
Reforms within Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) have become imperative in recent years, reflecting the evolving global economic landscape and the increasing complexity of development challenges. These institutions, including the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and regional development banks, play a pivotal role in providing financial assistance, technical expertise, and policy advice to member countries. However, to better address the diverse needs of their stakeholders and to enhance their effectiveness, MDBs are undergoing significant reforms. These reforms aim to streamline operations, improve governance structures, increase transparency, and ensure that resources are utilized efficiently and equitably. By adapting to changing global dynamics and fostering collaboration with diverse stakeholders, MDBs are poised to play a more impactful role in promoting sustainable development and reducing poverty worldwide.
Tags: GS Paper – 3, Banking Sector & NBFCs– Investment Models—Infrastructure
Prelims: Multilateral Development Banks, World War II, World Bank Group, Asian Development Bank, African Development Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
Mains: Key Challenges Related to MDBs and Reforms.
Contents
- 1 Context:
- 2 What are Multilateral Development Banks?
- 3 UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
- 4 FAQs
- 4.1 Q: What are Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)?
- 4.2 Q: Why are reforms necessary in Multilateral Development Banks?
- 4.3 Q: What are some common areas of reform in Multilateral Development Banks?
- 4.4 Q: How do reforms impact the functioning of Multilateral Development Banks?
- 4.5 Q: What are some recent examples of reforms in Multilateral Development Banks?
- 5 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Context:
- Recently, the UN Secretary-General underscored that the reform of multilateral development banks (MDBs) will take centre stage at this year’s Summit of the Future, coinciding with the UN General Assembly in September 2024.
What are Multilateral Development Banks?
- Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) are international financial institutions dedicated to financing and advising economic and social development projects in developing countries.
- They are established and funded by multiple countries through pooled resources and share representation on their governing boards.
- Originating in the aftermath of World War II to aid in the reconstruction of war-torn nations and stabilise the global financial system, MDBs prioritise development objectives over profit maximisation, unlike commercial banks. Their goals include eradicating extreme poverty and reducing economic inequality.
- MDBs typically offer loans at low or zero interest rates and provide grants to support projects in infrastructure, energy, education, environmental sustainability, and other sectors crucial for development.
- Major MDBs include the World Bank Group, Asian Development Bank, African Development Bank, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, and the Inter-American Development Bank.
Key Challenges Related to MDBs:
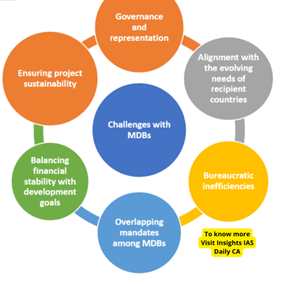
- Resource Constraints: MDBs often face limitations in the amount of capital available for lending, which can hinder their capacity to finance large-scale development projects, particularly in light of increasing demands.
- Keeping Pace with Global Challenges: Emerging global challenges like climate change, pandemics, and technological disruptions require MDBs to adapt their strategies and approaches to effectively tackle these issues. However, they have not fully integrated these challenges into their operations.
- Decision-Making: Developing nations advocate for a more equitable distribution of decision-making power to better reflect their needs and priorities. Transparency and accountability mechanisms are also called for to prevent corruption and ensure effective governance. For example, the voting power of the United States in the World Bank, at 15.85%, significantly influences the institution’s decisions.
- One-Size-Fits-All Approach: MDBs’ uniform lending conditions, such as fixed interest rates or repayment schedules, pose difficulties for countries with diverse economic structures and financial capacities in the global south. A more tailored approach is needed to address the specific needs and circumstances of each country.
Necessary Reforms in Multilateral Development Banks:
- Financing Climate Action: MDBs should focus on mobilising resources for climate change mitigation and adaptation projects in developing nations. This may entail establishing specialised climate finance facilities, issuing green bonds, and devising innovative risk-sharing mechanisms for renewable energy initiatives.
- Knowledge Sharing & South-South Cooperation: Encouraging MDBs to facilitate knowledge transfer among developing countries is vital. This involves connecting nations facing similar challenges and fostering collaboration on successful development approaches.
- Graduation Strategies: Clear pathways should be established for middle-income countries to transition from concessional loans to market-rate financing from private sources as they progress. This allows MDB resources to be directed towards low-income countries in greater need of support.
- Social and Environmental Safeguards: Strengthening safeguards to ensure that projects funded by MDBs avoid adverse social or environmental impacts and promote inclusive sustainable development is essential.
Key MDBs India is Affiliated With:
- World Bank Group: India is a member of four constituents of the World Bank Group, including the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), International Development Association (IDA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), and Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA).
- Notably, India is not a member of the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). World Bank assistance in India dates back to 1948, with the approval of funding for the Agricultural Machinery Project.
- Asian Development Bank (ADB): India is one of the founding members of ADB and holds the fourth-largest shareholder position. ADB began its operations in India in 1986 and has aligned its activities with the country’s development priorities, as outlined in the forthcoming country partnership strategy for 2023–2027.
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB): India is a founding member of AIIB and holds the second-highest voting share after China. The AIIB is headquartered in Beijing and aims to support infrastructure development projects across Asia.
- New Development Bank (NDB): India is also a founding member of the NDB, established in 2015 by the BRICS countries. India is the second-largest recipient of financial support from NDB, with funding totaling USD 7.5 billion, following China.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q:1 With reference to Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), consider the following statements: (2019)
- AIIB has more than 80 member nations.
- India is the largest shareholder in AIIB.
- AIIB does not have any members from outside Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q:1 India has recently signed to become a founding member of the New Development Bank (NDB) and also the Asian Infrastructure Bank (AIIB). How will the role of the two Banks be different? Discuss the strategic significance of these two Banks for India. (2012)
FAQs
Q: What are Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)?
Multilateral Development Banks are international financial institutions that provide financial and technical assistance for development projects in developing countries. Examples include the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank, and the African Development Bank.
Q: Why are reforms necessary in Multilateral Development Banks?
Reforms in MDBs are essential to enhance their effectiveness, efficiency, and responsiveness to evolving global challenges. They ensure that MDBs remain relevant in addressing contemporary development issues, such as climate change, inequality, and infrastructure gaps.
Q: What are some common areas of reform in Multilateral Development Banks?
Common areas of reform in MDBs include governance, transparency, accountability, project selection criteria, environmental and social safeguards, and alignment with national development priorities of borrowing countries. These reforms aim to improve decision-making processes, enhance project outcomes, and foster greater inclusivity and sustainability.
Q: How do reforms impact the functioning of Multilateral Development Banks?
Reforms can lead to more equitable distribution of resources, increased effectiveness in achieving development goals, and greater alignment with global development agendas such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). They also help MDBs adapt to emerging challenges and opportunities in the development landscape.
Q: What are some recent examples of reforms in Multilateral Development Banks?
Recent reforms in MDBs include efforts to strengthen governance structures, increase representation of developing countries in decision-making processes, enhance environmental and social standards, promote innovation in development financing, and improve coordination among MDBs and other development partners. These reforms aim to ensure that MDBs remain agile and responsive in supporting sustainable development worldwide.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

