
In a remarkable fiscal achievement, the net direct tax collections for the fiscal year 2023-24 have surpassed their target, marking a significant milestone in India’s economic landscape. Despite challenging economic conditions, the robust performance reflects the resilience and dynamism of the country’s tax administration system. This overachievement not only underscores the efficiency of tax collection mechanisms but also suggests a potential boost in government revenue, offering promising prospects for fiscal stability and developmental initiatives.
Tags: GS Paper – 3, GS Paper – 2, – Mobilization of Resources– Government Policies & Interventions — Economics
For Prelims: Direct tax, Corporation Tax, STT, Vivad se Vishwas Scheme
For Mains: Mobilisation of Resources, Government initiatives to check tax evasion
Contents
- 1 About the tax collection:
- 2 What Is the Net of Tax?
- 3 UPSC Civil Examinations PYQ:
- 4 FAQs
- 4.1 Q: What are Net Direct Tax collections?
- 4.2 Q: How do Net Direct Tax collections contribute to government revenue?
- 4.3 Q: What does it mean when Net Direct Tax collections exceed the 2023-24 target?
- 4.4 Q: What factors could contribute to the surpassing of the 2023-24 Net Direct Tax collection target?
- 4.5 Q: How might the government utilize the surplus from exceeding the Net Direct Tax collection target?
- 5 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Context:
- India’s net direct tax collections surged impressively by 17.7% in the fiscal year 2023-24, reaching a significant milestone of ₹19.58 lakh crore.
- The provisional Direct Tax collections (net of the refunds) have exceeded the BE by 7.40% and RE by 0.67%.

About the tax collection:
- Direct Tax collection
- In the fiscal year 2023-24, India’s net direct tax collections surged to ₹19.58 lakh crore, marking a substantial growth of 17.70% compared to the previous fiscal year’s ₹16.64 lakh crore.
- Gross direct tax collections before adjusting for refunds reached ₹23.37 lakh crore, reflecting a notable 18.48% increase over the previous year’s ₹19.72 lakh crore.
- Corporate tax collection :
- The provisional gross corporate tax collection for FY 2023-24 stood at ₹11.32 lakh crore, representing a growth of 13.06% over the previous year’s ₹10 lakh crore.
- The net corporate tax collection for the same period reached ₹9.11 lakh crore, indicating a growth of 10.26% compared to the previous year’s ₹8.26 lakh crore.
- Personal income tax collection :
- In terms of personal income tax, the gross collection (including STT) for FY 2023-24 amounted to ₹12.01 lakh crore, demonstrating a substantial growth of 24.26% over the previous year’s ₹9.67 lakh crore.
- The net personal income tax collection (including STT) reached ₹10.44 lakh crore, marking a growth of 25.23% compared to the previous year’s ₹8.33 lakh crore.
- Furthermore, refunds totaling ₹3.79 lakh crore were issued in FY 2023-24, indicating a significant increase of 22.74% over the refunds of ₹3.09 lakh crore issued in FY 2022-23.
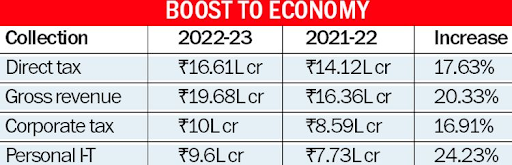
Direct Tax Collections Trends in this Fiscal:
- In this fiscal, there was a notable increase in Personal Income Taxes (PIT), which constituted 53.3% of the total tax revenue, up from 50.06% in the previous year.
- Conversely, the contribution of corporate taxes decreased to 46.5% from 49.6% in the previous fiscal. Although gross corporate tax collections rose, net tax receipts from Corporates, adjusted for refunds, saw a slight decline.
What Is the Net of Tax?
- Net of tax refers to the amount remaining after accounting for taxes.
- It is significant in various contexts, including financial decision-making for individuals and businesses, as well as expense analysis during tax assessments and business profit evaluations.
Types of Direct Taxes:
- Income Tax:
- The Government of India determines various tax slabs based on an individual’s age and earnings, which dictates the amount of Income Tax owed.
- Taxpayers must file Income Tax Returns (ITR) annually, facing penalties if they fail to do so. Depending on their ITR, individuals may receive refunds or owe taxes.
- Wealth Tax:
- Paid annually, Wealth Tax depends on property ownership and market value, irrespective of income generation. Corporate taxpayers, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), and individuals must pay Wealth Tax based on their residential status.
- Certain assets like gold deposit bonds, stock holdings, and commercially rented properties are exempt from Wealth Tax.
- Estate Tax:
- It is also referred to as an Inheritance Tax and is calculated based on the value of the estate or the assets left behind by an individual after their death.
- Corporate Tax:
- Domestic companies and foreign corporations earning income in India must pay Corporate Tax on various earnings, including those from asset sales, technical services, dividends, royalties, or interest sourced in India.
- Corporate Tax also encompasses other taxes such as Securities Transaction Tax (STT), Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT), Fringe Benefits Tax, and Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT).
- Capital Gains Tax:
- This direct tax applies to income from asset sales or investments, including farms, bonds, shares, businesses, art, and homes.
- Taxation is based on the holding period, with short-term gains applying to assets sold within 36 months and long-term gains to assets held for more than 36 months.
UPSC Civil Examinations PYQ:
Q:1 The sales tax you pay while purchasing a toothpaste is a
(a) Tax imposed by the Central Government
(b) Tax imposed by the Central Government but collected by the State Government
(c) Tax imposed by the State Government but collected by the Central Government
(d) Tax imposed and collected by the State Government [2014]
Ans: D
Q:2 .Which one of the following is not a feature of “Value Added Tax”? (2011)
a) It is a multi-point destination-based system of taxation
b) It is a tax levied on value addition at each stage of transaction in the production-distribution chain
c) It is a tax on the final consumption of goods or services and must ultimately be borne by the consumer
d) It is basically a subject of the Central Government and the State Governments are only a facilitator for its successful implementation
Ans – C
FAQs
Q: What are Net Direct Tax collections?
A: Net Direct Tax collections refer to the total tax revenue collected directly from individuals and corporations by the government, excluding any refunds.
Q: How do Net Direct Tax collections contribute to government revenue?
A: Net Direct Tax collections serve as a significant source of revenue for the government, funding various public services and developmental initiatives.
Q: What does it mean when Net Direct Tax collections exceed the 2023-24 target?
A: Exceeding the 2023-24 target indicates that the government has collected more revenue through direct taxes than it had anticipated, which could imply better compliance, economic growth, or improved tax administration.
Q: What factors could contribute to the surpassing of the 2023-24 Net Direct Tax collection target?
A: Factors contributing to surpassing the target might include increased economic activity, better tax compliance due to stricter enforcement measures, or changes in tax policies that incentivize higher reporting and payment.
Q: How might the government utilize the surplus from exceeding the Net Direct Tax collection target?
A: The surplus could be utilized for various purposes such as reducing fiscal deficit, funding infrastructure projects, social welfare programs, or debt repayment, ultimately contributing to overall economic stability and growth.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

