
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Women representation in defence forces
- 2 2023 World Malaria Report
- 2.1 In News:
- 2.2 Key Report Findings of the report
- 2.2.1 Global Malaria Landscape
- 2.2.2 Challenges to Global Malaria Response
- 2.2.3 Malaria Hotspots
- 2.2.4 India’s Malaria Status
- 2.2.5 Regional Variances
- 2.2.6 Impact of Climate Change
- 2.2.7 Global Eradication Goals
- 2.2.8 Challenges in Eradication Efforts
- 2.2.9 Malaria Vaccine Milestones
- 2.2.10 Call to Action
- 2.3 Global Initiatives
- 2.4 Initiatives in India
- 3 Tejas Jets and Prachand Helicopters
- 4 Climate Vulnerable Nations
- 5 Cyclone Michaung
- 6 Codex Alimentarius Commission
- 7 World AIDS Day 2023
- 8 Dr. Rajendra Prasad
- 8.1 In News:
- 8.2 Dr. Rajendra Prasad: A Notable Life
- 8.2.1 Early Life and Birth
- 8.2.2 Involvement with Mahatma Gandhi
- 8.2.3 Resistance Against Injustices
- 8.2.4 Leadership in Salt Satyagraha
- 8.2.5 Political Affiliation and Growth
- 8.2.6 Ministerial Role and Slogan
- 8.2.7 Presidency and Record
- 8.2.8 Bharat Ratna and Literary Contributions
- 8.2.9 Final Departure
- 9 Indian Navy Day 2023
- 10 Kra Isthmus
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Women representation in defence forces
Tag: GS- 2 Gender, Issues Related to Women, Role of Women, Government Policies & Interventions GS – 3 Various Security Forces & Agencies & Their Mandate
In News:
Recently, the Prime Minister stated the government’s dedication to enhancing the representation of women in the armed forces.
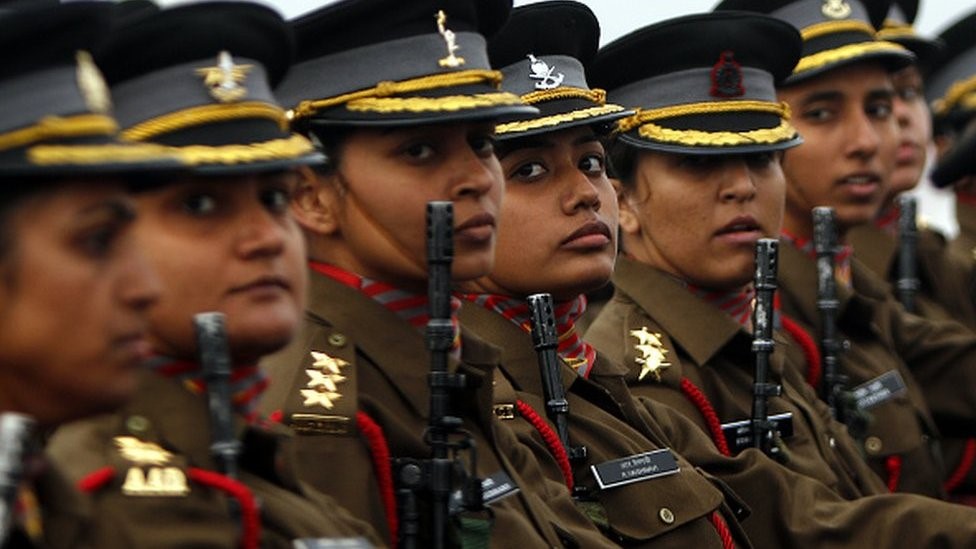

Advancements in Women’s Role in the Indian Military: A Comprehensive Overview
Exploring Women’s Participation in the Armed Forces
The inclusion of women in the Army, Air Force, and Navy commenced with short-service commission (SSC) roles in 1992, expanding beyond the medical stream.
A Defining Moment in 2015
- A significant milestone occurred in 2015 when the Indian Air Force (IAF) permitted women to join the fighter stream.
Legal Mandate for Equality
- In 2020, the Supreme Court mandated permanent commission (PC) for women officers in the Army’s non-combat support units, rejecting gender-based limitations.
Progress in the Army
- Women officers in the Indian Army now hold PC across all ten branches where they are inducted for SSC, allowing them to occupy command appointments on par with male counterparts.
- The Indian Navy, after a 25-year hiatus, deployed four women officers on warships in early 2021, showcasing a shift in gender roles.
Diversifying Roles
- In May 2021, the Army inducted women into the Corps of Military Police, marking their entry into the non-officer cadre.
Challenges and Restrictions
- Despite progress, combat arms like Infantry and Armored Corps remain inaccessible to women.
Numerical Growth and Representation
- Over the past six years, the number of women in the military has nearly tripled, reaching a total of 9,118 across the army, navy, and air force.
Global Perspectives
- Considering global trends, the move towards gender-inclusive military roles has gained momentum, as seen in the U.S. in 2013 and the UK in 2018.
Importance of Gender-Inclusive Military
- Highlighting that gender should not impede qualifications, emphasizing technical expertise and decision-making skills over physical strength.
Addressing Recruitment Challenges:
- Advocating for a mixed-gender force to enhance military readiness amid concerns of declining recruitment and retention rates.
- Overcoming Traditions
- Recognizing the need for training to integrate women into combat units and acknowledging the evolving nature of military culture.
Transformative Steps for Women’s Leadership in the Military
Driving Cultural Shifts
- Historically, women were excluded from command roles due to concerns about acceptance among the rank and file.
- Initiating changes in the Army’s culture, norms, and values, as well as societal attitudes, is crucial.
- The onus for these transformations rests on the shoulders of senior military and political leaders.
International Examples
- Several global military forces, including the United States, Israel, North Korea, France, Germany, Netherlands, Australia, and Canada, have successfully integrated women into front-line combat positions.
- These nations serve as examples of effective implementation and acceptance.
Empowering Equality
- Every woman has the right to pursue her chosen career path and ascend to leadership positions.
- Emphasizing that equality is not just a principle but a constitutional guarantee, it is imperative to create an environment that supports and nurtures the career ambitions of women.
Source: TH
2023 World Malaria Report
Tag: GS-3 Environment GS-2 Health
In News:
The recently published 2023 World Malaria Report from the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights the concerning malaria situation both in India and worldwide.

Key Report Findings of the report
Global Malaria Landscape
- The 2023 World Malaria Report discloses a worldwide upswing, surpassing pre-pandemic levels with an estimated 249 million cases in 2022.
Challenges to Global Malaria Response
- Disruptions caused by Covid-19, drug resistance, humanitarian crises, and climate change pose significant threats to global efforts in combatting malaria.
- Twenty-nine countries account for 95% of global malaria cases.
Malaria Hotspots
- Nigeria, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, and Mozambique collectively contribute to almost half of the global malaria cases.
- Nigeria leads with 27%.
India’s Malaria Status
- India, constituting 66% of malaria cases in the WHO South-East Asia Region, faces challenges, including a surge in 2023 linked to unseasonal rainfall.
- Plasmodium vivax accounts for nearly 46% of cases in the region.
Regional Variances
- Africa bears the highest malaria burden, with 94% of cases and 95% of global malaria deaths in 2022.
- The WHO South-East Asia Region, including India, achieved a 77% reduction in cases and deaths since 2000.
Impact of Climate Change
- Climate change emerges as a pivotal driver, increasing malaria transmission sensitivity.
- WHO underscores the substantial risk this poses to malaria progress, urging sustainable and resilient responses.
Global Eradication Goals
- WHO’s 2025 and 2030 malaria reduction targets face significant gaps, with a 55% shortfall in incidence reduction and a 53% gap in fatality rate reduction.
Challenges in Eradication Efforts
- Funding gaps for malaria control increased from USD 2.3 billion in 2018 to USD 3.7 billion in 2022.
- Research and development funding hit a 15-year low at USD 603 million.
Malaria Vaccine Milestones
- Phased introduction of the WHO-recommended malaria vaccine, RTS,S/AS01, reveals notable progress, with a second vaccine, R21/Matrix-M, recommended in October 2023.
- These advancements are expected to bolster malaria prevention efforts.
Call to Action
- WHO emphasizes the urgent need for increased resources, enhanced political commitment, data-driven strategies, and innovative tools in the fight against malaria.
- Sustainable and resilient responses aligned with climate change mitigation efforts are deemed crucial for progress.
Global Initiatives
WHO’s Global Malaria Program (GMP)
- Coordinates global efforts for malaria control and elimination.
- Guided by the “Global technical strategy for malaria 2016–2030” with a goal to reduce global malaria incidence and mortality rates by at least 90% by 2030.
Malaria Elimination Initiative
- Led by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Focuses on diverse strategies, including treatment accessibility, mosquito population reduction, and technology development.
E-2025 Initiative
- Launched by WHO in 2021.
- Aims to halt malaria transmission in 25 countries by 2025.
Initiatives in India
National Framework for Malaria Elimination 2016-2030
- Aligned with WHO’s strategy to eliminate malaria in India by 2030 and maintain malaria-free zones.
National Vector-Borne Disease Control Programme
- Addresses vector-borne diseases, including malaria, through prevention and control measures.
National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP)
- Launched in 1953 with key activities such as insecticidal residual spray, monitoring and surveillance of cases, and patient treatment.
High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) Initiative
- Initiated in 2019 in four states (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh).
- Focuses on malaria reduction through insecticidal net distribution.
Malaria Elimination Research Alliance-India (MERA-India)
- Established by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- Collaborates on malaria control research with various partners.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2010) Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine? (a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium (b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection (c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria (d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host Ans: (b) |
Source: TH
Tejas Jets and Prachand Helicopters
Tag: GS-3 Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate.
In News:
The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has approved acquiring 97 Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (Mark 1A) and 156 Prachand Light Combat Helicopters.
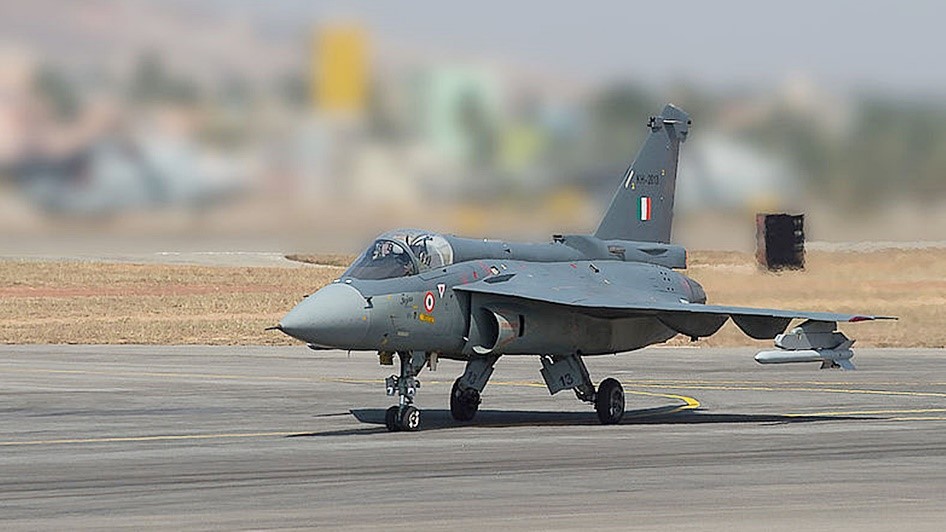

Light Combat Aircraft (LCA): An Overview
Program Commencement
- Initiated by the Government of India in 1984, the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) was established to oversee the LCA program.
Distinctive Features
- Engineered to accommodate a variety of air-to-air, air-to-surface, and precision-guided weapons, with added capabilities such as air-to-air refueling.
Tejas Variants
Tejas Trainer
- A two-seater operational conversion trainer designed to train air force pilots.
- Both twin- and single-seat configurations, tailored for carrier-based operations in the Indian Navy.
- Represents the second phase of the LCA Navy variant, indicating iterative advancements.
LCA Tejas Mk-1A
- An enhanced iteration of the LCA Tejas Mk1, featuring a higher thrust engine for improved performance.
Light Combat Helicopter (LCH): Overview
Exceptional Altitude Capabilities
- Distinguished as the world’s sole attack helicopter capable of landing and taking off at altitudes of 5,000 meters, carrying substantial weapon loads and fuel.
Advanced Design Features
- Utilizes radar-absorbing material to minimize radar signature, boasts a crash-resistant structure, and incorporates landing gear for enhanced durability.
- The pressurized cabin ensures protection against Nuclear, Biological, and Chemical (NBC) contingencies.
Defensive Systems
- Equipped with a countermeasure dispensing system, safeguarding against enemy radar and infrared seekers of hostile missiles.
Power Source
- Powered by two French-origin Shakti engines, manufactured by the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
Genesis of the Project
- Originating from the necessity felt during the 1999 Kargil war, the LCH project aimed to develop a domestically produced lightweight assault helicopter for precision strikes in diverse Indian battlefield conditions.
- This includes operating in hot deserts, cold high altitudes, and scenarios ranging from counter-insurgency to full-scale battles.
Historical Context
- India previously operated sub-3-ton category French-origin legacy helicopters, Chetak and Cheetah, along with the armed version, Lancer.
- The Mi-17 series, of Russian origin, has also been in use by the Indian Air Force and is slated for phasing out starting 2028.
Project Sanction and Development
- Government approval for the LCH project was granted in October 2006, with the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) entrusted with its development.
Operational Significance
- The LCH assumes crucial combat roles, encompassing the destruction of enemy air defense, counter-insurgency warfare, combat search and rescue, anti-tank operations, and counter surface force operations.
Source: TH
Climate Vulnerable Nations
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Former Maldives President suggests that Indian companies should consider investing in countries susceptible to climate impacts.
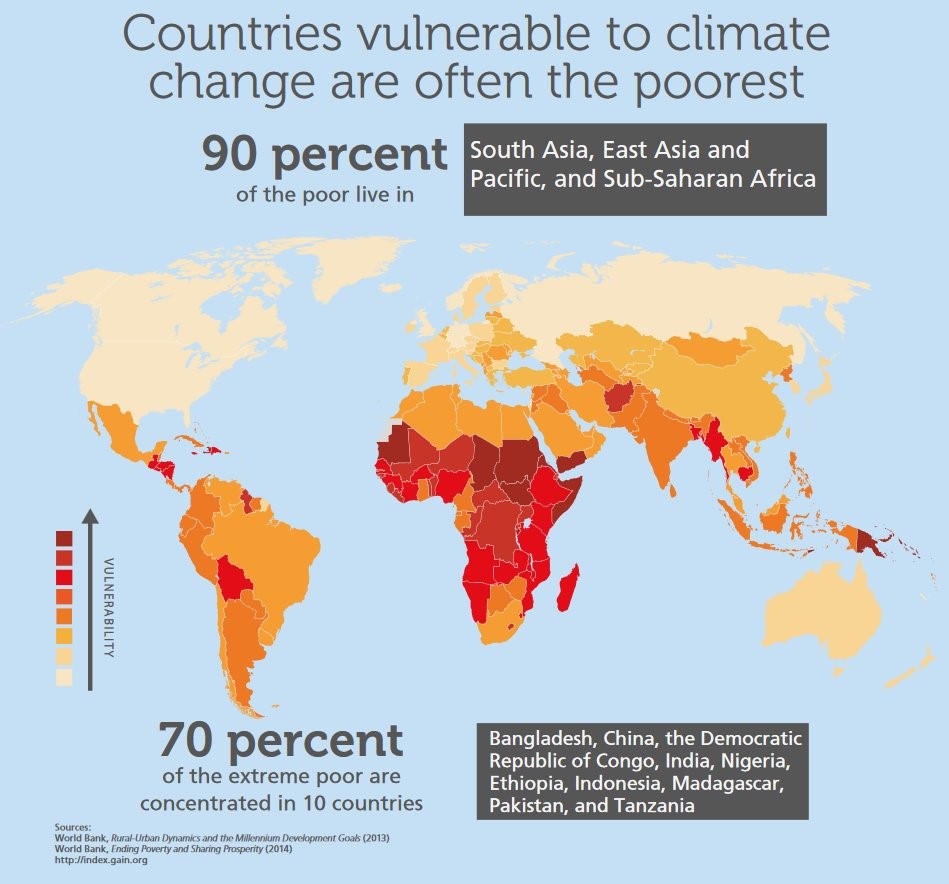
About Climate Vulnerable Nations
- Climate Vulnerable Nations (CVNs), also known as the Vulnerable Twenty (V20), refer to a coalition of countries that are particularly susceptible to the adverse impacts of climate change.
- These nations face severe challenges and risks associated with rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and the resultant environmental and socio-economic consequences.
- Here are key aspects related to Climate Vulnerable Nations:
Definition and Criteria
- CVNs are typically characterized by their high vulnerability to climate change impacts despite contributing minimally to global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Vulnerability criteria include factors such as geographical location, low-lying coastal areas, dependence on climate-sensitive sectors (agriculture, fisheries), and limited adaptive capacity.
Coalition Formation
- The CVN coalition was established to amplify the voices of these vulnerable nations in international climate negotiations.
- It aims to advocate for stronger global commitments to mitigate climate change, provide financial and technical support for adaptation, and address the loss and damage incurred.
Objectives
- Advocate for global climate action to limit global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
- Secure financial support for adaptation and mitigation efforts, recognizing the disproportionate burden on vulnerable nations.
- Promote sustainable development pathways that integrate climate resilience.
Challenges Faced by CVNs
Rising Sea Levels
- Many CVNs are low-lying island nations facing the imminent threat of sea-level rise.
Extreme Weather Events
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, cyclones, and droughts, have severe consequences for vulnerable communities.
Economic Impacts
- Climate change poses risks to key economic sectors like agriculture, tourism, and fisheries, impacting livelihoods.
Leadership and Advocacy
- CVNs actively participate in international climate forums, emphasizing the urgency of climate action and advocating for policies that address the specific needs of vulnerable nations.
- They often lead by example, implementing innovative climate resilience measures and adopting renewable energy solutions.
Global Initiatives and Support
- Various international organizations and initiatives, including the United Nations and the Green Climate Fund, aim to provide financial and technical assistance to CVNs.
- Developed nations are urged to fulfill commitments under climate agreements to support adaptation and mitigation efforts in vulnerable regions.
Progress and Collaboration
- CVNs collaborate on research, technology transfer, and capacity-building initiatives to enhance their resilience.
- They play a crucial role in shaping global climate policies and ensuring that the international community acknowledges and addresses the needs of the most vulnerable nations.
Source: TH
Cyclone Michaung
Tag: GS-1 Physical Geography and various phenomena GS-3 Environment
In News:
Heavy rain in Tamil Nadu’s capital caused havoc. Union Home assures Chief Minister of full support from the Centre.

About Cyclone Michaung
- Originating in the South-West Bay of Bengal, Cyclone Michaung has been named following a suggestion from Myanmar, signifying strength and resilience.
- Once fully formed, this cyclone will mark the fourth cyclonic storm in the Bay of Bengal and the sixth cyclone to develop in the Indian Ocean in the year 2023.
Naming of the cyclones
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is responsible for managing rotating name lists specific to each tropical cyclone basin.
- Cyclones in various global ocean basins receive their names from regional specialized meteorological centers (RSMCs) and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers (TCWCs) within those regions. There are a total of six RSMCs worldwide.
- Member nations of the RSMCs propose names for tropical cyclones, with the Indian RSMC, consisting of 13 nations, suggesting 13 names for cyclones in the region.
- In the past, before the official adoption of naming conventions, tropical cyclones were named based on locations, objects, or the feast days of saints on which they occurred.
- The naming sequence follows a sequential column-wise approach, beginning from the first row of column one and progressing sequentially to the last row in column thirteen.
- Once a name is assigned to a tropical cyclone over the north Indian Ocean, it will not be reused.
- Notably, if a tropical cyclone originates in the south China Sea, crosses Thailand, and emerges into the Bay of Bengal, its name will remain unchanged.
- This system ensures the unique identification of tropical cyclones and prevents the repetition of names over time.
Source: TH
Codex Alimentarius Commission
Tag: GS-3 Environment GS-IR
In News:
India has achieved unanimous election to the Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC), representing the Asian region.

About Codex Alimentarius Commission
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) is an international body for food standards jointly established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) in May 1963.
- Its primary aim is to safeguard consumer health and ensure equitable practices in food trade.
Recognition
- The World Trade Organization’s (WTO) Agreement on Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) acknowledges Codex standards, guidelines, and recommendations as reference standards for international trade and dispute resolution.
Membership
- Currently comprising 189 Codex Members, including 188 Member Countries and 1 Member Organization (The European Union).
- India joined the Codex Alimentarius in 1964.
Codex Standards
General Standards, Guidelines, and Codes of Practice
- Core texts addressing hygienic practices, labeling, contaminants, additives, inspection & certification, nutrition, and residues of veterinary drugs and pesticides.
- These standards apply broadly to various products and product categories.
Commodity Standards
- Specific standards for particular products, though Codex increasingly develops standards for broader food groups.
Regional Standards
- Standards formulated by Regional Coordinating Committees, applicable to their respective regions.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2010) Q. As regards the use of international food safety standards as reference point for the dispute settlements, which one of the following does WTO collaborate with? (a) Codex Alimentarius Commission (b) International Federation of Standards Users (c) International Organization for Standardization (d) World Standards Cooperation Ans: (a) |
Source: PIB
World AIDS Day 2023
Tag: GS-3 Environment GS Paper – 2HealthGovernment Policies & Interventions
In News:
Globally observed on December 1st annually, World AIDS Day aims to raise awareness about Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and commemorate those affected by it.

Unveiling the Realities of HIV/AIDS
Nature of the Infection
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is an infection that specifically targets and weakens the body’s immune system.
- Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the advanced stage of HIV infection, occurring when the immune system is severely compromised.
Target Cells and Immune System Impact
- HIV primarily attacks CD4 cells, a type of White Blood Cell (T cells) responsible for detecting anomalies and infections in the body.
- The virus multiplies and destroys these CD4 cells, causing substantial damage to the immune system.
- Once contracted, HIV cannot be eradicated from the body.
CD4 Count and Immune System Health
- In a healthy individual, the CD4 count ranges from 500 to 1600.
- However, in an HIV-infected person, this count can plummet to as low as 200, signifying significant immune system impairment.
Transmission Routes
- HIV spreads through direct contact with certain body fluids from an infected person with a detectable viral load.
- These fluids include blood, semen, rectal fluid, vaginal fluid, and breast milk.
Symptoms and AIDS Development
- After HIV progresses to AIDS, initial symptoms may include unexplained fatigue, fever, genital or neck sores, pneumonia, among others.
Global and Indian Prevalence
- Globally, an estimated 39 million people are living with HIV. In India, the figure is 2.4 million.
- In 2022, there were 1.3 million new HIV infections worldwide, with 63,000 reported in India.
- AIDS-related deaths in 2022 totaled 650,000 globally and 42,000 in India. Many of these infections are preventable and treatable.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2013) Q . Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? Chikungunya Hepatitis B HIV-AIDS Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
Source: TH
Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Tag: GS-2 Indian Polity
In News:
The President of India recently honored the birth anniversary of Dr. Rajendra Prasad, the inaugural President of India, by paying heartfelt tributes.

Dr. Rajendra Prasad: A Notable Life
Early Life and Birth
- Born on December 3, 1884, in Zeradei, Siwan, Bihar, Dr. Rajendra Prasad’s journey began in a small town.
Involvement with Mahatma Gandhi
- During the Champaran Satyagraha of 1917 in Bihar, he collaborated closely with Mahatma Gandhi, marking the early chapters of his involvement in India’s struggle for independence.
Resistance Against Injustices
- Dr. Prasad vehemently opposed the Rowlatt Act of 1918 and strongly reacted to the Jallianwala Bagh massacre in 1919.
- His call for non-cooperation in Bihar aligned with Gandhi’s broader non-cooperation movement.
Leadership in Salt Satyagraha
- A pivotal figure in the Salt Satyagraha of 1930 in Bihar, Dr. Prasad’s active participation led to his imprisonment, showcasing his commitment to the cause.
Political Affiliation and Growth
- Officially joining the Indian National Congress in 1911 during its annual session in Calcutta, Dr. Prasad’s political journey began to take shape.
Ministerial Role and Slogan
- In 1946, he assumed the position of Minister of Food and Agriculture in the Interim Government, where he championed the slogan “Grow More Food.”
Presidency and Record
- Elected as India’s first President on January 26, 1950, Dr. Rajendra Prasad held this esteemed position until May 13, 1962, setting a record as the longest-serving President in Indian history.
Bharat Ratna and Literary Contributions
- Honored with the Bharat Ratna in 1962, Dr. Prasad’s contributions extended beyond politics, encompassing notable literary works such as “Satyagraha at Champaran,” “India Divided,” and his autobiography, “Atmakatha.”
Final Departure
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad passed away on February 28, 1963, leaving behind a legacy of leadership, resilience, and unwavering dedication to India’s freedom struggle.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2010) Q. Consider the following statements: Dr. Rajendra Prasad persuaded Mahatma Gandhi to come to Champaran to investigate the problem of peasants. Acharya J.B. Kriplani was one of Mahatma Gandhi’s colleagues in his Champaran investigation. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) |
Source: PIB
Tag: GS-3
In News:
Annually on December 4, India commemorates Navy Day to pay tribute to Operation Trident, a pivotal offensive strategy executed during the 1971 India-Pakistan War.

- During the 1971 conflict, Operation Trident emerged as a decisive episode, highlighting the strategic capabilities of the Indian Navy.
- The operation involved the adept use of Soviet Osa missile boats, equipped with 4 SS-N-2 Styx missiles, to effectively neutralize three vessels in the vicinity of Karachi, a key Pakistani port city.
- In a recent milestone, Commander Prerna Deosthalee is set to make history as the first woman officer in the Indian Navy to assume command of an Indian Navy Warship, specifically the Waterjet FAC INS Trinkat.
Source: TH
Kra Isthmus
Tag: GS-2 IR, GS-1 Physical Settings and Geography of the world
In News:
The Kra Isthmus, situated on the Malay Peninsula in Thailand, has garnered strategic significance owing to a suggested transit route that has the potential to link the Andaman Sea with the Gulf of Thailand.
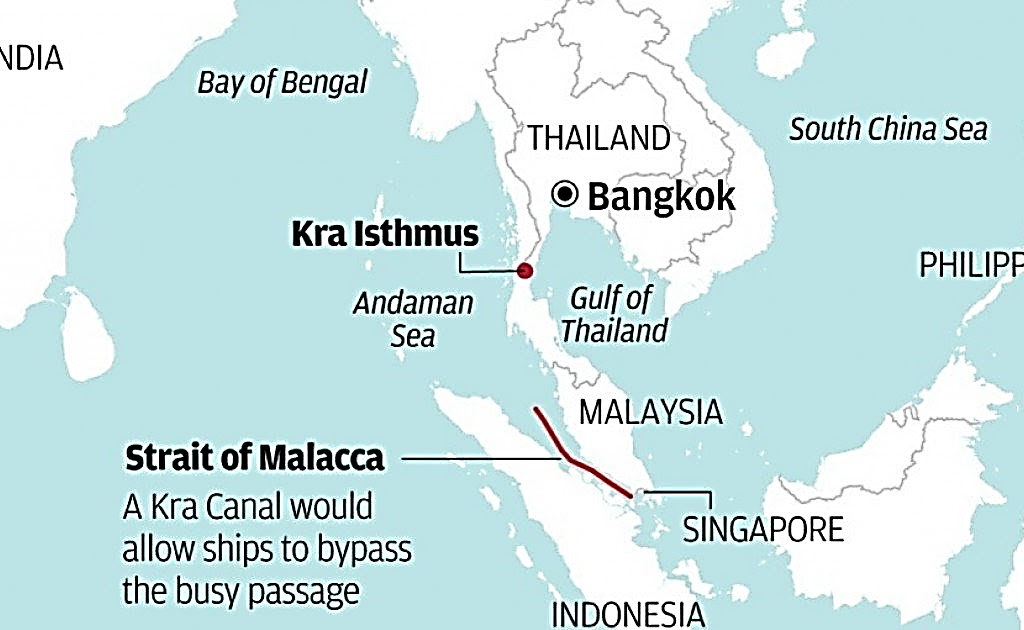
About Kra Isthmus
- The isthmus, with a width of merely 44 km at its narrowest, holds the potential to impact global trade and security, akin to the historical significance of the Suez and Panama Canals.
- Recently, the Thai Prime Minister officially introduced a multi-billion-dollar land-bridge project.
- An isthmus is a slender land strip connecting two larger masses and is surrounded by water on two sides.
- Situated in Thailand, the Kra Isthmus represents the narrowest segment of the Malay Peninsula, bordered by the Andaman Sea to the west and the Gulf of Thailand to the east.
Source: TOI
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

