In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Reformed Indian Criminal Law
- 2 IMF Quota Review
- 3 New Soil Health Card Scheme
- 4 Interventions under National Food Security Mission
- 5 Teaching in the mother tongue
- 6 China’s ‘Sponge Cities’ and Their Flood Challenges
- 7 Health Facilities for Tribal Women Report
- 8 Aromatic rice ‘Mushkbudji’
- 9 Inclusive Conservation Initiative (ICI)
- 10 Asian Elephant
- 11 Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- 12 FAQs
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Reformed Indian Criminal Law
Tags: GS Paper – 2: Judiciary; Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
The Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita Bill 2023, the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita Bill, 2023 and the Bharatiya Sakshya Bill, 2023, have been brought by repealing the Indian Penal Code, 1860, Criminal Procedure Code, (1898), 1973 and Indian Evidence Act, 1872 respectively.
About the 3 new Bills:
- Inclusive:
- Government has brought this law by taking a very principled decision to bring citizens at the centre, instead of governance.
- 18 States, 6 Union Territories, the Supreme Court, 16 High Courts, 5 Judicial Academies, 22 Law Universities, 142 Members of Parliament, around 270 MLAs and public have given their suggestions on these new laws.
- Intense discussions were held for 4 years.
- Broadens horizon:
- The law expands the definition of documents to include electronic or digital records, e-mails, server logs, computers, smart phones, laptops, SMS, etc.
- Provision to digitise the entire process from FIR to judgement.
- Videography has been made compulsory at the time of search and seizure which will be part of the case and will not implicate innocent citizens.
- Without such recording by the police, no charge sheet will be valid.
- A National Forensic Science University will be setup to promote forensic science in a bid to increase the conviction ratio.
- After three years, every year 33,000 forensic science experts and scientists will be available in the country.
- The visit of the forensic team is being made compulsory on the crime scene of crimes having provision for punishment of 7 years or more.
- The government is going to start Zero FIR for the first time.
- Provision of e-FIR is being added for the first time.
- Protecting the innocent:
- The statement of the victim has been made compulsory in the cases of sexual violence and the video recording of the statement has also been made compulsory in the cases of sexual harassment.
- It will be compulsory for the Police to give the status of the complaint in 90 days and thereafter every 15 days, to the complainant.
- No government will be able to withdraw a case of imprisonment of 7 years or more without listening to the victim.
- Scope of summary trial has been increased in petty cases, now crimes punishable up to 3 years will be included in summary trial.
- A time limit of 90 days is fixed for filing the charge sheet. The investigation will have to be completed within 180 days and trial should begin.
- Courts will now be bound to give notice of framing of charge to the accused person within 60 days, within 30 days after the completion of arguments, the Hon’ble Judge will have to give verdict.
- The order will have to be made available online, within 7 days
- Sex on the pretext of false promise of marriage, employment, promotion and false identity has been made a crime for the first time.
- For mob lynching, all three provisions of 7 years in jail, life imprisonment and capital punishment have been made.
- Other provisions:
- Government has to decide on permission within 120 days for trial against civil servant or police officer else it will be treated as deemed permission and trial will be started.
- A provision has been brought for attachment of property of declared offenders.
- Now the death penalty can only be changed to life imprisonment, life imprisonment to a minimum of 7 years and 7 years to a minimum of 3 years, no culprit will be freed.
- The government is going to repeal sedition law completely because India is a democracy and everyone has the right to speak.
- Earlier, there was no definition of terrorism, now crimes like armed insurgency, subversive activities, separatism, challenging the unity, sovereignty and integrity of India have been defined in this law for the first time.
- A historic decision regarding trial in absentia has been taken, a person declared fugitive by a Sessions Court judge will be tried and sentenced in his absence.
Source: PIB Gov.
IMF Quota Review
Tags: GS-II: International relations
In news:
RBI Governor’s Call for IMF Quota Review: Enhancing Assistance and Accessibility at a G20 Finance Track seminar on the global economy in Mumbai.
About IMF Quota Review
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governor has recently emphasized the importance of review of quotas at the IMF to enhance the IMF’s capabilities and reduce perceived stigma and limited access.
- Major highlights:
- The review’s completion can enhance the IMF’s ability to provide effective assistance to distressed countries.
- The IMF’s support is tied to member countries’ quota sizes which forces poor countries to seek help from other sources beyond the IMF due to stigma or access issues.
- The IMF and World Bank play a central role in addressing global debt vulnerabilities and are integral to the international monetary system.
- There is need for financing mechanisms that are timely, non-stigmatizing, and easily accessible to countries in need.
- Present limitations of IMF funding mechanisms, including precautionary lending lines and stand-by arrangements calls for both IMF and World Bank to do more for countries in debt distress.
- Overall, completing quota reforms will enhance the legitimacy of the IMF in overseeing the international monetary and financial system besides not letting the burden of debt hinder global economic growth.
Source: The Hindu
New Soil Health Card Scheme
Tags: GS-II: Government schemes
In News:
Union minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare deliberates on new Soil Health Card Scheme in Rajya Sabha
About New Soil Health Card Scheme
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare has recently introduced new soil health card scheme aimed at enhancing soil health and fertility for farmers across India.
- The Soil Health Card Scheme was first introduced in 2014-15 to provide soil health cards to all farmers in India.
- The Soil Health Card scheme is now a component of the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) cafeteria scheme under “Soil Health & Fertility” since 2022-23.
- Important features:
- The Soil Health Card portal has been integrated with a Geographic Information System (GIS) to map test results.
- Mobile application improvements include restricted sample collection regions, automated latitude and longitude selection, and QR code generation.
- It sets guidelines for setting up Village Level Soil Testing Labs (VLSTLs) besides training sessions for states to familiarize them with the new system.
- These VLSTLs can be established by rural youth, Self Help Groups (SHGs), schools, and agriculture universities.
- Entrepreneurs submitting applications for VLSTLs need to be aged between 18 and 27 years and provide necessary qualifications.
- The testing labs will receive training on soil sampling, testing, generation of soil health cards, and educating farmers on fertilizer and crop recommendations.
- Detailed soil mapping at 1:10000 scale will be conducted using satellite data and field surveys by Soil & Land Use Survey of India.
- This Soil Resource Information is distinct from Soil Health Cards and is generated separately.
- Overall, the new scheme will help enhance implementation, monitoring and information on soil nutrient status and appropriate nutrient dosages to improve soil health and fertility.
Source: PIB Gov.
Interventions under National Food Security Mission
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Food Security)
Why in News:
Recently, in a written response in the Lok Sabha, the Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare shared significant updates regarding the progress within the National Food Security Mission.
National Food Security Mission (NFSM):
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme launched in 2007 based on the recommendations of the agriculture sub-committee of National Development Council (NDC).
- Objectives of the mission:
- Sustainable increase in the production of targeted crops such as rice, wheat, pulses primarily and then extended to coarse cereals, nutri-cereals, and oilseeds as well.
- Restoration of soil fertility and productivity at the individual farm level and rise in farm level net income.
Major Interventions under NFSM:
- Cluster Demonstrations and Improved Practices: It facilitates farmers through States/Union Territories to conduct cluster demonstrations that showcase optimized agricultural practices and improved techniques for crop cultivation and management.
- Seed Production and Distribution: It focuses on the development, production, and distribution of HYV and hybrid crops to enhance both the quality and quantity of agriculture output contributing to food security.
- Farm Mechanization and Resource Conservation: It focuses on the implementation of modern and efficient farm machinery, coupled with the adoption of resource conservation tools to optimize resource utilization and contribute to sustainable production.
- Plant Protection and Nutrient Management: It emphasizes protective measures against pests and diseases. Effective nutrient management is also promoted for improved crop productivity.
- Oilseeds Production Focus: NFSM-Oilseeds initiative focuses on boosting oilseed production to achieve self-sufficiency in edible oil.
- National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP): It was launched in 2021 to reduce the dependency on edible oil imports. The mission aims to expand oil palm cultivation, increase crude palm oil production, enhance productivity, and alleviate the burden of imports.
Water Management for Sustainable Agriculture:
- Per Drop More Crop: Launched in 2015-16, it focuses on water use efficiency through micro-irrigation systems like drip and sprinkler irrigation.
- Command Area Development & Water Management: Part of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, it aims to enhance irrigation efficiency.
- Bureau of Water Use Efficiency: It promotes strategies to improve water use efficiency in irrigation, industries, and domestic settings.
- National Water Mission: It launched the ‘SahiFasal’ campaign in 2019, which encourages farmers in water-stressed regions to cultivate crops that are economically viable, water-efficient, and aligned with agro-climatic conditions.
Challenges Related to Food Security in India:
- Agricultural Challenges: India’s agricultural sector grapples with climate change impacts, unpredictable weather patterns, pest outbreaks, and soil degradation, all of which contribute to reduced crop yields and food scarcity.
- Land Fragmentation: Fragmented land holdings due to inheritance laws lead to small and uneconomical plots that hinder the adoption of modern farming techniques.
- Lack of Diversification: Overemphasis on staple crops like rice and wheat limits dietary diversity, contributing to malnutrition issues.
- Rising Food Prices: Fluctuations in global and domestic food prices can render essential food items unaffordable for vulnerable populations, leading to food insecurity.
Way Forward:
- The implementation of detailed agro-ecological zoning maps, incorporating advanced geospatial analysis, can identify the most suitable crops for specific regions based on their natural characteristics. It optimizes resource utilization and minimizes the risk of crop failure.
- Encouraging urban residents to convert lawns and unused spaces into edible landscapes can significantly contribute to local food production, fostering self-sufficiency and community involvement.
- Implementing systems to extract nutrients from wastewater and organic waste, followed by their conversion into fertilizers, offers a sustainable approach to nutrient management and reduces the dependence on synthetic fertilizers.
- The development of AI-powered cameras and sensors capable of detecting pest and disease outbreaks early can revolutionize pest management by enabling targeted interventions and minimizing the widespread use of pesticides.
- The integration of agriculture with renewable energy production, such as placing solar panels above crops, serves multiple purposes: providing shade, reducing water evaporation, generating clean energy, and optimizing resource use.
Source: PIB Gov.
Teaching in the mother tongue
Tags: GS – 2: Social Justice (Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education)
Why in News:
Recently, IMF’s executive Director has called the CBSE’s decision a right call. Their Bhasha, Their Future- Research has shown teaching in the mother tongue leads to better skilling as well as a better grasp of English.
Efforts made by India to teach children in their mother tongue:
Historical Efforts:
- Mahatma Gandhi believed that English as a primary medium created a divide between elites and the masses, hindering knowledge dissemination.
- Leaders like C Rajagopalachari, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Gopal Krishna Gokhale, and Annie Besant stressed an Indian-controlled education system that values the country’s ethos.
Government of India Efforts:
- The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) issued a directive, emphasizing the use of the mother tongue for instruction and displaying its commitment to native language education.
- The National Education Policy also encapsulates the intent to promote mother tongue instruction.
UNESCO Findings on Mother Tongue Instruction:
- Global Advocacy: Since 1953, UNESCO has consistently promoted mother tongue education through its Global Education Monitoring Reports.
- Learning Impact: Being taught in a language other than one’s own can have negative effects on learning, especially for children from poor backgrounds.
- Duration Recommendation: At least six years of mother tongue instruction is necessary to reduce learning gaps for minority language speakers.
- Pedagogical Reasoning: A background study for the 2005 UNESCO report emphasized that mother tongue-based bilingual schooling is rarely challenged based on its educational logic.
Way Forward:
- Implement the CBSE’s directive to prioritize mother tongue instruction.
- Address challenges in teacher recruitment, curriculum development, and teaching materials to accommodate linguistic diversity.
- Government schools like Kendriya Vidyalayas and Navodaya Vidyalayas should lead in implementing mother-tongue instruction.
Source: The Times of India
China’s ‘Sponge Cities’ and Their Flood Challenges
Tags: GS-III: Climate change
In News:
China’s “sponge city” initiative aimed at reducing urban flood risks has faced challenges in effectively preventing recent floods
About China’s Sponge Cities
- The initiative was launched in 2015 to enhance flood resilience in major cities and optimize rainwater usage through architectural, engineering, and infrastructural modifications.
- Heavy rainfall in recent weeks has led to devastating floods, highlighting the inadequacy of the sponge city approach.
- Important features:
- The sponge city scheme was initiated to address issues related to urbanization, flooding, and drought in densely populated areas.
- It incorporated Nature-based solutions involving permeable asphalt, construction of canals and ponds, and wetland restoration to improve water distribution, drainage, and storage.
- Traditional flood plains along major rivers were covered with impermeable concrete due to rapid urbanization, leading to waterlogging and floods.
- Local pilot initiatives demonstrated positive results, with green roofs and rain gardens effectively reducing run-offs.
- Challenges:
- Sponge city approach has been inconsistent as out of 30 pilot sponge cities chosen in 2015 and 2016, only 64 out of 654 cities had established legislation to follow guidelines as per mandates.
- There has been lack of significant government attention to sponge city construction and called for urgent national legislation.
- Despite sponge city efforts, the initiative couldn’t prevent recent floods, exemplified by Zhengzhou, which allocated a substantial budget but couldn’t cope with record-breaking rainfall in 2021.
- These cities infrastructure can handle a maximum of around 200 millimetres (7.9 inches) of rain per day, while some areas experienced much higher rainfall in short periods.
- Besides, Climate change has also added to the challenge with heavy rain affecting regions that are less advanced in sponge city development, particularly in the arid north.
- Overall, despite it challenges balancing infrastructure development, environmental restoration, and effective policies is crucial for future flood resilience.
Source: Reuters
Health Facilities for Tribal Women Report
Tags: GS-II: Government Policies
In news:
Parliamentary Committee flags lack of disaggregated Data on Tribal Populations
About Health Facilities for Tribal Women Report
- The Parliamentary Committee on the empowerment of women has recently presented a report addressing the absence of disaggregated data on the health conditions of tribal populations in India.
- The committee advocates for more empowerment of the Tribal Affairs Ministry and underscores the need for sectoral policies in health, education, nutrition, and more.
- Major findings:
- The report underscores the persistent health challenges faced by tribal women across the country with diseases like sickle cell anaemia and leprosy remain prevalent among tribal populations.
- High rates of anaemia, child marriage, early motherhood, and low body mass index contribute to elevated mortality rates among tribal women.
- Lack of disaggregated data on the health and absence of proper maternal mortality ratio data has impede the formulation of effective policies for maternal and infant health among tribals.
- Tribal populations are disproportionately affected by communicable diseases such as leprosy, tuberculosis, and cholera compared to other social groups.
- Over half of tribal women in the reproductive age group suffer from anaemia with sickle cell disease testing reveals a significant number of carriers and diagnosed cases among tribal populations.
- Major recommendations:
- The report calls for empowering the Tribal Affairs Ministry to enable better planning and resource allocation.
- It also recommends that the ministry should be granted authority for designing sector-specific policies related to health, education, nutrition, skill development, and livelihood.
- Extracting a sub-sample of tribal populations from the National Family Health Survey-5 to gather targeted data with regular examination of data collected through the center of excellence.
- Establishment of self-help kiosks at the block level to facilitate health data registration for tribes lacking access to technology.
- Empowerment of the Tribal Affairs Ministry to formulate area-specific, sector-specific, and group-specific schemes for tribal welfare.
- Overall, by addressing challenges, gathering data, and empowering the Tribal Affairs Ministry, steps can be taken to enhance the health and well-being of tribal communities in India.
Source: The Hindu
Aromatic rice ‘Mushkbudji’
Tag: GS-1 Geography
Why in news?
Cultivation of aromatic rice ‘Mushkbudji’ gives Kashmir farmers high returns.
About
- Mushkbudji is a short, bold aromatic rice cultivated in the elevated regions of the Kashmir valley.
- It showcases a distinct combination of flavors, fragrances, and appealing sensory qualities.
- Its predominant cultivation areas include Sagam, Panzgam, and Soaf Shali in the Anantnag district, as well as the Beerwah region in the Budgam district.
- The utilization of this aromatic rice in Kashmir is primarily reserved for significant events such as special gatherings, weddings, and festive celebrations.

Source: Deccan Herald
Inclusive Conservation Initiative (ICI)
Tag: GS-3 Environment
Why in news?
Less than 1% of mitigation & adaptation funding went to the world’s indigenous groups despite more commitment.
About
- Inclusive Conservation Initiative endorsed by Global Environment Facility (GEF) in 2022.
- ICI supports Indigenous Peoples and local communities- ILPC to secure and enhance their stewardship over landscapes, seascapes, and territories with high biodiversity and irreplaceable ecosystems.
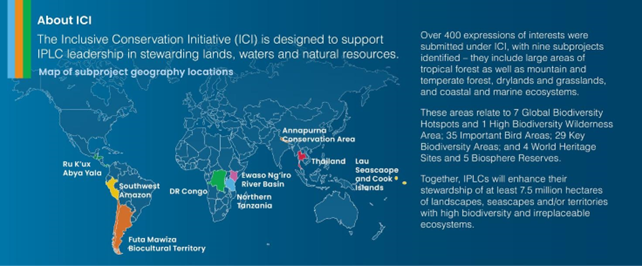
Source: Down To Earth
Asian Elephant
Tag: GS- 3 Environment
Why in news?
Recently, the environment minister has emphasized mainstreaming biodiversity conservation in India’s economic development to ensure ecological well-being and sustainability.
About
- Asian elephants are listed as “Endangered” on the IUCN Red List of threatened species.
- Elephants are important ecosystem engineers.
- They make pathways in dense forested habitat that allow passage for other animals.
- An elephant footprint can also enable a micro-ecosystem that, when filled with water, can provide a home for tadpoles and other organisms.
- As keystone species, they help maintain biodiversity of the ecosystems they inhabit.
- During the dry season, elephants use their tusks to dig for water, which provides water for other animals that share harsh habitats.
- They are also one of the major ways in which trees disperse their seeds; some species rely entirely upon elephants for seed dispersal.

Source: PIB Gov.
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
Tag: GS-3 Economy
Why in news?
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) and Common Service Centre (CSC) launch “Niveshak Sarathi” Vans for Delhi-NCR.
About
- IEPFA was established in 2016 under the Companies Act, of 2013.
- The Authority is entrusted with the responsibility of administration of the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF) and making refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc to investors and promote awareness among investors.
- IEPF is under the control of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs
Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF).
It has been established under Section 205C of the Companies Act, 1956 by way of the Companies (Amendment) Act, 1999.
The following amounts that remained unpaid and unclaimed for a period of seven years from the date they became due for payment are credited to the Fund:
- Amounts in the unpaid dividend accounts of the companies
- The application money received by companies for allotment of any securities and due for refund
- Matured deposits with companies
- Matured debentures with companies
- Grants and donations are given to the fund by the Central Government, State Governments, companies or any other institutions for the purposes of the Fund
- The interest or other income received out of the investments made from the fund
Source: PIB Gov.
FAQs
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


