce is crucial.
- Incentives: Government policies and subsidies currently favour conventional farming; shifting these to support natural farming is essential.
- Research and Development: Investment in R&D for organic farming methods and local crop varieties is needed.
Government Initiatives to Promote Natural Farming in India:
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY):
- Launched in 2015 as an extended component of Soil Health Management (SHM) under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS), National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- Aims to support and promote organic farming, thereby improving soil health.
- Bharatiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhati (BPKP)/ZBNF:
- A sub-scheme of PKVY launched with a total outlay of ₹4,645 crore for six years (2019-20 to 2024-25).
- Provides financial assistance of ₹12,200/ha for three years for cluster formation, capacity building, continuous hand holding by trained personnel, certification, and residue analysis.
- Aims to cover 12 lakh ha in 600 major blocks of 2000 hectares in different states.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF):
- The Union Agriculture Ministry is preparing to launch this mission to motivate farmers to adopt chemical-free farming.
- The success of NMNF requires a behavioural change in farmers, shifting from chemical-based inputs to cow-based, locally-produced inputs.
Union Budget 2024-25 Announcements regarding Natural Farming:
- Farmer Inclusion: In the next two years, one crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming, supported by certification and branding.
- Implementation: Implementation will be through scientific institutions and willing gram panchayats. Additionally, 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres will be established.
- Rationale for Shift: The need for the shift from targeting area coverage to the number of farmers arose because 30-40% of about 10 lakh farmers reverted to chemical farming after three years when they received complete financial incentives under the BPKP.
Way Forward:
- Rigorous Scientific Tests: Conduct rigorous scientific tests, especially surrounding crop yields, before nationwide implementation to allay fears of potential risk to national food security.
- Localised Implementation: Adopt natural farming at a localised level, as large-scale adoption may not be successful.
- Supplementary Foodstuffs: Use natural farming to grow supplementary foodstuffs instead of staples like wheat and rice.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 How is permaculture farming different from conventional chemical farming? (2021)
- Permaculture farming discourages monocultural practices but in conventional chemical farming, monoculture practices are predominant.
- Conventional chemical farming can cause an increase in soil salinity but the occurrence of such phenomenon is not observed in permaculture farming.
- Conventional chemical farming is easily possible in semi-arid regions but permaculture farming is not so easily possible in such regions.
- Practice of mulching is very important in permaculture farming but not necessarily so in conventional chemical farming.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 4
- 4 only
- 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q.2 Which of the following is the chief characteristic of ‘mixed farming’? (2012)
- Cultivation of both cash crops and food crops
- Cultivation of two or more crops in the same field
- Rearing of animals and cultivation of crops together
- None of the above
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What are the present challenges before crop diversification? How do emerging technologies provide an opportunity for crop diversification? (2021)
Q.2 How has India benefited from the contributions of Sir M. Visvesvaraya and Dr. M. S. Swaminathan in the fields of water engineering and agricultural science respectively? (2019)
Source: TH
FAQs
Q: What is natural farming?
- Answer: Natural farming is a method of farming that avoids using synthetic chemicals like pesticides and fertilizers. Instead, it relies on natural processes and organic materials to grow crops, promoting healthier soil and produce.
Q: Why is India focusing on natural farming?
- Answer: India is focusing on natural farming to promote sustainable agriculture, improve soil health, and produce healthier food. It also aims to reduce the environmental impact of chemical farming and support the livelihoods of farmers by lowering their costs for inputs like fertilizers and pesticides.
Q: How does natural farming benefit farmers?
- Answer: Natural farming benefits farmers by reducing their expenses on chemical inputs and improving the health of their soil, which can lead to better yields over time. It also opens up new markets for organic produce, which can often be sold at higher prices.
Q: What are some practices involved in natural farming?
- Answer: Practices in natural farming include using compost and manure as fertilizers, employing crop rotation and intercropping to maintain soil health, and using natural pest control methods like neem oil or introducing beneficial insects. Mulching and no-till farming are also common techniques.
Q: How can consumers benefit from natural farming?
- Answer: Consumers benefit from natural farming by having access to healthier, chemical-free food. Natural farming practices can lead to more nutritious and tastier produce, and buying these products supports sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

