
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Pros and Cons of Diabetes Reversal
- 2 Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023
- 3 Model Prisons Act, 2023
- 4 Genetically Engineered Insects
- 5 Char Dham All Weather Road Project
- 6 Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA)
- 7 PM 2.5
- 8 The University Grants Commission (UGC)
- 9 Iceland
- 10 Baler Machine
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Pros and Cons of Diabetes Reversal
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech.
In News:
The surge in popularity of diabetes reversal has led to various commercial entities making bold claims. It’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of this trend.
About Diabetes
- Diabetes is a health condition affecting the body’s ability to process blood glucose, also known as blood sugar.
- There are three main types: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
- Also called juvenile diabetes, it occurs when the body doesn’t produce insulin, a hormone crucial for sugar breakdown.
- Typically diagnosed in childhood, there’s no cure.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Characterized by ineffective insulin use or production; it’s strongly linked to obesity and is the most common type.
- Develops in people of any age
Gestational Diabetes
- Develops during pregnancy when sensitivity to insulin decreases.
- Management during pregnancy involves staying active, monitoring foetal growth, adjusting diet, and tracking blood sugar levels.
- Increases the risk of high blood pressure during pregnancy.
What is Diabetes Reversal?
- Diabetes reversal refers to the process of mitigating or eliminating the symptoms and complications of diabetes, ultimately restoring the body’s ability to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
- This can be achieved through various means, including lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, weight management, and sometimes medical interventions.
- It’s important to note that while significant improvements can be made in managing diabetes, complete and permanent reversal may not be achievable in all cases.
Approaches to diabetes reversal
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, incorporating regular physical activity, and maintaining a balanced diet.
- For individuals with obesity-related diabetes, losing excess weight can have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels.
- Emphasizing whole foods, reducing refined sugars and carbohydrates.
- In some cases, medications or medical procedures may be prescribed to assist in diabetes management e.g., Bariatric surgery.
Pros of Diabetes Reversal
- Successful diabetes reversal can lead to better overall health, increased energy levels, and an improved sense of well-being.
- Individuals may experience a decrease in the need for diabetes medications or insulin, leading to fewer potential side effects associated with these drugs.
- Reversing diabetes can help prevent or delay the onset of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
- By reducing the need for ongoing medication and healthcare expenses associated with diabetes management, individuals may experience cost savings.
- Achieving diabetes reversal goals can positively influence mental health, reducing stress and anxiety associated with managing a chronic condition.
Cons of Diabetes Reversal
- Diabetes reversal may not be possible for everyone, and success can vary based on individual factors such as the type and duration of diabetes, overall health, and genetic predisposition.
- Maintaining the lifestyle changes necessary for diabetes reversal can be challenging, and there is a risk of relapse if healthy habits are not sustained.
- Rapid changes in blood sugar levels during reversal attempts may pose risks, and it’s essential to manage these changes carefully to avoid hypoglycaemia or other complications.
- Sustaining the lifestyle changes necessary for diabetes reversal requires ongoing commitment to dietary and exercise habits, which may be challenging for some individuals.
- What works for one person may not work for another, and there is a lack of one-size-fits-all solutions in diabetes reversal. Personalized approaches are often needed.
Status of Diabetes in India
- 77 million people above the age of 18 years are suffering from diabetes (type 2) and nearly 25 million are prediabetics (at a higher risk of developing diabetes in near future)
- Thirty-one million Indians became diabetic between 2019-2021
Interventions to Tackle Diabetes in India
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS)
- National Health Mission (NHM)
- Ayushman Bharat
- Rastriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram
- National Programme for the Health Care of the Elderly
- National Rural Health Mission
- Eat Right India
- National Diabetes Control Program
Source: TH
Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023 pertains to the ability to convert forest land for non-forest purposes. The Central and State governments emphasize their right to undertake such conversions.
Background
- After Independence, extensive forest lands were designated as reserved and protected forests.
- However, certain forested areas were excluded, and areas devoid of standing forests were classified as ‘forest’ lands.
- The 1996 Godavarman case led the Supreme Court to suspend nationwide tree felling, applying the Forest Conservation (FC) Act to all lands resembling the dictionary definition of forest.
- In June 2022, the government amended the Forest Conservation Rules to enable developers to establish plantations on non-FC Act applicable land and exchange such plots for compensatory afforestation obligations.
Key Highlights of the act
- The Act broadens the scope of the Van (Sanrakshan Evam Samvardhan) Adhiniyam, 1980 by introducing a Preamble and modifying its name to reflect its potential provisions.
- Initially applicable to notified forest land, the Act now encompasses revenue forest land, lands recorded as forest in government records, and private forest lands.
- Exemptions are proposed for specific purposes, such as habitation connectivity, security-related infrastructure, and public utility projects in Left Wing Extremism Affected Districts, Strategic projects near international borders.
- Provisions for leasing forest land to government companies are extended to facilitate development projects.
- New forestry activities, including frontline staff infrastructure, ecotourism, zoos, and safaris, are incorporated.
- The Act aligns with climate change mitigation by recognizing these areas as contributions to India’s conservation efforts and international commitments like Net Zero Emission by 2070.
- It empowers local communities through government-owned establishments like zoos, safaris, and ecotourism, fostering awareness, wildlife protection, and creating livelihood opportunities.
- The objections to the Act’s new Hindi name raised concerns about its non-inclusivity, particularly for the non-Hindi speaking populations in South India and the North-East.
- The proposed exemptions, especially regarding strategic projects near international borders, have sparked worries about potential forest clearances in ecologically sensitive areas like the Himalayan and northeastern regions, impacting biodiversity and triggering extreme weather events.
- The act could erode the rights of indigenous communities residing on India’s borders. Its limited applicability to areas recorded as forests after October 1980 might leave significant portions of forest land and biodiversity hotspots outside the Act’s jurisdiction, making them susceptible to sale, diversion, clearance, and exploitation for non-forestry purposes.
- Additionally, concerns have been raised about the impact on the balance between the Centre and State governments in forest conservation matters, with some states arguing that forest conservation falls under the Concurrent List, potentially affecting the authority of the State governments.
Way forward
- It is essential to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the act and their potential repercussions on forests, biodiversity, and local communities.
- This assessment must encompass ecological, social, and environmental aspects and incorporate input from a wide array of stakeholders, including experts, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), tribal communities, and State governments.
- Continuing meaningful consultations and dialogues with all stakeholders is crucial to grasp their viewpoints and address any concerns they may have.
- This approach will foster transparency, inclusivity, and informed decision-making.
Source: TH
Model Prisons Act, 2023
Tag: GS- 2 Government Policies & Interventions, Social Empowerment, Issues Arising Out of Design & Implementation of Policies
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs has stated that states are allowed to employ tracking devices on individuals released on parole.
About Model Prisons Act, 2023
- The need for a new prison act arises from the deficiencies in the old Prisons Act of 1894, which lacks a correctional focus, emphasizing custody and discipline without provisions for prisoner reform and rehabilitation.
- The Model Prisons Act of 2023 addresses these lacunae and introduces significant reforms.
- Key features of the new act include provisions for punishment regarding prohibited items, establishment of high-security and open jails, measures to protect society from habitual offenders, legal aid, parole, furlough, and premature release for good conduct.
- It emphasizes security assessment, individual sentence planning, grievance redressal, attitudinal change toward prisoners, and provisions for women and transgender prisoners.
- The act integrates technology for transparency, incorporating video conferencing with courts and technological interventions in prison administration.
- As a State subject in India, the Model Prisons Act, 2023 serves as a guiding document for states, bringing much-needed reforms and aligning the Indian prison system with international standards.
- It consolidates and updates relevant provisions from the outdated Prisoners Act of 1900 and the Transfer of Prisoners Act, 1950.
Issues of Prisons in India
- The occupancy rate of jails exceeds capacity, reaching 118.5%, with around 4,78,600 prisoners in facilities designed for 4,03,700.
- Overcrowding leads to poor living conditions and the spread of communicable diseases.
- Many prisons lack adequate medical facilities, resulting in neglect and untreated health issues among inmates.
- Hygiene standards are also inadequate.
- Numerous cases remain pending for years, disrupting the prison administration.
- The right to a speedy trial is recognized by the Supreme Court, but delays persist.
- Despite restrictions on third-degree torture, custodial abuses are prevalent.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs reported 146 cases of death in police custody, with Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh having the highest numbers.
- Female prisoners face physical and mental challenges, including insufficient sanitation and inadequate care during pregnancy.
- Children, housed in correctional homes, undergo abuse and psychological trauma in their rehabilitation process.
Way Forward
- In 2018, the Supreme Court established a committee, led by retired Justice Amitava Roy, to address Prison Reforms.
- The committee proposed several recommendations to alleviate overcrowding, such as expediting trials, increasing the lawyer-to-prisoner ratio, establishing special courts, and minimizing adjournments.
- Additionally, it suggested providing a free phone call to every new prisoner during their first week in jail and improving kitchen facilities.
- Pertinently, Section 304 of the Indian Penal Code outlines the punishment for custodial deaths, and Section 30 of the Protection of Human Rights Act mandates the installation of CCTV cameras inside jails.
- All these provisions must be diligently complied with for effective prison management.
Source: TH
Genetically Engineered Insects
Tag: GS- 3 Biotechnology GS– 2 Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
India’s goal, as articulated in the ‘Bioeconomy Report 2022’ by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), is to elevate the Bioeconomy’s share of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) from the current 2.6% to 5% by the year 2030.
Key Highlights of the Bioeconomy Report 2022
- India’s bioeconomy is experiencing robust growth, set to reach USD 150 billion by 2025 and surpass USD 300 billion by 2030.
- In 2021, the sector saw a remarkable 14.1% increase, reaching USD 80 billion, with daily contributions of USD 219 million.
- The year witnessed the establishment of three biotech startups daily, totalling 1,128. With over USD 1 billion invested in research and development, the industry showcases a commitment to innovation.
- Despite the global pandemic, India administered 4 million Covid-19 vaccine doses daily, reflecting resilience.
- Over the past decade, biotech startups have surged from 50 to over 5,300, expected to double by 2025.
- The Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) and 74 bio-incubation centres across 21 states/UTs have played a pivotal role, fostering a supportive environment.
- India ranks second globally in the number of USFDA-approved manufacturing plants outside the US, highlighting its prominence in the biotech industry.
About Genetically Modified Insects and their challenges
- Genetically engineered (GE) insects are organisms with altered genetic material for specific traits.
- Applications include vector and crop pest management, healthcare protein production, and genetic improvement of beneficial insects.
- Challenges include ecological impacts, unintended consequences, ethical concerns, regulatory challenges, and ensuring long-term stability.
- Guidelines lack specificity on GE insect purposes in India, leading to uncertainty for researchers and hindering progress.
- Ambiguities in definitions and regulatory frameworks pose challenges to funding and scientific advancements.
- Ensuring cost-effectiveness and scalability in large-scale applications remains an ongoing challenge.
Way Forward
- Establishing comprehensive and transparent policies is essential to attain the ambitious goals outlined for the bioeconomy.
- Effectively addressing the challenges associated with GM insects necessitates a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach, involving scientists, policymakers, ethicists, and the public.
- This ensures the realization of the benefits of genetically engineered insects while minimizing potential risks.
- Continuous research and open dialogue are imperative for responsibly navigating these complexities.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2012) Q. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? To enable them to withstand drought To increase the nutritive value of the produce To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations To increase their shelf life Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 and 4 only (c) 1, 2 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 Ans: (c) |
Source: IE
Char Dham All Weather Road Project
Tag: GS – 2 Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Arising Out of Design & Implementation of Policies GS Paper – 3
In News:
Teams engaged in rescue operations are racing against time to save 40 laborers trapped following the collapse of a section of an under-construction tunnel in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
About Char Dham All Weather Road Project
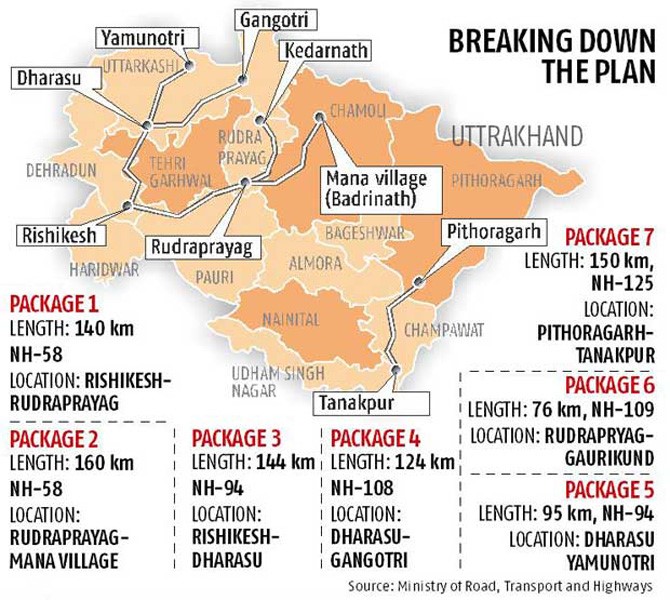
- Chardham Pariyojana is designed to enhance connectivity to the Himalayan pilgrimage centres of Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri, with the goal of making journeys to these sites safer, faster, and more convenient.
- The project encompasses the widening of nearly 900 km of highways connecting the pilgrimage sites and the Tanakpur-Pithoragarh stretch of National Highway 125, a segment of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra route.
- In terms of national security, the project serves as strategic feeder roads connecting the India-China border with Army camps in Dehradun and Meerut, where missile bases and heavy machinery are stationed.
- The implementing agencies include the Uttarakhand State Public Works Department (PWD), Border Roads Organisation (BRO), and the National Highway & Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL), a fully owned company of the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways.
- However, the project raises environmental concerns, potentially impacting around 690 hectares of forests, including 55,000 trees, and involving the removal of an estimated 20 million cubic meters of soil.
- The extensive widening of roads, coupled with the ruthless harvesting or uprooting of vegetation, poses risks to biodiversity and regional ecology.
- Noteworthy species, such as the Kalij Pheasant, Tragopans, various species of Vultures, and the endangered Golden Mahseer fish, inhabit the area.
- Although the CharDham project is not directly linked to the recent Chamoli glacier tragedy, indiscriminate blasting during road construction could create cracks in soil and rocks, increasing the risk of future flash floods.
Source: TH
Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA)
Tag: GS-3 Internal Security
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) extended the ban, under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), on eight “Meitei extremist organizations” that advocate for the secession of Manipur from India through armed struggle.
About Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA)
- Enacted in 1967, the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) is geared towards effectively preventing associations involved in unlawful activities in India.
- Unlawful activities, as defined by the Act, encompass actions taken with the intent to disrupt India’s territorial integrity and sovereignty.
- The Act confers absolute power to the central government, allowing it to declare an activity as unlawful through an Official Gazette.
- The UAPA prescribes severe penalties, including the death penalty and life imprisonment.
- It applies to both Indian and foreign nationals, treating offenders the same way even if the crime occurs on foreign soil.
- The investigating agency under the UAPA must file a charge sheet within a maximum of 180 days after arrests, with the possibility of extensions after informing the court.
- An important amendment in 2004 added “terrorist act” to the list of offenses, leading to the banning of 34 outfits involved in terrorist activities.
- Prior to this amendment, “unlawful” activities primarily referred to actions related to secession and cession of territory.
- In August, Parliament approved the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Bill, 2019, allowing the designation of individuals as terrorists based on specified grounds.
- The Act grants the Director General of the National Investigation Agency (NIA) the authority to approve the seizure or attachment of property in cases investigated by the agency.
- Furthermore, it empowers NIA officers, ranked Inspector or above, to investigate terrorism cases in addition to those conducted by state officers of the rank DSP or ACP or above.
Source: TH
PM 2.5
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Post Diwali celebrations, three major Indian cities appeared on the list of the world’s most polluted cities, as per a ranking by the Swiss air purifier company, IQAir.
About PM 2.5 pollution
- Fine particles, known as particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5), are minuscule particles or droplets in the air measuring two and a half microns or less in width.
Health Impact of PM2.5
- Particles in the PM2.5 size range can penetrate deep into the respiratory tract, reaching the lungs.
- Exposure to these fine particles can lead to short-term health effects such as irritation of the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, along with symptoms like coughing, sneezing, runny nose, and shortness of breath.
- Prolonged exposure is associated with increased rates of chronic bronchitis, reduced lung function, and higher mortality from lung cancer and heart disease.
Sources of PM2.5
- Outdoor sources include vehicle exhausts, industrial operations, and natural events like forest fires.
- Indoors, common activities like smoking, cooking, burning candles, and using fireplaces or fuel-burning heaters contribute to PM2.5 levels.
International Impact
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution causes an estimated seven million deaths globally each year, with 9 out of 10 people breathing air containing high pollutant levels.
- NASA satellite data reveals that over 4 in 10 Indians are exposed to particulate matter levels in the air that exceed five times the recommended safety limit.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2016) Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? Carbon dioxide Carbon monoxide Nitrogen dioxide Sulphur dioxide Methane Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 2, 3 and 4 only (c) 1, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (b) Exp: National Air Quality Index (AQI) is a tool for effective communication of air quality status to people in terms which are easy to understand. It transforms complex air quality data of various pollutants into a single number (index value), nomenclature and colour. There are six AQI categories, namely Good, Satisfactory, Moderately Polluted, Poor, Very Poor, and Severe. It considers eight pollutants namely: Carbon Monoxide (CO), hence, 2 is correct. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), hence, 3 is correct. Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), hence, 4 is correct. Ozone (O3), PM 2.5, PM 10, Ammonia (NH3), Lead (Pb). Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer. Mains (2021) Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? |
Source: TH
The University Grants Commission (UGC)
Tag: GS-2 Statutory Bodies
In News:
The University Grants Commission (UGC) has officially published the regulations governing foreign universities intending to establish campuses in India.
About The University Grants Commission
- The University Education Commission, formed in 1948, recommended the establishment of the University Grants Commission (UGC) in India.
- The UGC was formally inaugurated in December 1953 and established as a statutory body in November 1956, entrusted with coordinating, determining, and maintaining standards in university education.
- The UGC operates through regional centres and its head office in New Delhi.
- It holds a unique role as both a grant-giving agency and a coordinator for higher education institutions.
- Its responsibilities include promoting and coordinating university education, setting standards for teaching and research, framing regulations, monitoring education developments, and advising governments on educational improvement.
- The UGC oversees accreditation through various autonomous statutory bodies, including AICTE, ICAR, BCI, NCTE, and others.
- Recent developments include plans in 2018 to repeal the UGC Act, later reworked in 2019, and the UGC’s announcement in 2022 allowing students to pursue two academic programs simultaneously, aligning with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s emphasis on diverse learning pathways.
Source: TH
Iceland
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Recently, Iceland declared a state of emergency following a sequence of strong earthquakes in the southwestern Reykjanes peninsula, which could be indicative of an imminent volcanic eruption
About Iceland
- Iceland is a Nordic Island country located in the North Atlantic Ocean.
- It is known for its stunning landscapes, including glaciers, hot springs, waterfalls, and volcanic activity.
- Iceland is situated at the juncture of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates, leading to a high level of geological activity.
- It has numerous geysers, hot springs, and volcanic features.
- The country is also characterized by vast glaciers, fjords, and a rugged coastline.
- Reykjavik is the capital and largest city of Iceland.
- Other significant towns include Akureyri, Hafnarfjörður, and Kópavogur.
- Iceland has a relatively small population, with a focus on cultural homogeneity.
- The majority of the population is of Icelandic descent.
- The official language is Icelandic.
- Iceland is a parliamentary republic with a multi-party system.
- The President of Iceland is the head of state, and the Prime Minister is the head of government.
- Despite its name, Iceland has a relatively mild climate compared to other northern regions.
- Winters can be cold, and summers are cool.
- The country experiences long days during the summer months due to its high latitude.
- Due to its high latitude, Iceland experiences the phenomenon of the midnight sun during summer, where the sun remains visible for most of the night.
- Conversely, during winter, there are extended periods of darkness known as polar nights.
- Iceland is prone to earthquakes due to its location on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a tectonic plate boundary where the North American and Eurasian plates are drifting apart.
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a divergent or constructive plate boundary where tectonic plates are moving away from each other.
- In the case of Iceland, the North American plate and the Eurasian plate are moving apart, leading to the formation of new crust.
- This process results in volcanic activity and frequent earthquakes.
- The movement of tectonic plates is not smooth; it involves constant pressure, stress, and occasional release of energy.
- When the stress along the boundaries of these plates becomes too much, it is released in the form of earthquakes.
- In Iceland, the plates are actively moving, causing a higher frequency of seismic activity.
- Iceland is situated on a hot spot, a location where magma from the Earth’s mantle reaches the surface.
- This volcanic activity is a consequence of the tectonic plate movement.
- The combination of volcanic activity and plate boundaries makes the region highly prone to earthquakes.
Source: TH
Baler Machine
Tag: GS-3 Environment, Cropping Patterns, Direct & Indirect Farm Subsidies, E-Technology in the Aid of Farmers, Indigenization of Technology
In News:
Given the Supreme Court’s attention to the issue of farm fires, there is a growing demand for Belar, a machine designed for off-site stubble management, in Punjab and neighbouring regions.
About Baler Machine
- Balers play a crucial role in stubble compression, functioning as hydraulic presses to compact crop residues into dense and manageable packages.
- These compressed stubbles are securely bound using twine, wire, or strapping.
- Before employing a baler machine, farmers use a tractor-mounted cutter to cut the crop residue.
- A tractor-mounted baler machine then compresses the stubble into compact bales using netting.
Significance:
- Environmental Preservation: Eliminates the necessity for crop stubble burning, contributing to a reduction in air pollution and soil degradation.
- Farmers traditionally burn stubble after harvesting, contributing to air pollution. Balers provide an eco-friendly alternative by compressing stubble into bales.
- Resource Efficiency: Efficiently compresses stubble, facilitating easier handling, transport, and storage.
- It enables farmers to promptly plough the field and sow the next crop.
- Economic Gain: Creates opportunities for revenue generation through the sale of compressed stubble as a valuable resource.
Source: TH
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

