
Welcome to our monthly current affairs update for September 2023. In this ever-changing world, staying informed about the latest events, trends, and developments is crucial. This month, we’ll take you on a journey through the most significant and noteworthy happenings across the globe. From politics to technology, from culture to the environment, we’ll cover it all. Join us as we explore the stories shaping our world and the issues that demand our attention. Our goal is to provide you with a concise and insightful overview of the events that are shaping our times, enabling you to engage in informed conversations and make well-informed decisions. So, without further ado, let’s dive into the whirlwind of current affairs for this month.
Contents
- 1 Five Eyes Alliance
- 2 UNCITRAL South Asia Conference
- 3 India-Saudi Arabia Relationships
- 4 India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC)
- 5 African Union in G20
- 6 ASEAN summit
- 7 French laïcité
- 8 Artifacts to grace G-20 corridor
- 9 National Carbon Registry
- 10 Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
- 11 Operation Sajag
- 12 Three Years of Abraham Accords
- 13 FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – September 2023
- 14 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Five Eyes Alliance
In News:
The recent India-Canada standoff regarding allegations of Indian government involvement in the killing of a separatist leader in Canada has brought attention to the role of the Five Eyes Alliance.
About:
- “Five Eyes” refers to an intelligence-sharing alliance of the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, Canada and New Zealand.
- It was founded in 1941.
- Origins of the Alliance:
- The alliance traces its origins back to World War II when the UK and the US decided to share intelligence after successfully breaking German and Japanese codes.
- It began as the Britain-USA (BRUSA) agreement, later evolving into the UK-USA (UKUSA) agreement, with Canada joining in 1949 and New Zealand and Australia in 1956.
- Features:
- The Five Eyes agreement parties are “diverse societies, governed by rule of law and robust human rights and are bonded by a common language.
- These nations collaborate closely on intelligence matters, sharing information to protect their shared national interests.
UNCITRAL South Asia Conference
In News:
Recently, India hosted the inaugural United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) South Asia Conference.
United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL):
- It is the principal legal entity in the UN system that is dedicated to international trade law.
- It is a legal body with universal membership that specializes in commercial law reform worldwide.
- It is an international organization of lawyers that focuses on changing business law around the globe.
- For more than 50 years, it has worked to update and harmonise the laws governing transnational commerce.
- The main objective of UNCITRAL is to promote fairness, transparency, and efficiency in cross-border commercial transactions by developing legal frameworks and tools.
- India has been a member of UNCITRAL since its inception being one of the first 29 member states.
UNCITRAL South Asia Conference:
- The conference aimed to strengthen India’s engagement with UNCITRAL and encourage interaction between UNCITRAL, the judiciary, bureaucracy, academia, and the legal fraternity.
- It was organized jointly by the Ministry of External Affairs, UNCITRAL, and the organization’s national coordination committee for India.
- The conference covered various topics, including the digital economy, MSMEs and access to credit, insolvency, investor-state dispute settlement reform, international commercial arbitration, and mediation.
- It also discussed on alternative dispute resolution developments and how to make India a hub for arbitration.
India-Saudi Arabia Relationships
In News:
The relationship between New Delhi and Riyadh has been improving steadily. During the recent visit of Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, India is engaging with Saudi Arabia on a multitude of issues.
Background of India –Saudi relationship:
- The two countries established diplomatic relations in 1947, and since then there have been cordial and friendly relations reflecting their historical socio-cultural and economic ties.
- The visit of King Abdullah to India in January 2006 saw the signing of the Delhi Declaration, which laid the framework for upgrading ties to the level of “strategic partnership” in 2010 by the Riyadh Declaration.
- The visits of the Indian PM to Riyadh in 2016 and the conferment of Saudi’s highest civilian honor to the Indian PM indicated the mutual importance of India and Saudi Arabia for each other.
- The 2019 visit of the Crown Prince brought an investment of approximately $100 billion in India. An agreement was also signed to pave the way for Saudi Arabia to join the International Solar Alliance (ISA)
- The Indian PM’s visit to Riyadh again in October 2019 led to the signing of the Strategic Partnership Council (SPC) Agreement, which established a high-level council to steer the Indo-Saudi relationship.
Highlights of the visit of Saudi Arabia’s Crown Prince:
- The Crown Prince visited New Delhi for the G20 Leaders’ Summit, where he, along with the Indian PM and US President, announced the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor.
- The Crown Prince and Indian PM co-chaired the first meeting of the India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council.
- Eight agreements were signed between the two sides, which include upgrading their hydrocarbon energy partnership to a comprehensive energy partnership for renewable, petroleum, and strategic reserves, and creating a joint task force for $100 billion in Saudi investment.
- The possibility of trading in local currencies, and expediting negotiations for a free trade agreement between India and the Gulf Cooperation Council was also discussed.
Pillars of the India- Saudi Arabia relationship:
Economic Ties
- Trade Ties: India is Saudi Arabia’s second-largest trade partner; Saudi Arabia is India’s fourth-largest trade partner. Trade with Saudi Arabia accounted for 4.53% of India’s total trade in FY23 and bilateral trade was valued at $52.76 billion.
- Indian Companies in Saudi: Around 2,800 Indian companies are registered as joint ventures/ 100% owned entities with investments worth $2 billion in Saudi. Indian companies such as L&T, Tata, Wipro, TCS, Shapoorji Pallonji etc. have strong presence in Saudi.
- Investment in India: Saudi’s direct investments in India amounted to $3.15 billion (March 2022) with major investors being Aramco, SABIC, Zamil, e-holidays, Al Batterjee Group.
- Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF) has invested in several Indian startups such as Delhivery, FirstCry, Grofers, Ola, OYO, Paytm, and PolicyBazaar through SoftBank Vision Fund.
- Proposed Investments: A major proposed investment is the $44 billion West Coast Refinery & Petrochemicals Project in Maharashtra is being jointly built by Saudi Aramco, Abu Dhabi National Oil Company, and an Indian consortium (IOCL, HPCL, BPCL).
Energy Cooperation
- Crude and Petroleum imports: Saudi Arabia was the third largest crude and petroleum products source for India in FY23. India sourced 16.7% of India’s total crude imports in FY23 from Saudi.
- India’s LPG imports from Saudi Arabia stood at 11.2% of its total petroleum product imports, in FY 23.
Defence Partnership
- Defence Exercises: There is extensive naval cooperation between India and Saudi Arabia. There have already been 2 editions of the bilateral naval exercise, Al Mohed al Hindi.
- Defence Cooperation: There is an increasing defence cooperation, and both sides have agreed to continue working together to consider possibilities of joint development and production of defence equipment.
Diaspora in Saudi
- Diaspora as a Living bridge: The Indian community in Saudi is more than 2.4 million strong, widely respected for its contribution to the development of Saudi Arabia.
- Support to Indian diaspora: Supporting the evacuation of Indian nationals stranded in Sudan through Jeddah under Operation Kaveri, and facilitating Indian Hajj & Umrah pilgrims.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC)
In News:
Recently, on the side-lines of the G20 Summit in New Delhi, an MoU was signed between India, the US, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, the UAE, France, Germany, and Italy to establish the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC).
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC):
- It is an infrastructure development project that aims to create connectivity through rail and shipping networks, energy cables, and data links.
- It is part of the Partnership for Rail and Shipping Corridors Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII) and focuses on enhancing global trade and cooperation through critical infrastructure development.
- PGII is a collaborative effort by G7 nations to fund infrastructure projects in developing nations. It emphasizes loans over charity, benefiting both lending and receiving countries.
- It seeks to boost trade, clean energy, and economic growth while providing an alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Components of the Corridor:
- It will comprise two separate corridors, the Eastern Corridor, and the Northern Corridor. The former will connect India to the Arabian Gulf and the latter will connect the Arabian Gulf to Europe.
- It will include a rail link as well as an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline and a high-speed data cable.
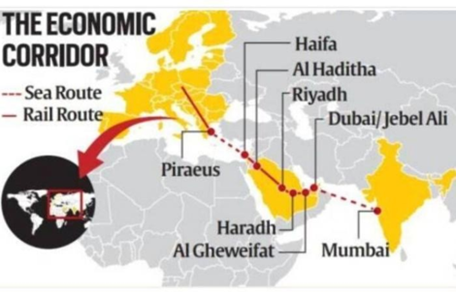
Significance of IMEE-EC Project:
- This would speed up trade between India and Europe by up to 40%.
- The plan is expected to be a possible game changer for global trade, presenting an alternative to China’s wide-ranging strategic infrastructure investments.
- Enhancing food security, regional supply chains, trade accessibility, environmental considerations, economic cohesion, job creation, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- It offers India a crucial role in global commerce, digital communication, and energy networks.
- It firmly positions India along the trade route spanning South East Asia to the Gulf, West Asia, and Europe.
Other Initiatives announced under PGII:
- Trans-African Corridor: It will connect the port of Lobito in Angola with Katanga province in Congo and the copper belt in Zambia.
- Clean Energy Projects in Indonesia: The PGII announced clean energy projects in Indonesia to support sustainable energy sources and infrastructure development.
- Investments in India’s Health Infrastructure: The US government’s International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) pledged over $15 million to invest in India’s health infrastructure, including eye clinics and women’s hygiene products.
- EU’s Global Gateway Program: The European Union (EU) committed to activating 300 billion USD in investments for critical connectivity projects, with a focus on Africa and various regions around the world.
African Union in G20
In News:
Recently, the African Union (AU) became a new permanent member of the G20 during the 18th G20 Heads of State and Government Summit in New Delhi.
G20 Group:
- The G20 or Group of 20 is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 sovereign countries, the European Union (EU), and the African Union (AU) (Added in 2023).
- It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation and sustainable development.
- It accounts for around 80% of gross world product (GWP), 75% of international trade, two-thirds of the global population, and 60% of the world’s land area.
- There is no permanent Secretariat or Headquarters of G20. 19 Countries are divided into 5 groups and the presidency rotates annually between each group.
- Troika is a working association between the current presidency, past presidency and the future presidency.
Key Highlights of G20 Summit 2023:
- The G20 leaders agreed to admit the African Union as a permanent member of the G20. It offers an opportunity to reshape global trade, finance, and investment and would provide a greater voice to the Global South within the G20.
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Governments of India, the US, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, the UAE, France, Germany and Italy to establish the India – Middle East – Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
- The World Bank prepared the G20 Global Partnership for Financial Inclusion document in which the transformative impact of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) over the past decade under the Central Government has been praised. It emphasized various initiatives like JAM Trinity, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), UPI Dominance, Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA), etc.
- G20 countries promised to work towards tripling the global renewable energy capacity by 2030. It aligns with global efforts to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- The agriculture working group during the G20 Presidency reached a historic consensus on two aspects: Deccan G20 High-level principles on Food Security and Nutrition and the Millet initiative called MAHARISHI.
- India’s G-20 presidency has laid the foundation for a coordinated and comprehensive policy and regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies.
- Prime Minister of India handed over the customary gavel of the G20 chair to Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva, who will officially take over the presidency on December 1, 2023.
African Union (AU):
- The African Union (AU) is a continental body consisting of 55 member states in Africa.
- In 1963, the Organization of African Unity (OAU) was founded to promote cooperation among African states.
- In 2002, the OAU was succeeded by the AU with a goal to accelerate economic integration of the continent.
- African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) was established in 2018 which seeks to create a single continental market for goods and services.
ASEAN summit
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister attended the 20th ASEAN-India Summit and the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Jakarta.
About:
- ASEAN was established in 1967 with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- It initially consisted of five member states: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- Over the years, it expanded to include Brunei Darussalam, Lao PDR, Cambodia, Myanmar, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN’s core principles include regional cooperation in various fields, promotion of regional peace and stability, and adherence to the principles of the United Nations Charter.
- The chairmanship of the ASEAN Summit and Ministerial Conferences has rotated annually in alphabetical order between member states.
- ASEAN Secretariat: Indonesia, Jakarta.
Highlights of 20th ASEAN-India summit:
- Theme: ‘ASEAN Matters: Epicentrum of Growth’
- KeyPoints of PM’s address:
- ASEAN is the central pillar of India’s Act East Policy.
- India supports ASEAN’s outlook on ASEAN-India centrality and Indo-Pacific.
- The progress of a free and open Indo-Pacific and elevating the voice of the Global South is in the common interest of all.
More Information:
- India is part of the ASEAN Plus Six grouping, which includes China, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, and Australia.
French laïcité
In News:
Recently, the French government announced that the practice of wearing an abaya would be banned in state-run schools
About
Laïcité, the principle of secularism in France, represents the complete separation of religious values from the public sphere, with a strong emphasis on promoting secular values such as liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Its primary objective is to encourage tolerance and assimilation while relegating religion to the private sphere. The French state plays a pivotal role in enforcing and upholding Laïcité principles.
History of French laïcité
- Emergence Post-French Revolution: Laïcité began to take shape after the French Revolution in 1789 when the revolutionary government aimed to establish a clear separation between the Church and the state. During this period, there were efforts to diminish the influence of the Catholic Church in public affairs.
- The Law of 1905: Laïcité became more concrete and institutionalized with the passage of the Law of 1905 during the Third Republic. This law officially separated religious institutions from the state and established state-run secular schools. It also ensured that the state would not fund religious organizations.
- 20th Century: Laïcité was not a prominent issue for much of the 20th century when France was relatively homogeneous in terms of religious and cultural identity. During this time, the French state upheld secularism as a core value.
- Demographic Changes in the 1950s and 1960s: Demographic shifts resulting from decolonization in the 1950s and 1960s brought significant numbers of immigrants from predominantly Muslim countries to France. This led to tensions and debates about the application of Laïcité principles in a more diverse and multicultural society.
Artifacts to grace G-20 corridor
In News:
Several objects of cultural significance will be displayed at the special Culture Corridor which will be set up at the venue of the G-20 summit in New Delhi.
About:
- A copy of the Magna Carta, United Kingdom’s famous charter of rights, a 15th century bronze statue of Belvedere Apollo from Italy, and an 18th century Fahua-lidded jar from China would be Some of the physical items on display.
- India’s contribution would be Panini’s Ashtadhyayi, the ancient text.
- Notable digital contributions include France’s Mona Lisa, Germany’s Gutenberg’s Bible, and Mexico’s statue of the deity ‘Coatlicue’.
- The Culture Corridor-G-20 Digital Museum has been conceptualised by the Ministry of Culture to represent and celebrate the shared heritage of G-20 members and invitee countries and will create a “museum in the making”.
- The Culture Corridor-G-20 Digital Museum will be unveiled at the G-20 Leaders’ Summit venue, ‘Bharat Mandapam,’.
- This project is based on India’s G20 theme Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’ and the Culture Working Group’s (CWG) hallmark campaign ‘Culture Unites All”.
More Information:
- Submissions were requested from G-20 countries and nine guest nations under five categories:
- Object of Cultural Significance (as a physical display); Iconic Cultural Masterpiece (as a digital display); Intangible Cultural Heritage (digital display); Natural Heritage (digital display); and Artefact Related to Democratic Practices (physical or digital display).
National Carbon Registry
In news:
UNDP deliberates on a transformative tool National Carbon Registry for climate action
About National Carbon Registry
- The National Carbon Registry is an innovative digital platform developed by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to enhance global climate action efforts.
- It is the result of ongoing collaboration within the Digital4Climate (D4C) Working Group, comprising UNDP, the World Bank, UNFCCC, EBRD, and others.
- It has been accredited as a Digital Public Good (DPG) as an open-source software is designed to facilitate the management of carbon credits and revolutionizing the carbon credit ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- The National Carbon Registry utilizes open-source code, allowing countries to customize it to meet their specific needs and contexts.
- Its modular structure and technical documentation enable easy adaptation, potentially reducing production costs and implementation timelines for nations.
- It is aligned with the Global Goals for sustainable development, the registry promotes integration and collaboration across different sectors and stakeholders.
- The registry adheres to national and international best practices, incorporating inputs from various countries.
- It is designed as an interoperable digital system, it seamlessly integrates with national measurement, reporting, and verification (MRV) systems.
- It also interfaces with international digital systems like UNDP’s cooperation platform and the World Bank’s Climate Action Data Trust (CAD Trust), expanding its capabilities.
Benefits:
- Digital market infrastructure is significant to amplify high-integrity and transparent carbon markets recognised by World Bank’s Climate Warehouse program.
- By offering an open-source carbon registry platform, it enables countries to elevate their climate action and ambition levels.
- National Carbon Registry can address broader issues related to nature, climate, and energy especially for countries striving to meet their climate targets and contribute to a sustainable future.
- To achieve effective climate action, developing countries require over US$6 trillion by 2030 to fund their climate goals outlined in their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- Carbon finance is instrumental in NDC implementation, and the Paris Agreement’s Article 6 provisions enable the use of market mechanisms.
- Overall, the National Carbon Registry can help fill critical gaps in climate financing and will help in accelerating global climate action and supporting the transition to a low-carbon world.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Ports extended an invitation for an Indo-Russian Workshop on Eastern Maritime Corridor in Chennai
About
- The Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC) is a proposed sea route that would connect the Indian port of Chennai with the Russian port of Vladivostok.
- This corridor is expected to reduce the transportation time between Indian and Russian ports in the Far East Region by as much as 40 percent, bringing it down from the current 40 days to 24 days.
- Currently, the trade route between Mumbai, India, and St. Petersburg, Russia, covers a distance of 8,675 nautical miles.
- EMC is projected to cover a distance of approximately 5,600 nautical miles, which is significantly shorter than the existing route via the Suez Canal.
- Once completed, the EMC is expected to facilitate the transportation of goods from India to Far East Russia in just 24 days, which is a significant improvement over the current journey duration of over 40 days.
- For India, the EMC holds the potential to offer a more efficient and shorter route to access the markets of the Far East, including countries like China and Japan. This improved connectivity can have positive implications for trade and economic relations in the region.

Operation Sajag
In News:
Recently, the coastal security drill ‘Operation Sajag’ conducted by the Indian Coast Guard along the west coast
About
- Operation Sajag was organized by the Indian Coast Guard along the western coastline and engaged all key participants within India’s coastal security framework.
- A total of 118 vessels, including those representing Customs, Marine Police, Ports, and the Indian Navy, actively participated in this exercise.
- The primary objective of this drill is to reaffirm and evaluate the effectiveness of the coastal security apparatus while concurrently raising awareness among fishermen operating at sea.
- Operation Sajag has formalized efforts related to island security and community interaction programs under the broader coastal security framework.
Three Years of Abraham Accords
In News:
The Abraham Accord between the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Israel has completed three years.
Abraham Accords:
- The Abraham Accord (2020), brokered by the USA, is a normalisation pact to establish formal diplomatic ties between the UAE and Israel.
- The name “Abraham Accords” was chosen as a sign of unity and as a reference to the historical figure of Abraham, who is said to be the ancestor of both Jews and Arabs.
- Bahrain, Sudan, and Morocco also joined the agreement, and in return Israel agreed to put a halt to its aspirations to annexe portions of the occupied West Bank.
- After Egypt (in 1979) and Jordan (1994), the UAE is the third Arab country to recognise Israel as a result of this agreement.
Significance of the Abraham Accords:
- The accord demonstrates how the Arab nations are rapidly disengaging from the Palestine issue.
- Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain will establish full diplomatic connections, which will benefit the whole region.
- The agreement restores the UAE’s reputation in the US, where its participation in the Yemen conflict has damaged it.
- Pakistan will be forced to choose between following the UAE’s lead (which would be perceived as giving up the Islamic cause of Palestine) and not doing so (because it is already at odds with the Saudis over its refusal to take up the Kashmir issue and cannot afford another unfriendly Islamic country).
- Trade between Israel and other West Asian countries increased by 74% between 2021 and 2022.
- Tourism, mostly non-existent in the past, has skyrocketed. In 2021, visits from Israel to the UAE increased by 172%.
- In a region where 65% of the population is under 30 years of age, providing the younger generation with opportunities is a key factor in preventing instability.
- The Prosperity Green & Blue agreement between Israel, the UAE, and Jordan determined that a solar field to supply 600 megawatts of electricity to Israel and a desalination plant in Israel would deliver 200 million cubic meters of water to Jordan.
- The Abraham Accord encourages collaboration and education. The UAE incorporated Holocaust education into its school curriculum as a mandatory subject, fostering coexistence and religious tolerance.
India’s Interest:
- The Abraham Accords create the right conditions for India to forge closer connections with both Arab nations and Israel.
- As a result of the Abrahamic Accords, the formation of I2U2 was witnessed. Additionally, it was referred to informally as the “West Asian Quad” and the “Indo-Abrahamic construct.”
- The coalition promotes collaboration in six sectors—food security, health, transportation, space, water, and energy.
- Collaboration between the three countries may result from Israel’s inventive qualities, UAE financial support, and India’s technological prowess. For example, Eccopia, an Israeli company with a manufacturing base in India, supported an Emirati project for a robotic solar panel.
- There are now convenient direct flights between Bahrain and Israel as well as the UAE, benefiting the expanding Indian diaspora in the Gulf.
- Indian students now have easier access to colleges, more opportunities to explore overseas education options, and greater travel convenience.
FAQs on Monthly Current Affairs – September 2023
Q1: What are monthly current affairs?
A1: Monthly current affairs refer to the latest and most significant events, developments, and news stories that have occurred within a particular month. These events encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, culture, and more. They are a reflection of the dynamic nature of our world and provide a snapshot of what’s happening globally or within a specific region during a given month.
Q2: Why are monthly current affairs important?
A2: Monthly current affairs are important for several reasons:
- Informed Citizenship: Staying updated with monthly current affairs is crucial for informed citizenship. It empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions, including voting in elections, advocating for causes, and engaging in meaningful discussions about societal issues.
- Professional Relevance: Professionals, such as journalists, policymakers, and business leaders, need to be aware of current affairs to make strategic decisions, create informed content, and respond to changes in their respective fields.
- Academic and Competitive Exams: Many academic institutions and competitive exams assess students’ knowledge of current affairs, making it essential for academic and career success.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding current events helps individuals appreciate and understand different cultures, societies, and global interconnections.
- Safety and Preparedness: Some current affairs, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies, can directly impact personal safety and require timely awareness and preparedness.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

