
Strategically nestled in the Bay of Bengal, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands stand as a beacon of potential for strategic projects. As the Indian government increasingly focuses on bolstering its maritime capabilities and tapping into the economic potential of the region, the islands have emerged as a key focal point. With their strategic location providing a gateway to vital sea routes, these islands have garnered attention for their significance in defense, tourism, and environmental conservation. Against the backdrop of evolving geopolitical dynamics and the imperative of sustainable development, strategic projects in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands promise to reshape not only the region’s landscape but also its place in the broader narrative of maritime geopolitics and economic prosperity.
Tags: GS – 3, Environmental Pollution & Degradation- Government Policies & Interventions
For Prelims: National Green Tribunal (NGT), Great Nicobar Island, Coastal Regulation Zones, Turtles, Dolphins, Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), Mangroves, Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve.
For Mains: Significance and Issues Related to Great Nicobar Island Project.
Contents
- 1 Context:
- 2 Malacca Dilemma:
- 3 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- 4 FAQs
- 4.1 Q: What are the strategic projects being undertaken in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
- 4.2 Q: Why are strategic projects being emphasized in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
- 4.3 Q: What are some key initiatives under strategic projects in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
- 4.4 Q: How do these strategic projects benefit India?
- 4.5 Q: Are there any environmental considerations in these strategic projects?
- 5 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Context:
Andaman and Nicobar (A&N) Islands are seeing a major strategic security upgrade.
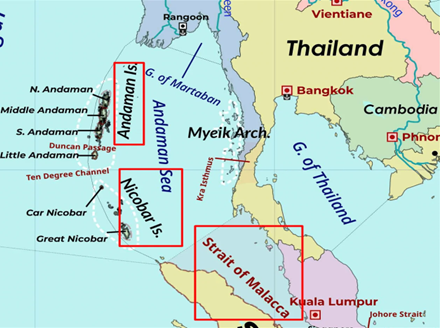
Recent strategic upgradations in A&N:
- Enhanced infrastructure: Revamped airfields and jetties, additional logistics and storage facilities, habitat for troops, robust surveillance infrastructure, etc., are being constructed.
- Capacity for greater deployment: Such upgradation will facilitate the deployment of additional military forces and warships, aircraft, missile batteries and troops.
- Road construction: A road from the north of the islands to Port Blair in the south is being proposed.
- Expansion of IAF station: Includes expansion of the runway and station. It can result in the holding of fighter squadrons for longer durations.
- Great Nicobar Island Project: A project that includes an international container transhipment terminal, a greenfield international airport, and a township development is being proposed.
- Naval capabilities: Upgrades in hangers, Precision Approach Radar (PAR), Surveillance System at INS Utkrosh in Port Blair and Naval Communication Network (NCN) Centres enhanced naval capacities.
- Remote Sensing: The National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) will increase its manpower to analyse satellite imagery and technical capacity to improve surveillance in the A&N Islands and Lakshadweep.
Strategic Importance of A&N Islands:
- Closeness to maritime choke point: Its location at the western entrance/exit of the Strait of Malacca makes it essential in case of a “Malacca Dilemma”.
- India’s opportunity: It allows India to monitor the flow of traffic from the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean) to the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean).
- Closer to other nations: The A&N islands are closer to Myanmar, Indonesia, and Thailand than to the Indian cities of Chennai and Kolkata.
- Exclusive economic zone (EEZ): It adds 300,000 sq km to India’s EEZ and promises undersea hydrocarbon and mineral deposits.
- Uninhibited islands: Less than 40 of the archipelago’s 836 islands and islets are inhabited, leaving a possibility of surreptitious occupation — a la “Kargil heights’ ‘ — by a covetous neighbour.
- China’s expanding influence: China is building a military facility at Myanmar’s Coco Islands north of the A&N Islands, which raises concerns.
Malacca Dilemma:
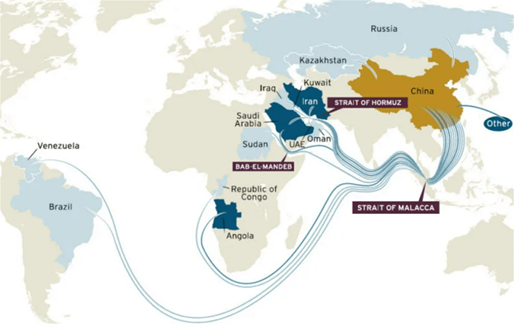
- Malacca Dilemma is a word coined in 2003 by then-Chinese President Hu Jintao.
- The Strait of Malacca’s location, which falls between the Sumatra Islands, the Malay Peninsula, and Singapore to its east, makes it a chokepoint for Chinese oil imports.
- Hu Jintao argued that the rival nations of China could easily block this narrow stretch of water.
Historical evolution of security presence in A&N:
- British Period: Dark symbolism of Kalapani to Cellular jail in A&N island in the aftermath of the 1857 revolution led to long neglect of the island chain.
- Liberated by INA: Japan occupied it during World War II. For a brief period, it remained liberated under the Provisional Government of INA.
- Part of independent India: Despite some British advisors suggesting it to be retained as the Crown’s possession, it became part of India.
- A&N Naval garrison: In 1962, after a reported sighting of a Chinese submarine, India stationed a few navy personnel in the A&N islands.
- Post-Kargil war: India’s first unified theatre operational command, the Andaman Nicobar Command (ANC) in Port Blair, was established in 2001 after the Kargil security review report.
Way forward: India’s future role in A&N
- Extension of defensive and diplomatic capabilities: A security infrastructure upgrade will not only extend India’s defensive perimeter but also bestow the ability to project power or extend a hand of friendship to maritime neighbours.
- Peace in the region: India, with the cooperation of like-minded partners, can contribute to maintaining peace and tranquillity in the Indo-Pacific.
- Transhipment hub: Port Blair could become a regional hub for navies to acquire interoperability in areas such as disaster relief, medical aid, countering piracy, and human smuggling.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q3. In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
(a) Nilgiri Hills
(b) Nicobar Islands
(c) Spiti Valley
(d) Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)
FAQs
Q: What are the strategic projects being undertaken in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
Several strategic projects are underway in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, including infrastructure development, enhanced connectivity, and military installations to bolster national security.
Q: Why are strategic projects being emphasized in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands hold immense strategic importance due to their proximity to crucial international shipping routes and their strategic location in the Indian Ocean region. Strengthening infrastructure and military presence in these islands enhance India’s maritime security and defense capabilities.
Q: What are some key initiatives under strategic projects in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
Some key initiatives include the expansion of the Port Blair airport, development of new ports and harbors, establishment of naval bases, construction of road and communication networks, and installation of radar systems for surveillance.
Q: How do these strategic projects benefit India?
These projects bolster India’s strategic presence in the Indian Ocean, enhancing maritime security and surveillance capabilities. Improved infrastructure and connectivity also facilitate economic development, tourism, and trade in the region, contributing to overall national growth.
Q: Are there any environmental considerations in these strategic projects?
Yes, environmental sustainability is a key consideration in the planning and execution of strategic projects in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Measures are taken to minimize ecological impact, preserve biodiversity, and ensure responsible use of natural resources in line with environmental regulations and international conventions.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

