
Welcome to our monthly current affairs update for September 2023. In this ever-changing world, staying informed about the latest events, trends, and developments is crucial. This month, we’ll take you on a journey through the most significant and noteworthy happenings across the globe. From politics to technology, from culture to the environment, we’ll cover it all. Join us as we explore the stories shaping our world and the issues that demand our attention. Our goal is to provide you with a concise and insightful overview of the events that are shaping our times, enabling you to engage in informed conversations and make well-informed decisions. So, without further ado, let’s dive into the whirlwind of current affairs for this month.
Contents
- 1 India’s GDP measurement and its limitations
- 2 JP Morgan global bond index
- 3 India’s supply Chain Opportunities
- 3.1 In News:
- 3.2 About India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
- 3.3 What are Supply Chains?
- 3.4 Reasons for shifting of global supply chains moving away from China:
- 3.5 India as an attractive supply chain hub:
- 3.6 Strategies to promote regional supply chains in South Asian:
- 3.7 Way Forward:
- 4 2023 World Trade Report: Re-globalization
- 5 Vidya Samiksha Kendras
- 6 Self-Regulatory Organisation (SRO) for fintech entities
- 7 Hallmarking in India
- 8 World food price index
- 9 India Progress in Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) – World Bank
- 9.1 In News:
- 9.2 About
- 9.3 DPIs serve as the conduits for the seamless movement of three critical components:
- 9.4 Steps taken by the government in shaping the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) landscape:
- 9.4.1 Government to Person (G2P) Payments (World’s largest digital G2P):
- 9.4.2 UPI:
- 9.4.3 DPIs’ Potential Added Value for the Private Sector:
- 9.4.4 Lower Cost of Compliance for Banks for KYC
- 9.4.5 Cross-Border Payments:
- 9.4.6 Account Aggregator (AA) Framework:
- 9.4.7 Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA):
- 10 New UPI features
- 11 Financial inclusion to reduce inequality and fasten growth
- 12 UPI QR Code-Central Bank Digital Currency interoperability
- 13 Malaviya Mission – Teachers Training Programme
- 14 Vizag International Cruise Terminal
- 15 Multi-Purpose Seaweed Park (Tamil Nadu)
- 16 Omission of disability-related questions from NFHS-6
- 17 Third Rail of Kolkata Metro Railway
- 18 Agricultural Cess
- 19 Curbs on rice exports
- 20 AYUSHMAN BHAV CAMPAIGN
- 21 PM-WANI (Prime Minister Wi-Fi Access Network Interface)-India’s Digital Landscape
- 22 PM-WANI Ecosystem:
- 23 Old Pension Scheme (OPS): Red Flag by RBI
- 24 SHREYAS scheme
- 25 Kisan Rin Portal
- 26 Data-driven innovations in agriculture
- 27 ‘Bima Sugam’ online platform
- 28 Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan
- 29 Indian Standards on Biofuel to Aid GBA’s Clean Energy Goals
- 30 National Policy on Research & Development and Innovation in the Pharma-MedTech Sector
- 31 Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) scheme
- 32 Social bonds
- 33 FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – September 2023
- 34 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
India’s GDP measurement and its limitations
In News:
Recently, a number of experts have drawn attention to a disparity in India’s GDP numbers that masks underlying problems including growing inequality.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- GDP is the gross valuation of all the goods and services generated within a country’s borders for a specific period, generally one financial year.
- The GDP of a nation may be utilized to measure its growth and economic advancement.
- India’s GDP is calculated by the Central Statistics Office (CSO), which is part of the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI).
Types of GDP:
Real GDP:
- Real GDP is an economic metric that is used to describe the economic output of a country within a specific year. It reflects the value of all goods and services produced while factoring inflation into its calculation. At present, the base year for calculating India’s Real GDP is 2011-12.
Nominal GDP:
- Nominal gross domestic product (GDP) is GDP given in current prices, without adjustment for inflation.
- Nominal GDP is seen by the government as a more realistic indication of economic growth.
Calculation of GDP:
Expenditure Method:
- This method considers the total expenditure on goods and services made by every individual inside a single economy.
- GDP = Consumption Expenditure (C) + Investment Expenditure (I) + Government Spending (G) + Net Export (Nx)
Income Method:
- This method takes account of the gross revenue generated inside a nation’s borders by different production factors, such as labor and capital.
- GDP calculated based on this approach is known as GDI or Gross Domestic Income.
- GDP = Wage + Rent + Interest + Profit
Output Method:
- This approach is used to determine the market value of all the services and products produced within a country.
- This method aids in removing any discrepancy in GDP measurement brought on by fluctuations in pricing levels.
Limitations Of GDP:
- GDP excludes non-market activities including domestic, volunteer, and other participations that have a beneficial effect on productivity. Additionally, goods produced for personal use are not included.
- GDP does not reflect the unequal distribution of income as seen in the case of India.
- The Standard of Living cannot be estimated by GDP, India has a high GDP but the living standards is relatively low in India.
- The Environmental Impact of growth and social well-being are not explained by GDP.
Concerns with the current calculation of GDP:
- The country’s GDP is presently computed with the base year of 2011-12 which is now more than 10 years old. Under normal circumstances, the base should have been revised after five years in 2016-17, with the readiness for another revision for 2021-22.
- GDP estimates based on an outdated base would not adequately capture new activities being undertaken in the economy like large investments in infrastructure, large inflow of foreign investment, value addition due to diversification, adoption of efficient technologies, and increased capacity.
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has not come out with the results of various surveys like the consumer expenditure survey and the annual survey on unincorporated enterprises which are crucial for the base revision exercise.
- There is a need for the introduction of Supply Use Tables (SUTs) which are critical for the validation of national accounts statistics. This would also take care of confusion faced by some of the followers of national account statistics in understanding the “discrepancies” brought out in the estimates as a balancing term on the expenditure side of GDP.
Way Forward:
- MoSPI should initiate the process by constituting an advisory committee on National Accounts Statistics with professional experts from academia, industry and civil society and also set up working groups for the revision of the base year.
- A decision on the new base year should be taken at the highest level after due consideration of data availability and an assessment of whether the year has been normal or not.
- Steps should also be taken to change the base for all relevant price and production indices.
JP Morgan global bond index
In News:
Recently, JP Morgan Chase & Co. has announced the inclusion of Indian government bonds into its emerging markets bond index, effective from June 2024, which will likely to attract 25 billion dollars foreign investments.
About:
- The GBI-EM (Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets) is a global bond index maintained by JP Morgan, and it plays a crucial role in shaping international capital flows.
- The JP Morgan GBI-EM is a widely followed and influential benchmark index that tracks the performance of local-currency-denominated Sovereign Bonds issued by emerging market countries.
- It is designed to provide investors with a representative measure of the fixed income market within emerging market economies.
- It Includes government bonds issued by various emerging market countries.
- These bonds are denominated in various currencies, including the US dollar and local currencies of the respective countries.
- Criteria for inclusion:
- Bonds included in the index must meet certain criteria set by JP Morgan, including minimum outstanding issue size, liquidity, and credit quality standards.
- The composition may change over time based on eligibility criteria.
Significance of Inclusion:
- India will reach a maximum weight of 10 per cent in the GBI-EM Global Diversified Index (GBI-EM GD) as part of the inclusion.
- Analysts estimate that the inclusion could result in nearly $26 billion in passive inflows, with the potential for additional active flows of around $10 billion, bringing the total inflows to approximately $40 billion over the next one and a half years.
India’s supply Chain Opportunities
In News:
Amidst the efforts to cut dependence on China-centric global supply chains, the G20 announcement on the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to make India an Asian hub in global supply chains.
About India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
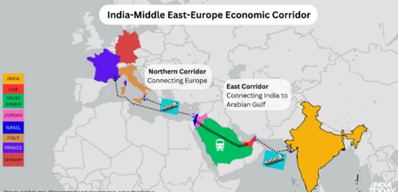
- The launch of IMEC was announced by the Indian PM at the G20 leader’s summit. The project includes India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, European Union, France, Italy, Germany and the US.
- The rail and shipping corridor is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII), a collaborative effort by G7 nations to fund infrastructure projects in developing nations. PGII is considered to be the bloc’s counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- The corridor will include a rail link as well as an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline and a high-speed data cable to enable greater trade among the involved countries.
What are Supply Chains?
- Supply chains, also known as global production networks or global value chains, refer to the geographical location of various stages of production such as design, production, assembly, marketing, and service activities in a cost-effective manner.
- The shift in industrial production from local and regional supply to global supply took place gradually over the last 100 years. Global supply chains have been the leading model of industrial production since the 1980s
Reasons for shifting of global supply chains moving away from China:
- Declining preference for China: Even before Covid-19 pandemic, Western firms had begun to reduce their reliance on China, and its popularity as a sourcing market was diminishing.
- Shift to cost-effective locations: Some production stages in Chinese supply chains, particularly the labor-intensive ones, are moving to lower-cost locations due to rising wages and supply chain bottlenecks within China, and investor concerns about tighter regulation of foreign firms.
- Risks of concentration of Supply chains in China: The global risks of supply chains concentrated in mainland China and Hong Kong together account for 20% of world exports of intermediate goods.
- Geopolitical relations of China: Internal risks and the country’s trade war with the US, are forcing multinational companies to rethink their global sourcing strategies.
- Considerations of profitability are influencing a trend of relocating production either to friendly countries or back to the US despite high costs of shifting a supply chain.
India as an attractive supply chain hub:
- Emerging Manufacturing Hubs: India can become a complementary Asian manufacturing hub to China by reaping gains from foreign technology transfers and creating value-adding jobs.
- Mature sectors: Manufacturing sectors in India such as automotives, pharmaceuticals, and electronics assembly are already mature sectors, and likely to emerge as winners in this race.
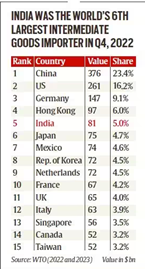
- Geopolitical and economic factors: WTO lists India as the fifth largest importer of intermediate goods in 2022 Q4, suggesting that geopolitical and economic stability will attract foreign investors.
- New Trade Policy: Trade policy has placed renewed emphasis on preferential trade through a flurry of bilateral deals with trading partners.
- India’s Free Trade Agreements (FTA) with several countries such as UAE-India CEPA, early harvest for the Australia-India FTA. These new deals reflect plans for deep economic integration.
Strategies to promote regional supply chains in South Asian:
- Upscaling the Make in India Programme into a Make in South Asia Programme: India can provide fiscal incentives to Indian manufacturers to expand into Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, which are in apparel supply chains.
- Conclusion of comprehensive bilateral FTA with Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to support regional rules-based trade and investment.
Way Forward:
- Promotion of export-oriented FDI: Maintaining an open-door policy toward FDI in manufacturing and facilitating investment at a high level, with competitive fiscal incentives and creation of modern SEZ as public-private partnerships.
- Local companies need smart business strategies to join global supply chains as compared to big companies who have advantages due to the larger scale of production and access to foreign technology, and ability to spend more on marketing.
- Cautious approach towards adopting China’s interventionist styles as there is a significant risk of government failure and cronyism
- Better targeting of multinationals in new industrial activities in which there may be a potential comparative advantage and better coordination between the central and state governments.
- Upstream investment in tertiary-level education in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
2023 World Trade Report: Re-globalization
In News:
Recently, the World Trade Organization (WTO) published its World Trade Report 2023 which emphasizes the role of International Trade in building a more secure, inclusive, and sustainable world.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- The report promotes “re-globalization,” which would include extending trade integration to additional economies, individuals, and problems.
- It places a focus on political objectives outside trade efficiency, such as world peace, security, alleviating poverty, and sustainability.
- The paper discusses the change in the globalization narrative.
- The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of resilient supply chains.
- Global trade trends have been influenced by geopolitical tensions such as the crisis in Ukraine, and the emergence of China.
- Geopolitical boundaries are progressively being followed in trade. Trade flows are increasing more quickly inside fictitious geopolitical “blocs” than they are between them, pointing to a move towards friend-shoring.
- Despite challenges, bilateral trade between China and the United States reached record highs.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, international supply networks were crucial in addressing supply shortages.
- Millions of people have been rescued from poverty via trade integration. Trade may promote sustainability by making green technology more accessible.
Re-Globalization:
- Re-globalization is a theory that promotes increasing and bolstering global economic and trade interconnectedness with an emphasis on making it more equitable, secure, and sustainable.
- It emphasises the requirement for more international collaboration and trade integration in order to handle today’s global concerns, such as geopolitical conflicts, economic inequality, and climate change.
- Benefits:
- It may spur economic growth and lower the rate of poverty, as was the case in India from 1994 to 2005.
- It can help reduce poverty by enhancing economic possibilities and income distribution, as seen by the roughly 1.5-point drop in the headcount poverty rate.
- International cooperation on environmental issues can be facilitated by re-globalization.
- As seen in India between 1990 and 2010, resource reallocation from inefficient to efficient enterprises can result in a substantial reduction in emission intensity.
Role of WTO in encouraging Re-Globalization:
- By enforcing trade regulations and agreements among member nations, WTO can support multilateral trading laws.
- Addressing Global Challenges by Promoting Policies to Reduce Poverty and Inequality Through Trade and Facilitating Discussions on Trade’s Role in Peace and Security.
- Increasing Economic Security by Stressing the Value of Crisis-Resilient Supply Chains.
- Implementing agreements like the Fisheries Subsidies Agreement and the Trade Facilitation Agreement will facilitate trade. Reducing trade costs for middle and low-income nations is the key to addressing trade cost disparities.
Vidya Samiksha Kendras
In News:
Under the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), the Ministry of Education is pushing States to open Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs).
About
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra (VSKs) is a significant initiative aimed at creating a comprehensive data repository that will encompass information from all schemes administered by the Ministry of Education (MoE) in India.
- These centers will serve as control rooms to collect and manage data, enabling the tracking of key performance indicators and the analysis of data through the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
The repository will include regularly updated data from various educational programs and initiatives, including:
- PM-POSHAN Mid-day Meal Programs: Information related to the implementation and impact of the mid-day meal programs aimed at providing nutritious meals to schoolchildren.
- Teacher Training Data: Data regarding teacher training activities conducted through the National Initiative for School Heads’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement portal.
- Textbook Content: Content related to textbooks and educational materials available through the Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing.
- School Dropout and Attendance Data: Data on school attendance and dropout rates, managed under the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE+).
- Students Learning Outcomes: Information on students’ learning outcomes, typically assessed through initiatives like the National Achievement Survey.
- Performance Grading Index: This index evaluates the performance of the school education system at the state and union territory (U.T.) level.
Funding:
- The central government has allocated funds ranging from 2 to 5 crore rupees to each state for the adoption and establishment of Vidya Samiksha Kendras.
Significance:
- Mapping School Locations with Population: VSKs will facilitate the mapping of school locations with population distribution, allowing for the assessment of the Gross Access Ratio. This can help identify areas with a shortage of educational facilities and guide the establishment of new schools where needed.
- Planning for Industry Clusters: By analyzing data from VSKs, policymakers can gain insights into the skill requirements of specific regions or industry clusters. This information can be instrumental in tailoring educational and skill development programs to meet local demands.
- Higher Education Planning: VSKs can aid in the planning of higher educational institutions based on current and future educational needs and scenarios. This can lead to more strategic and efficient resource allocation in the higher education sector.
Self-Regulatory Organisation (SRO) for fintech entities
In News:
Recently, Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor Shaktikanta Das has asked fintech entities to form a Self-Regulatory Organisation (SRO).
About:
- Fintech, short for “financial technology,” refers to the innovative use of technology to deliver a wide range of financial services and products.
- Fintech companies leverage cutting-edge technology, including software, applications, and digital platforms, to create more efficient, accessible, and user-friendly solutions in the financial industry.
- They often operate in areas such as digital payments, lending, investing, insurance, and wealth management.
- Some examples include mobile banking, peer-to-peer payment services (e.g., Gpay, PhonePe), automated portfolio managers (e.g., Fintoo, Motilal Oswal), or trading platforms (e.g., Zerodha, Groww).
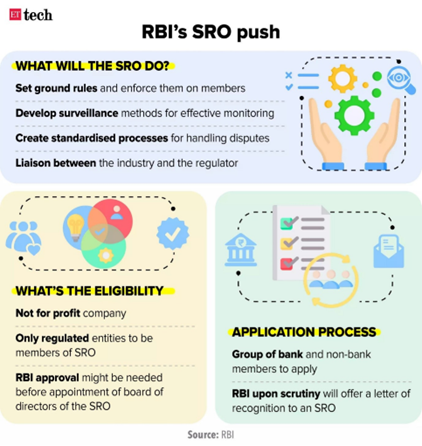
Self-Regulatory Organisation (SRO)
- Self-Regulatory Organisation (SRO) is a non-governmental organization that sets and enforces industry rules to protect customers, and promote ethics, equality, and professionalism.
- Framing of Rules: SROs typically collaborate with all stakeholders in framing rules and regulations.
- Their self-regulatory processes are administered through impartial mechanisms such that members operate in a disciplined environment and accept penal actions by the SRO.
- SRO regulations complement existing laws and regulations.
- Recognition: Reserve Bank of India will be authority of issuing letters of recognition.
Functions of SROs:
- Establishing codes of conduct: To foster transparency, fair competition, and consumer protection.
- Communication Channel: Serve as a link between members and regulatory bodies like the RBI.
- Establishing Standards: Set industry benchmarks and encourage professional conduct.
- Training and Awareness: Provide member training and awareness programs.
- Grievance Redressal: Establish a uniform grievance resolution framework.
- Others: SRO is expected to address concerns such as to protect workers, customers or other participants in the ecosystem.
Advantages of SROs
- SROs are experts in their industries, providing valuable knowledge and insights to their members.
- They enforce ethical standards among their members, fostering trust in the industry.
- SROs act as watchdogs, preventing unprofessional practices.
Hallmarking in India
In News:
The third phase of the mandatory hallmarking vide Hallmarking of Gold Jewellery and Gold Artefacts (Third Amendment) Order, 2023 comes into force from September 8, 2023.
About:

- It will include an additional 55 districts, making the total number of districts covered under mandatory hallmarking as 343.
Hallmarking
- Hallmarking is like a quality stamp for jewellery and precious metal items.
- Hallmarks are thus official marks used in many countries as a guarantee of the purity or fineness of precious metal articles.
- The principle objectives of the Hallmarking Scheme:
- to protect the public against adulteration
- to obligate manufacturers to maintain legal standards of fineness.
Hallmarking in India:
- At present two precious metals namely gold and silver have been brought under the purview of Hallmarking.
- Mandatory hallmarking order is applicable on 14, 18 and 22 carats of gold jewellery/artefacts only.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) assigns a unique HUID (Hallmarking Unique ID) number to all hallmarked items.
- HUID is a six-digit alphanumeric code.
- It is given to every piece of jewellery at the time of hallmarking and is unique for each piece.
- The Government has made it mandatory the introduction of a HUID number in every piece of jewellery.
- Consumers can verify the authenticity of hallmarked items using the ‘verify HUID’ feature in the BIS Care app.
- Applicable since: It is applicable for gold since 2000 and for silver since 2005.
World food price index
In News:
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reported that the world food price index fell to a new two-year low recently.
About:
- The FAO Food Price Index (FFPI) is a measure of the monthly change in international prices of a basket of food commodities.
- It consists of the average of five commodity group price indices – cereals, oilseeds, dairy products, meat and sugar, weighted by the average export shares of each of the groups over 2014-2016.
- Recent decline reversed a previous month’s rebound, with most food commodities experiencing decreases, although rice and sugar prices.
| Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) |
| It is a specialized agency established by the United Nations in 1945 that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. It is headquartered in Rome, Italy. It strives to provide information and support sustainable agriculture through legislation and national strategies, with a goal of alleviating hunger. It works to achieve food security for all and make sure that people have regular access to enough high-quality food to lead active, healthy lives. |
India Progress in Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) – World Bank
In News:
Recently, the World Bank has lauded the transformative impact of DPIs in India over the past decade.
About
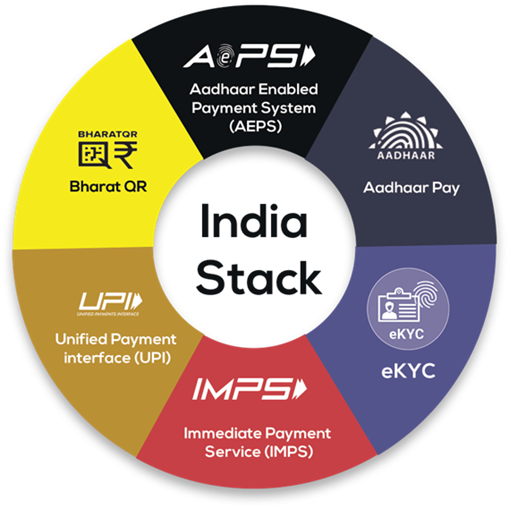
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) encompasses fundamental building blocks and platforms, such as digital identification, payment infrastructure, and data exchange solutions. These elements play a pivotal role in facilitating a country’s ability to provide essential services to its citizens, ultimately fostering empowerment and an enhanced quality of life through digital inclusion.
DPIs serve as the conduits for the seamless movement of three critical components:
- First, they enable the smooth flow of individuals through a robust digital identification system.
- Second, they facilitate the swift transfer of financial resources via a real-time, high-speed payment system.
- Third, they govern the secure and consent-driven exchange of personal information, thereby unlocking the full potential of DPIs and granting citizens genuine control over their data.
Steps taken by the government in shaping the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) landscape:
- Financial Inclusion: The World Bank document notes that India has achieved in just 6 years what would have taken about five decades.
- JAM Trinity has propelled the financial inclusion rate from 25% in 2008 to over 80% of adults in the last 6 years, a journey shortened by up to 47 years thanks to DPIs.
- Since its launch, the number of PMJDY accounts opened tripled from 147.2 million in March 2015 to 462 million by June 2022; women own 56 percent of these accounts, more than 260 million.
- The Jan Dhan Plus program encourages low-income women to save, resulting in over 12 million women customers (as of April 2023) and a 50% increase in average balances in just five months, as against the entire portfolio in the same time period.
Government to Person (G2P) Payments (World’s largest digital G2P):
- This approach has supported transfers amounting to about $361 billion directly to beneficiaries from 53 central government ministries through 312 key schemes.
- As of March 2022, this had resulted in a total savings of $33 billion, equivalent to nearly 1.14 percent of GDP.
UPI:
- More than 9.41 billion transactions valuing about Rs 14.89 trillion were transacted in May 2023 alone. For the fiscal year 2022–23, the total value of UPI transactions was nearly 50 percent of India’s nominal GDP.
DPIs’ Potential Added Value for the Private Sector:
- The DPI in India has also enhanced efficiency for private organizations through reductions in the complexity, cost, and time taken for business operations in India.
- NBFCs have been enabled 8% higher conversion rate in SME lending, a 65% savings in depreciation costs and 66% reduction in costs related to fraud detection.
- According to industry estimates, banks’ costs of onboarding customers in India decreased from $23 to $0.1 with the use of DPI.
Lower Cost of Compliance for Banks for KYC
- India Stack has digitized and simplified KYC procedures, lowering costs; banks that use e-KYC lowered their cost of compliance from $0.12 to $0.06. The decrease in costs made lower-income clients more attractive to service and generated profits to develop new products.
Cross-Border Payments:
- The UPI-PayNow interlinking between India and Singapore operationalized in February 2023, aligns with G20’s financial inclusion priorities and facilitates faster, cheaper, and more transparent cross-border payments.
Account Aggregator (AA) Framework:
- India’s Account Aggregator (AA) Framework aims to strengthen India’s data infrastructure, enabling consumers and enterprises to share their data only with their consent through an electronic consent framework. The framework is regulated by RBI.
- Total of 1.13 billion cumulative accounts are enabled for data sharing, with a 13.46 million cumulative number of consents raised in June 2023.
Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA):
- India’s DEPA grants individuals control over their data, enabling them to share it across providers. This promotes tailored product and service access without requiring new entrants to invest heavily in pre-existing client relationships, fostering innovation and competition.
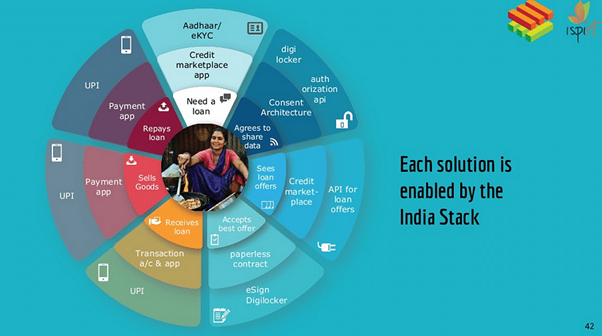
New UPI features
In News:
Recently, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has introduced new features for the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the goal of achieving 100 billion monthly transactions.
About:
- UPI is a system that powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing & merchant payments into one hood.
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) launched UPI with 21 member banks in 2016.
New UPI features:
- The latest offerings by NPCI encompass a credit line on UPI, a conversational payment mode known as ‘Hello UPI,’ BillPay Connect, UPI Tap & Pay, and UPI Lite X.
- The credit line on UPI allows users to make purchases by scanning a QR code with their UPI-linked app, choosing their bank, entering the transaction amount, and opting for the credit line as the payment option.
- ‘Hello UPI’ is a conversational payment mode that can understand spoken language and silence, convert text to numerical values, and offer text-to-speech capabilities.
- UPI Tap & Pay involves small cards with NFC chips linked to a user’s QR code and UPI ID.
- Users can obtain these cards from partner banks, personalize them, and attach them to their mobile phones for convenient tap-based payments.
- UPI Lite X enables peer-to-peer transactions without an internet connection, using near field communication (NFC) functionality on compatible phones.
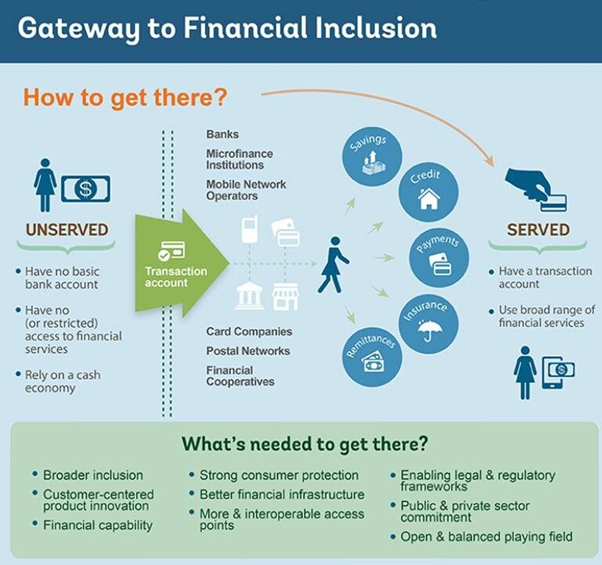
Financial inclusion to reduce inequality and fasten growth
In News:
Recently, G20 deliberations identified three policy pillars with priority themes aimed at achieving inclusion
About
Financial inclusion means that individuals and businesses have access to useful and affordable financial products and services that meet their needs – transactions, payments, savings, credit, and insurance – delivered in a responsible and sustainable way.
- Financial inclusion has been identified as an enabler for 7 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals.
- The G20 committed to advancing financial inclusion worldwide and reaffirmed its commitment to implement the G20 High-Level Principles for Digital Financial Inclusion.
- The World Bank Group considers financial inclusion a key enabler to reduce extreme poverty and boost shared prosperity.
- Financial Inclusion helps strengthen the livelihoods of those at the bottom of the economic pyramid and also contributes to global economic growth.
Challenges in Promoting Financial Inclusion
- Limited Financial Access: Approximately 24% of adults worldwide do not have access to formal financial accounts, which impedes their participation in the financial system.
- Low Savings and Borrowing Rates: Globally, only 29% of adults deposit their savings in financial institutions, and a mere 28% borrow from formal financial institutions.
- Disparities in MSME Financing: Micro-enterprises in developing countries often encounter obstacles, such as loan rejections or unfavourable loan terms, affecting 21% of them. Small and medium-sized enterprises face even greater barriers, with 30% experiencing difficulties accessing financing.
- Gender Disparities: Women face unique challenges in financial inclusion due to restrictive social norms, limited mobility, and lower financial literacy. This gender gap is particularly pronounced in low-income and developing countries, leading to disparities in bank account ownership.
- Limited Adoption of Digital Payments: In developing nations, men with bank accounts are more likely to utilize digital payment methods, creating a 6-percentage-point gap compared to women. This further excludes women from accessing digital financial services.
- Limited Access to Emergency Funds: Women in developing countries encounter more significant difficulties in accessing emergency funds, with only 50% reporting consistent access, compared to 59% of men.
UPI QR Code-Central Bank Digital Currency interoperability
In News:
Recently, RBI launched the UPI QR Code-Central Bank Digital Currency interoperability
About
- The interoperability of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the digital rupee means that all UPI Quick Response (QR) codes are now compatible with Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) apps.
- During the pilot phase of the retail digital rupee, users of the e₹-R (retail digital rupee) had to scan a specific QR code to perform transactions related to the digital rupee.
However, with the introduction of interoperability between UPI and the digital rupee, payments can now be made using a single QR code.
How does this interoperability work?
- Digital Rupee Wallet: The e₹ is stored in a digital wallet, which is linked to a customer’s existing savings bank account. This digital wallet holds the digital rupee, allowing users to make transactions and payments seamlessly.
- UPI Integration: UPI is a widely used payment system in India, directly linked to a customer’s bank account. With the interoperability of UPI and the digital rupee, users can now use their existing UPI-enabled apps to make payments related to the digital rupee.
- Single QR Code: Instead of needing a separate QR code for digital rupee transactions, users can now use a single QR code. This QR code can be scanned using CBDC apps or UPI-enabled apps, making the process more user-friendly and efficient.
Malaviya Mission – Teachers Training Programme
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister for Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship launched the Malaviya Mission – Teachers Training Programme by the University Grants Commission.
About
The Malaviya Mission is an initiative aimed at enhancing the quality of education in India, particularly focusing on the training and development of teachers in higher educational institutions (HEIs).
About Malaviya Mission:
- Teacher Training Programs: The mission is designed to provide customized training programs for teachers, with a specific focus on capacity building within higher educational institutions.
- Capacity Building: Its primary objective is to enhance the professional development of faculty members in HEIs. This initiative seeks to empower and build the capacities of approximately 15 lakh (1.5 million) teachers in higher education across India.
- Nationwide Presence: The Malaviya Mission is planned to operate through 111 centers across the country, ensuring broad coverage and a time-bound approach to teacher capacity building.
- Alignment with NEP: The mission aligns with the goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) and aims to improve the quality of teacher training, foster leadership skills among educators, and contribute to the realization of NEP objectives.
- Career Progression: It intends to map capacity-building activities under the Mission to a credit framework, enabling career progression pathways for educators, thereby recognizing and rewarding their professional development efforts.
- Incorporation of Indian Knowledge System: The program modules include aspects of the Indian Knowledge System, emphasizing the importance of indigenous knowledge in education.
About Madan Mohan Malaviya
He was a prominent Indian educationist, freedom fighter, and moderate political leader. Some key facts about him include:
- Presidency of Indian National Congress: He was elected as the president of the Indian National Congress four times during his political career.
- Round Table Conference: Malaviya attended the Round Table Conference in 1931, representing India’s interests and discussing constitutional reforms.
- Founding Hindu Mahasabha: He played a significant role in founding the Hindu Mahasabha in 1906, a socio-political organization.
- Banaras Hindu University (BHU): Malaviya is most renowned for founding Banaras Hindu University (BHU) in Varanasi in 1916. BHU was established under the B.H.U. Act, 1915, and it has since become a prominent educational institution in India.
- Vice Chancellor of BHU: He served as the Vice Chancellor of Banaras Hindu University from 1919 to 1938, contributing significantly to its development and growth.
Vizag International Cruise Terminal
In News:
The Vizag International Cruise Terminal (VICT) in Visakhapatnam will be inaugurated by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways.
About:
The enhancements at the Visakhapatnam Port Authority (VPA) include the Vizag International Cruise Terminal, which is designed to accommodate passenger vessels with a capacity of 2,000 passengers per vessel and a draft of 8.1 meters.
Key statistics and facts about India’s port sector:
- India enjoys a strategic geographical advantage with a coastline spanning 7,517 kilometers.
- Maritime transport plays a pivotal role in handling 70% of India’s trade.
- India commands a significant share, accounting for 30% of the global ship-breaking market.
- The Sagar Mala Program is a prominent initiative that prioritizes port-led development and involves a substantial investment of $123 billion.
- India permits 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the port sector through both government approval and automatic routes.
- India’s port infrastructure includes 12 major ports and approximately 200 non-major or intermediate ports.
- Among major ports, the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust stands out as the largest, while Mudra Port holds the distinction of being the largest private port in the country.
- The Jawaharlal Nehru Port is notably India’s first 100% Landlord Major Port.
Multi-Purpose Seaweed Park (Tamil Nadu)
In News:
Recently, On the third day of Sagar Parikrama Phase VIII, the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying laid the Foundation Stone for a Multi-Purpose Seaweed Park in Tamil Nadu.
About:
- In the Union Budget 2021, the finance minister announced the proposal to set up ‘Multipurpose Seaweed Park in Tamil Nadu’.
- Seaweeds are a type of marine algae, often found in coastal waters.
- It can vary in size and color and is used in various industries, including food, cosmetics, and agriculture.
- Seaweed is rich in nutrients and has diverse applications worldwide.
- The park aims to promote seaweed cultivation for employment, value-added products, and conservation.
Key Features:
- The seaweed park includes the promotion of seaweed cultivation in 136 coastal fishing villages in 6 coastal districts of Tamil Nadu namely Nagapattinam, Thanjavur, Tiruvarur, Pudukottai, Ramanathapuram and Thoothukudi.
- The Multipurpose Seaweed Park is a significant investment to promote seaweed cultivation and research, benefiting scientists, researchers, and local communities.
- The seaweed park will also provide a single window support for the entrepreneurs, processors etc. to access information on schemes, licenses/approvals required, while also providing space to set up processing centers.
| Sagar Parikrama Yatra |
| Main core objectives of the “Sagar Parikrama Yatra” are; to create awareness among fishers, fish farmers and other stakeholders on the sustainable use of marine fishery resources and protection of marine ecosystems. to disseminate information of various fisheries related schemes and programs being implemented by the government. to demonstrate solidarity with all fishers, fish farmers and stakeholders as a spirit of Aatmanirbhar Bharat. to protect the marine life and sea from pollution. |
In News:
The decision to omit disability-related questions from the sixth round of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-6) has raised concerns about the understanding and representation of disability issues in India.
About:
- Persons with disabilities make up around 2.21% of the country’s population, which is approximately 2.68 crore people according to the 2011 Census.
- The questions on disability were included for the first time in the NFHS-5 which was carried out during 2019-21.
- Based on the NFHS-5 report, it was observed that disability prevalence was only 1% for rural areas and 0.9% for urban areas.
- However, National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) estimates for the year 2018 showed 2.3% for rural areas and 2% for urban areas.
- According to the Ministry of Health, the disability related questions are not included in NFHS-6 as the disability data will not change very fast and there is no reason to collect this data every time.
- This decision has been criticized as the persons with disabilities make up around 2.21% of India’s population, totaling about 2.68 crore people according to the 2011 Census.
- The Census data does not fully represent the current disabled population due to population growth over the past decade and the limited categories of disabilities recognized in the Census.
Reasons for under representation of Persons with Disabilities:
- Limited Understanding of Disability: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation report on ‘Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan) in India — A Statistical Profile: 2021’ refers to only eight categories of disabilities.
- It fails to acknowledge and account for the 21 categories of disabilities recognised in law after the enactment of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (RPWDA).
- Invisible disability not acknowledged: Niti Aayog’s visionary blueprint, ‘Strategy for New India @ 75’, which delineates the government’s goals for 2022-23, recognises the challenges posed due to a lack of detailed data in drafting policies for persons with disabilities.
- However, the document lacks measures for those with invisible disabilities such as mental health conditions.
Issues because of under representation of Persons with Disabilities:
- Lack of Accurate Data
- Invisibility of Invisible Disabilities
- Limited Policy Insights
- Exclusion from Development Goals
- Barriers to Accessing Services
- Underreporting of Disabilities
- Stigmatization and Discrimination
- Missed Opportunities
Third Rail of Kolkata Metro Railway
In News:
Recently, Indian Railways’ Kolkata Metro has decided to replace its steel third rail with a composite aluminum third rail.
About:

- The third rail system is a means of providing electric power to a train through a conductor placed alongside the rails.
- Kolkata Metro Railway has been using steel Third Rail for the last 40 years.
- Kolkata Metro Railway has now decided to use composite Aluminium Third Rail in all the upcoming corridors being undertaken for construction along with retrofitment in existing corridors with steel Third Rail.
- This move aligns Kolkata Metro with prestigious international metro systems like those in London, Moscow, Berlin, Munich, and Istanbul, which have also made the shift from steel to aluminium third rails.
The advantages of aluminium composite third Rail over steel third Rail include:
- Reduction in resistive current loss and improved Traction voltage level.
- Reduced maintenance and life cycle cost.
- Improved acceleration with the same rolling stock.
- Enhanced efficiency of train operations.
- Significant improvements in energy efficiency and a reduction in carbon footprint.
- Improved train headway, leading to better train scheduling and operations.
Agricultural Cess
In News:
The government has recently exempted imports of LPG (liquid petroleum Gas), liquified propane, and liquified butane from the 15% Agriculture Infrastructure Development Cess (AIDC) with effect from September 1.
About:
- This exemption reverses the previous imposition of the agriculture cess (also called Agriculture infrastructure and development cess (AIDC)) on these goods in July.
- It is also imposed on Crude Palm Oil.
Cess
- Cess is a kind of special-purpose tax which is levied over and above basic tax rates.
- It is levied by the government for a specific purpose.
- For example, a cess for financing primary education – the education cess (which is imposed on all central government taxes) is to be spent only for financing primary education (SSA) and not for any other purposes.
Agriculture Infrastructure Development Cess (AIDC)
- The AIDC was introduced in the Budget 2021.
- It is a type of special-purpose tax that aims to raise funds specifically for financing the development of agriculture infrastructure in India.
- The purpose of the AIDC is to raise funds to finance spending on developing agriculture infrastructure.
Curbs on rice exports
In News:
Recently, government has levied certain restrictions on rice export to check the domestic rise in prices and to ensure domestic food security.
Rice Production in India and Export:
- India is the second-largest producer of rice in the world, after China. As per Second Advance Estimates, the estimated production of Rice for 2022-23 is 1308.37 Lakh Tonnes.
- West Bengal is the largest rice producer in India. In certain states like Tamil Nadu, some farmers anticipate delayed planting due to insufficient rainfall from the southwest monsoon.
- India is the world’s largest exporter of rice, with a 45% share.
- Shipments of non-Basmati rice recorded a growth of 7.5% in May despite the imposition of a 20% export duty on white rice and the prohibition of broken rice exports by the government in September last year.
- The export of non-Basmati rice has demonstrated a consistent upward trend over the past three years.
- According to government-provided statistics, up until August 17 of this year, total rice exports have surged by 15%. It reached 7.3 million tonnes in contrast to the 6.3 million tonnes during the same period last year.
Restrictions on Rice Export:
- In May 2022, the government banned wheat exports.
- In June 2023, restrictions on stock holdings were imposed.
- In September 2022, the export of broken rice was prohibited, and a 20% tariff was imposed on non-parboiled white grain shipments.
- In July 2023, non-basmati white rice exports were entirely prohibited, with only parboiled non-basmati and basmati rice allowed.
- Recently, a 20% duty was introduced on all parboiled non-basmati rice exports.
Benefits for the farmers:
- Increase in MSP– The government has increased the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for rice.
- Increase in price– Paddy procurement by rice millers are at a price higher than the MSP.
- Check in price rise– The prices will not decline for farmers, restrictions on exports will ensure that there is no steep climb in rice prices in the market.
Challenges of the restriction:
- Export limitations can be bypassed through inaccurate classification. White non-basmati rice has been exported using codes intended for parboiled and basmati rice.
- The $1,200 Minimum Export Price is considered too high. Only specific rice varieties achieve these prices, accounting for just around 15% of basmati exports.
- The earnings of the farmers are impacted due to the restrictions.
Way Forward:
- Proper classification of rice should be done as common and speciality rice, rather than just as Basmati and non-Basmati.
- Protect varieties of rice with Geographical Indication (GI) recognition from general market interventions.
- For Basmati rice, permit exports to continue or set a minimum export value, such as $900 per tonne, as new crop arrivals are expected to meet demand due to good quality and consistent supply.
AYUSHMAN BHAV CAMPAIGN
In News:
Recently, the President of India virtually launched the Ayushman Bhav Campaign.
About
Ayushman Bhava is an umbrella campaign that will ensure the optimum delivery of health schemes to every intended beneficiary, including those in the last mile.
Component of Ayushman Bhava Campaign
- Ayushman Apke Dwar 3.0: It aimed at the creation and distribution of Ayushman cards to all remaining eligible beneficiaries;
- Ayushman Mela: Weekly health melas will be held at the level of AB-HWCs and Community Health Centres (CHCs) and
- Ayushman Sabha: A village/ward level sabha to be held to enhance awareness about various health care schemes and services.
- Ayushman Gram Panchayat’: The campaign will eventually ensure gram/nagar panchayat to attain the status of ‘Ayushman Gram Panchayat’ or ‘Ayushman Ward’ with saturation of selected health indicators.
PM-WANI (Prime Minister Wi-Fi Access Network Interface)-India’s Digital Landscape
In News:
The (PM-WANI) scheme is set to revolutionize public Wi-Fi in India. PM-WANI can be a potential game-changer for India’s digital public infrastructure.
About Digital Public Infrastructure
- DPI is a digital network that enables countries to safely and efficiently deliver economic opportunities and social services to all residents.
- DPI allows people to open bank accounts and receive wages faster and more easily. It allows governments to support citizens more quickly and efficiently, especially during emergencies. And it enables entrepreneurs to reach customers far and wide.
- DPI can be compared to roads, which form a physical network that connects people and provides access to a huge range of goods and services.
About PM-WANI
- PM-WANI, initiated by the Department of Telecom (DoT) in December 2020, is a significant program aimed at enhancing the accessibility of public WiFi hotspots to establish a robust digital communication network across the country, especially in rural areas.
- This framework enables various entities, such as shopkeepers, tea stall owners, or Kirana store owners, to establish public Wi-Fi hotspots and offer internet services to customers.
- PM-WANI aligns with the objectives outlined in the National Digital Communications Policy, 2018 (NDCP), which focuses on building a strong digital communications infrastructure.
Importance:
- To promote ease of doing business and encourage local businesses to provide Wi-Fi, it has been decided that last-mile Public Wi-Fi providers do not need licenses, registrations, or fees to the DoT.
PM-WANI Ecosystem:

Status:
- As of November 2022, the PM-WANI central registry recorded 188 PDO aggregators, 109 app providers, and 11,50,394 public WiFi hotspots.
Benefits of PM-WANI:
- Expanding internet access in rural and remote areas.
- Offering an affordable and convenient alternative to internet access compared to expensive options like 5G.
- Encouraging innovation and competition in the internet market.
Sachet Internet:
- The introduction of sachet-sized internet packages priced at Rs 5 to 10 has been a game-changer in promoting internet usage among the masses.
- For students, in particular, these affordable plans have become a preferable alternative to purchasing other consumables like chips or soft drinks from their pocket money.
- The availability of sachet internet plans has democratized access to information and educational resources, making it easier for individuals from all walks of life to harness the power of the internet for learning and personal growth.
Challenges of PM-WANI:
- Ensuring Wi-Fi quality and user experience, involving bandwidth, user management, device compatibility, and data security.
- Addressing security concerns like data breaches, hacking, and malware.
- Potential challenges for mobile telecom companies regarding market share and revenue due to PM-WANI’s affordability.
- Expanding and maintaining PM-WANI in areas with low internet demand and high operational costs.
PM-WANI as a Game-Changer for India’s Digital Public Infrastructure:
- PM-WANI is a vital component of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), making internet access more inclusive and bridging the digital divide.
- Leveraging existing physical and social infrastructure like shops, post offices, and schools to create a widespread network of Wi-Fi hotspots.
- Utilizing existing digital infrastructure, such as Aadhaar and UPI, for secure authentication and payment of Wi-Fi services.
- Empowering citizens and communities by granting access to information, knowledge, opportunities, and services, fostering participation in the digital economy and society.
Old Pension Scheme (OPS): Red Flag by RBI
In News:
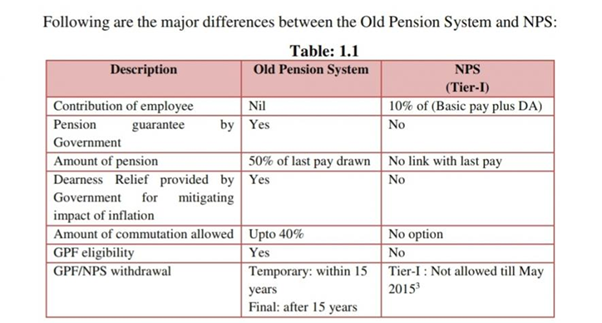
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has warned that reverting to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) from the New Pension Scheme (NPS) can be a “major step backwards” in fiscal management.
Key Points of the Observations by RBI:
- Reverting to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) might briefly reduce state expenses, but it will surpass the New Pension Scheme (NPS) contributions by the 2030s.
- This shift could inflate the pension burden by around 4.5 times compared to NPS.
- By 2060, this additional OPS burden could reach about 1% of GDP annually for states.
- This action is seen as fiscally unsustainable and goes against the prevalent pattern of adopting defined contribution plans.
New Pension Scheme (NPS):
- Proposed by the Project OASIS report became the basis for pension reforms and what was originally conceived for unorganised sector workers, was adopted by the government for its own employees.
- The NPS was for prospective employees; it was made mandatory for all new recruits joining government service from January 1, 2004.
- The defined contribution comprised 10 percent of the basic salary and dearness allowance by the employee.
- In 2019, the government increased its contribution to 14 percent of the basic salary and dearness allowance.
- Schemes under the NPS are offered by nine pension fund managers. It is sponsored by SBI, LIC, UTI, HDFC, ICICI, Kotak Mahindra, Aditya Birla, Tata, and Max.
Advantages of New Pension Scheme:
- NPS subscribers have complete freedom to allocate their savings to equities, corporate bonds or government securities, or any combination of the three.
- Risk-averse investors can simply allocate all their money to bonds or gilts in NPS, altogether skipping stocks.
- A review of Nifty50 over the past 20 years reveals that while it commonly provided losses during one-year intervals, extending one’s holding time to 10 years lowered the loss probability to zero while earning an 11–12% return.
- Over the past ten years, NPS managers have achieved a 13–14% return on stocks and a 5–9% return on bonds and government securities, compared to the EPFO’s struggle to report an 8–8.5% return on its “safe” debt portfolio.
- With NPS, an employee has greater control over his pension as he can save more or allocate more to equities.
SHREYAS scheme
In News:
According to the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment the “SHREYAS” has played a significant role in empowering students from Scheduled Castes (SC) and Other Backward Classes (OBC) in India since 2014-15.
About
The umbrella scheme of “SHREYAS” comprises 4 central sector sub-schemes namely “Top Class Education for SCs”, “Free Coaching Scheme for SCs and OBCs”, “National Overseas Scheme for SCs” and “National Fellowship for SCs”.
About the Subscheme of SHREYAS
- Free Coaching Scheme for SCs and OBCs: The objective of the Scheme is to provide coaching of good quality for economically disadvantaged Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) candidates to enable them to appear in competitive and entrance examinations
- Top-Class Education for SCs: The Scheme aims at recognizing and promoting quality education amongst students belonging to SCs, by providing full financial support. The Scheme will cover SC students pursuing studies beyond the 12th class.
- National Overseas Scheme for SCs: Under this scheme financial assistance is provided to the selected students from SCs (115 slots); De-notified, Nomadic, and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (6 slots); landless agricultural laborers and traditional artisan categories (4 slots), for pursuing masters and Ph.D. level courses abroad.
- National Fellowship for SC Students: Under the scheme, fellowship is provided to Scheduled Castes students for pursuing higher education leading to M.Phil/Ph.D. degrees in Sciences, Humanities, and Social Sciences in Indian Universities/Institutions/ Colleges recognized by University Grants Commission (UGC).
Kisan Rin Portal
In News:
Recently, the government launched the Weather Information Network Data Systems (WINDS) portal and the “Kisan Rin Portal”.
About Kisan Rin Portal:
- The Kisan Rin digital platform aims to provide a holistic perspective on farmer-related information, encompassing details about scheme utilization progress, loan disbursement specifics, and claims for interest subvention.
- Kisan Rin Portal was launched as part of the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme to revolutionize the agriculture sector.
- This initiative seeks to foster improved collaboration with financial institutions, streamlining the process of granting agricultural credit for enhanced efficiency.
Weather Information Network Data Systems (WINDS) portal:
- WINDS harnesses sophisticated weather data analytics to furnish stakeholders with actionable insights for making informed decisions pertaining to agriculture and weather-related matters.
- The portal also comprises a comprehensive manual designed to assist stakeholders in comprehending its functionalities, interpreting data, and maximizing its effective utilization.
Data-driven innovations in agriculture
In News:
Recently, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to co-create data-driven innovations in agriculture and food systems to support smallholder farmers.
About:
- The partnership’s focus is on improving climate resilience in agriculture, and it involves the dissemination of collaborative digital public goods such as DiCRA (Data in Climate Resilient Agriculture).
- DiCRA provides open access to key geospatial datasets relevant to climate-resilient agriculture and is curated by UNDP and partner organizations.
- This collaboration aims to enhance the lives and livelihoods of smallholder farmers by sharing open-source data for product development, technology transfer, and policy framing.
- This is seen as a significant opportunity to leverage data and present it as a digital public infrastructure for India’s rural farming community.
- Open data innovations like this can promote best practices, optimize agricultural investments, and enhance the resilience of smallholders, especially women, against various risks.
‘Bima Sugam’ online platform
In News:
Recently, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has formed a steering committee to act as the apex decision-making body for the creation of its ambitious ‘Bima Sugam’ online platform.
About:
Bima Sugam platform:
- Bima Sugam will be a ‘one-stop destination’ for people’s insurance-related needs. These include services such as policies, portability facilities, change of agents, settling of claims, and more.
- Buyers can directly purchase life, motor, or health policies through web aggregators, brokers, banks, and insurance agents.
- Insurance companies will be major shareholders in the platform, which will offer services via an ‘e-insurance account’ (E-IA).
- Ownership:
- Life insurance and general insurance companies will own a 47.5 per cent stake each, while brokers and agent bodies will own 2.5 per cent each.
- Benefits of the portal:
- Act as a centralised database;
- Assist the insured/buyers in porting their respective policies based on coverage and pricing;
- Give people a wide choice to pick and choose policies and view all their policies;
- Reduce commission paid to intermediaries; and,
- Pave the way for a speedy acceptance of new/sandbox products.
| IRDAI: |
| The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) (founded 1999; HQ: Hyderabad) is a statutory body (under the IRDA Act 1999). It is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance and is tasked with regulating and licensing the insurance and re-insurance industries in India. |
Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan
In News:
Recently, The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti has introduced a Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan to streamline the registration of Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) and biogas plants nationwide.
About:
- Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) is an umbrella initiative of the Government of India.
- It aims to transform organic waste, including cattle dung, agricultural residues, and biomass, into valuable resources like biogas, CBG, and organic manure.
- The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti is the coordinating department for GOBARdhan.
- This initiative supports high-value Biogas/CBG production and promotes the use of bio-slurry to improve soil health, carbon content, and water retention.
Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan:
- Anyone who operates or intends to set up a biogas/ CBG/ Bio CNG plant in India can obtain a registration number by registering in this unified registration portal.
- The registration number is required to avail benefits/ support from other Ministries/ Departments.
More information about the news:
- Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (Nodal Department for GOBARdhan) announced that over 1163 biogas plants and 426 CBG plants have successfully registered on the portal to date.
- These registered CBG/Biogas plants are eligible for assistance under the Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme of the Department of Fertilizers, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
| Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme: |
| The Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme, launched by the Department of Fertilizers aims to promote the production and adoption of organic fertilizers generated from GOBARdhan plants. It seeks to encourage sustainable/organic agricultural practices, reduce reliance on chemical fertilizers, and boost the use of bio-slurry in agriculture. |
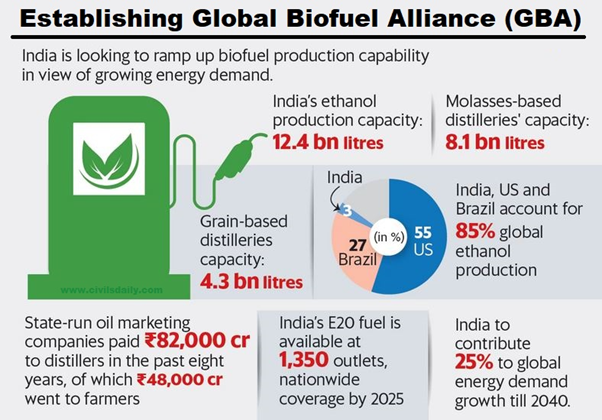
Indian Standards on Biofuel to Aid GBA’s Clean Energy Goals
In News:
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the National Standards Body of India commits to complement the green initiatives of the country through the development of relevant standards.
About
- The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has developed nine Indian standards on biofuels, including specifications for anhydrous ethanol, biodiesel, biogas, biodiesel-diesel fuel blends, hydrous ethanol, E85 fuel, E20 fuel, aviation turbine fuel containing synthesized hydrocarbons, and ethanol as a fuel for spark-ignition engine-powered vehicles.
- BIS is working on a standard for paraffinic (green) diesel derived from 2G feedstock.
National Policy on Research & Development and Innovation in the Pharma-MedTech Sector
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister of Chemicals and Fertilizers and Minister of Health & Family Welfare in India, has launched the National Policy on Research and Development and Innovation in the Pharma-MedTech Sector.
About the Policy:
- The Policy will help to create an ecosystem of skills and capacities including the academia and the private sectors, and give impetus to new talent among the youth through start-ups.
- The Scheme will focus on transforming India into a high volume, high value player in the global market of pharmaceuticals, meeting the quality, accessibility, and affordability goals.
Benefits of the Scheme:
- Development of research infrastructure– The scheme would help in building a world-class research atmosphere at NIPERs and other institutes and help in creating talent pool of qualified trained students.
- This scheme will promote industry-academia linkages by promoting collaboration between the private sector and govt institutes.
- Focus on certain priority areas which will help India’s pharma industry leapfrog and radically strengthen its position in the world market as innovation accounts for 2/3rd of global pharmaceutical opportunities.
- The scheme would help in launching of commercially viable products which will accelerate the growth of the Indian pharmaceutical sector by increased revenue and creating employment opportunities.
- The scheme would help in the development of affordable, accessible solution for primary area of health concern thus reducing healthcare burden.
Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) scheme
In News:
Recently, the government extended export benefits under the RoDTEP scheme for one more year till June 2024.
About:
- The RoDTEP scheme provides exporters with refunds for taxes, duties, and levies incurred during the manufacturing and distribution of goods, which are not reimbursed through other mechanisms at the central, state, or local levels.
- The scheme is operational since September 2021.
- It will help the exporting community to negotiate export contracts in the present international environment on better terms.
- The RoDTEP scheme replaced the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS), which concluded the previous year.
- The RoDTEP Committee operates within the Department of Revenue.
- Its primary responsibility is to review and recommend ceiling rates for different export sectors under the RoDTEP Scheme.
Social bonds
In News:
Recently, The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (Nabard) issued India’s first ‘AAA’ rated Indian Rupee-denominated Social Bonds aggregating ₹1,040.50 crores at a coupon rate of 7.63 percent.
About:
- The social bonds issued by NABARD have received ‘AAA’ ratings from CRISIL and ICRA, and they will be listed on the BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange).
Social bonds
- A social bond is a type of financial instrument issued by governments, international organizations, or corporations to raise funds for projects and initiatives that have a positive social impact on society.
- These bonds are designed to finance projects that address various social issues, such as healthcare, education, affordable housing, poverty alleviation, and environmental sustainability.
Sustainability Bond Framework:
- NABARD recently introduced a Sustainability Bond Framework, aimed at financing and refinancing green and social projects.
- Eligible social projects include affordable basic infrastructure, access to essential services, affordable housing, employment generation, food security, socioeconomic advancement, and empowerment.
FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – September 2023
Q1: What are monthly current affairs?
A1: Monthly current affairs refer to the latest and most significant events, developments, and news stories that have occurred within a particular month. These events encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, culture, and more. They are a reflection of the dynamic nature of our world and provide a snapshot of what’s happening globally or within a specific region during a given month.
Q2: Why are monthly current affairs important?
A2: Monthly current affairs are important for several reasons:
- Informed Citizenship: Staying updated with monthly current affairs is crucial for informed citizenship. It empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions, including voting in elections, advocating for causes, and engaging in meaningful discussions about societal issues.
- Professional Relevance: Professionals, such as journalists, policymakers, and business leaders, need to be aware of current affairs to make strategic decisions, create informed content, and respond to changes in their respective fields.
- Academic and Competitive Exams: Many academic institutions and competitive exams assess students’ knowledge of current affairs, making it essential for academic and career success.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding current events helps individuals appreciate and understand different cultures, societies, and global interconnections.
- Safety and Preparedness: Some current affairs, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies, can directly impact personal safety and require timely awareness and preparedness.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

