
This critical examination delves into Alfred Weber’s Theory of Industrial Location, a cornerstone in geographical discourse. Offering a balanced assessment, it scrutinizes the theory’s strengths and limitations without resorting to industry jargon. Through meticulous analysis, the essay dissects Weber’s propositions on factors influencing industrial location, evaluating their applicability in diverse contexts. By elucidating empirical evidence and scholarly critiques, it paints a comprehensive picture of the theory’s relevance and shortcomings. This exploration aims to equip candidates preparing for the UPSC Geography Optional Mains in 2021 with a nuanced understanding, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills essential for navigating complex geographical theories and their implications in contemporary contexts.
Contents
Answer:
Introduction:
Alfred Weber’s Theory of Industrial Location, developed in 1909, posits that industries select locations to minimize production costs, with a focus on transport costs, labor, and agglomeration economies. While foundational, the theory has faced criticism for its simplistic assumptions and limited applicability to the complexities of the modern economic landscape.
Body
Alfred Weber’s Theory of Industrial Location:
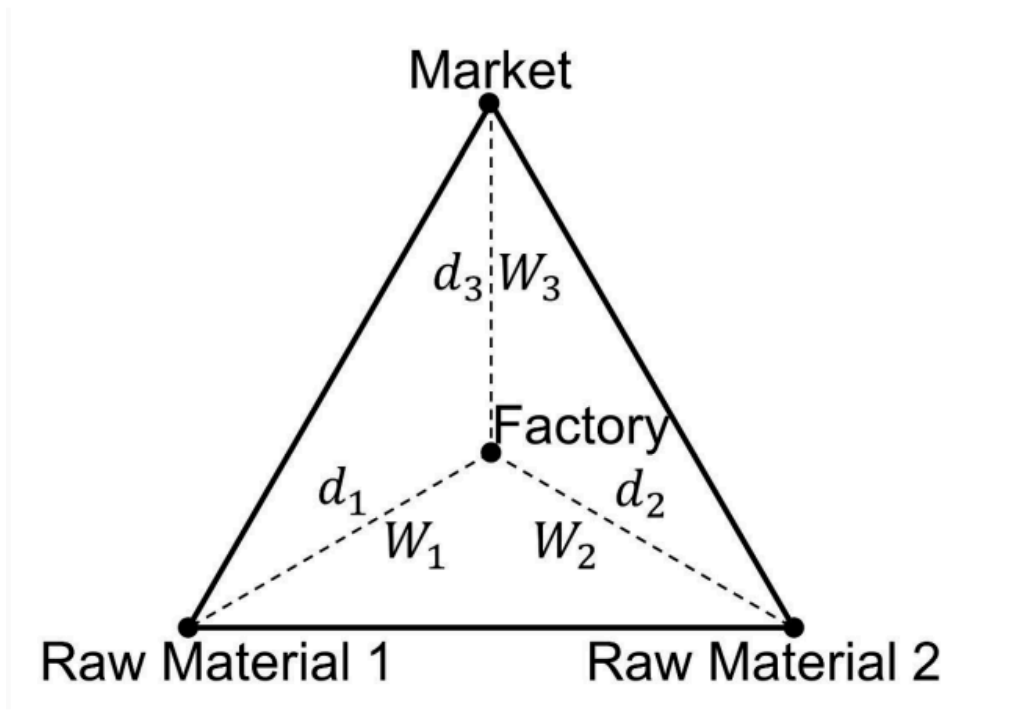
- Least-Cost Location: Industries aim to minimize transportation, labor, and agglomeration costs for optimal location selection.
- Transportation Costs: Industries locate near raw material sources or markets to reduce transportation expenses.
- Labor Costs: Assumes mobile labor moving to areas with industries, emphasizing minimizing labor expenses.
- Agglomeration Economies: Recognizes the benefits of industries clustering together for efficiency and shared resources.
Criticism of Alfred Weber’s Theory of Industrial Location:
- Simplistic Assumptions: Criticized for assuming fixed raw material and market points, overlooking real-world dynamism.
- Limited Scope: Neglects the service sector, government policies, infrastructure, and social factors in modern economic geography.
- Transport and Labor Cost Limitations: Overemphasis on transport and labor costs, neglecting other vital factors in the contemporary economic landscape.
- Static Nature: Fails to account for dynamic changes in technology, consumer preferences, and political boundaries.
- Homogeneous Labor: Ignores the diversity of skills and specialization in labor, assuming a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Globalization Challenges: Inadequate in explaining the globalized nature of industries and the interconnectedness of markets.
- Weber also neglected the political factors of a location but, it has been experienced that the migration of labours also caused due to political and governmental factors.
Usefulness of Alfred Weber’s Theory of Industrial Location:
- Historical Insight: Useful in explaining historical industrial locations, especially in contexts where transport costs were critical, e.g., coal and steel industries in the early 20th century.
- Bulk-Gaining Industries: Provides insights into industries like steel production, often located near raw material sources to minimize transportation costs.
- Labor-Intensive Industries: Explains the spatial distribution of labor-intensive industries, such as garment manufacturing, in regions with low labor costs.
- Conceptual Foundation: Serves as a foundational theory, shaping economic geography research and understanding of industrial location dynamics.
Conclusion:
While Alfred Weber’s Theory of Industrial Location offers historical and industry-specific insights, its limitations in addressing the complexities of the contemporary economic environment necessitate a more comprehensive approach. Future research should consider a broader spectrum of factors, including technological advancements, globalization, and evolving market dynamics.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

