
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Challenges posed by sand and dust storms (SDSs)
- 2 The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023
- 3 Online Gaming Tax and its implications
- 4 Air Pollution Control and its Measures
- 5 Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour
- 6 National Human Rights Commission and UN Human Rights Council
- 7 Welfare Schemes and Brain Development
- 8 GSI survey of the Siachen
- 9 Right to Remain Silent
- 10 National Asset Reconstruction Company (NARCL)
- 11 France
- 12 Sanipreneurs
- 13 Phosphate Discovery in Norway
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 14.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 14.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 14.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 14.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 14.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 15 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Challenges posed by sand and dust storms (SDSs)
Tag: GS-1 Geography
In News:
Sand and dust storms (SDS) have increased dramatically in frequency and severity in recent years, according to the United Nations.
About
- Sand and dust storms are meteorological phenomena characterized by strong winds that carry and transport large amounts of airborne particles, such as sand, dust, and dirt. SDS also known as haboobs or siroccos.
- SDS are common meteorological hazards in arid and semi-arid regions, usually caused by thunderstorms/ strong pressure gradients associated with cyclones, which increase wind speed over a wide area.
- Sand and dust storms can be triggered by various factors, including strong winds, drought conditions, and the presence of large open areas with exposed soil or desert regions. They are most common in desert areas, but they can also occur in coastal regions, dry lake beds, and agricultural lands.
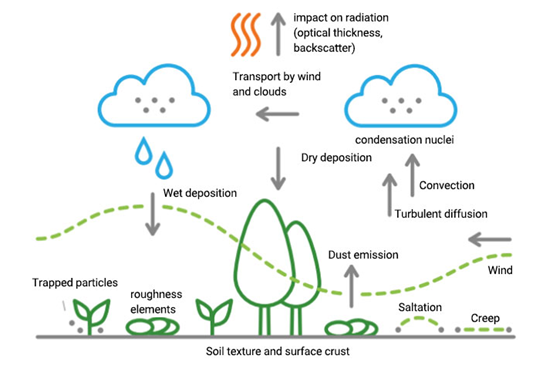
Impacts of Sand and dust storms (SDS)
Environmental Impact:
Sand and dust storms can have adverse effects on ecosystems, vegetation, and agricultural lands. They can strip away topsoil, damage crops, and affect wildlife habitats.
- Affect Precipitation: Dust particles act as condensation nuclei for cloud formation affecting the amount and location of precipitation.
- Green house effect: Airborne dust functions in a manner similar to the greenhouse effect, which affects the energy reaching the Earth’s surface.
- Air Pollution: SDS are recurring environmental phenomena which reduce air quality, and visibility.
Impact on human health:
- Dust particles larger than 10 μm in size are unable to be inhaled and therefore can only cause harm to external organs upon contact.
- Particles smaller than 10 μm have a tendency to become trapped in the upper respiratory tract, nose, and mouth, potentially leading to respiratory disorders like asthma.
On the land and marine ecosystems:
- Surface dust deposits are a source of micronutrients for both continental and maritime ecosystems. For example, Saharan dust is thought to fertilise the Amazon rainforest.
Negative impacts on agriculture:
- Burying seedlings and reducing crop yields.
- Resulting in the loss of plant tissue.
- Decreasing photosynthetic activity, which is essential for plant growth.
- Contributing to increased soil erosion, leading to the degradation of agricultural land.
Infrastructure damage:
The abrasive nature of sand and dust particles can cause damage to buildings, vehicles, and other infrastructure. Fine particles can infiltrate machinery, electronics, and ventilation systems, leading to operational issues.
Hot Spot of Dust Storm
Sahara Desert, Middle East, Taklamakan Desert in northwest China, Southwest Asia, Central Australia, Etosha and Makgadikgadi basins of southern Africa, Salar de Uyuni in Bolivia and Great Basin in the US.

Concerns raised by the UN:
- Approximately 2 million tonnes of sand and dust are introduced into the atmosphere each year.

- Sand and dust storms frequently originate in dryland regions, which constitute 41% of the Earth’s land surface and include some of the most vulnerable ecosystems susceptible to the effects of global climate change.
- The frequency and intensity of sand and dust storms have been amplified by human-induced climate change.
- The impact of sand and dust storms is experienced worldwide, affecting regions across the globe, regardless of their level of development.
- The increasing intensity and frequency of sand and dust storms pose a significant challenge to the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- These will especially affect Africa and the Middle East where desertification is most common. Global recognition of SDS as a hazard is generally low.
Way Forward:
- The United Nations General Assembly, acknowledging the significant impact of sand and dust storms on the sustainable development of affected nations and regions, recognized this challenge in 2015. Furthermore, the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) recently marked the inaugural International Day of Combating Sand and Dust Storms on July 12, 2023.
- To address the issue of sand and dust storms, policy and planning efforts should focus on reducing societal vulnerability by mitigating the effects of wind erosion. This requires a comprehensive approach involving multiple sectors, supported by effective information-sharing. Both short-term and long-term interventions are necessary, and engaging various stakeholders is crucial. Additionally, raising awareness about sand and dust storms is an essential component of these efforts.

Source: Down to Earth
The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023
Tags: GS – 2: Social Justice (Issues related to poverty and hunger)
Why in News:
Recently, the State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023 report was released.
About the Report:
- The report was released by the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), World Food Programme (WFP), and World Health Organization (WHO).
- Theme of the report was “Urbanisation, agrifood systems transformation, and healthy diets across the rural-urban continuum”.
- It is an annual report which aims to inform on progress towards ending hunger, achieving food security and improving nutrition and to provide an in-depth analysis of key challenges for achieving this goal in the context of the SDG.
Key findings of the report:
- Over 700 million people was facing hunger in the world in 2022.
- Around 2.4 billion individuals did not have consistent access to nutritious, safe, and sufficient food in 2022.
- In 2021, 22.3% (148.1 million) children were stunted (too short for their age), 6.8% (45 million) were wasted (too thin for their height), and 5.6% (37 million) were overweight.
- Due to urbanization, there is increase in the consumption of processed and convenience foods which is leading to increase in overweight and obesity rates across urban, peri-urban, and rural areas.
- The rural regions which were previously self-sustaining (especially in Asia and Africa), are now dependent on national and global food markets.
Challenges identified by the report:
- Persistent Food Crisis: There are many places in the world facing deepening food crises.
- Inequitable access to Nutritious Food especially for women and residents of rural areas.
- Alarming high child malnutrition.
- It is projected that by 2050, 70% of the global population will reside in cities, posing significant challenges for food systems to cater to these urban populations.
A case study from India – The Role of urban proximity in agricultural intensification:
- The town of Doddaballapura, located in Bangalore’s Rural district, serves as evidence of the essential role of small and intermediate cities and towns in increasing the use of modern agricultural inputs in rural areas.
- Farmers located farther from Bangalore show a higher use of modern inputs due to the influence of Doddaballapura.
Way Forward:
- There is necessity of a reorientation of food systems to cater to these new urban populations and eradicate hunger, food insecurity, and malnutrition.
- The policy can strengthen intensification and increase productivity in farming close to small and intermediate cities and towns (SICTs).
- This will improve connectivity between farms and input-output markets, which will further reduce the cost of access to markets and also boost farmers’ access to and use of modern inputs.
Source: ORG Media
Online Gaming Tax and its implications
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Indirect tax)
Why in News:
At its 50th meeting, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council made changes to tax rates on various items and resolved the tax treatment for online gaming, casinos, and horse racing.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council:
- The GST Council is a constitutional body responsible for making recommendations on issues related to the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India.
- As per Article 279A (1) of the amended Constitution, the GST Council was constituted by the President.
- GST is imposed on both manufacturers and sellers of goods, as well as suppliers of services.
- GST is divided into five tax slabs – 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Uniform tax on online gaming:
- The uniform levy of 28% tax will be applicable on:
- The face value of the chips purchased in the case of casinos.
- The full value of the bets placed with the bookmaker/totalisator in the case of horse racing.
- The full value of the bets placed in the case of online gaming.
- The government will include online gaming and horse racing as taxable actionable claims – goods under the CGST Act, 2017.
- So far, lottery, betting, and gambling were classified as actionable claims.
Online Gaming Market in India:
- The Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of the industry between 2017-2020 was 38% whereas it is 8% in China and 10% in USA.
- It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% to reach Rs 153 billion in revenue by 2024.
Source: Indian Express
Air Pollution Control and its Measures
Tag: GS-3 Environmental Pollution
In News:
According to the analysis of Climate Trends, a nonprofit institution, the annual average of the most toxic air pollutant, particulate matter (PM) 2.5, was as poor in rural India as urban India in 2022. This challenges the government’s policy of investing in urban areas of the country for controlling air pollution
Key Findings of the Analysis:
- According to the analysis, in 2022, the average annual PM 2.5 level was 46.4 µg (micrograms) in rural India, barely below the urban level of 46.8 µg . The national limit is 40 µg
- Rural PM 2.5 pollution was found to be significantly high in Delhi (87.7 µg) and states like Bihar (74.5 µg), Haryana (67.8 µg), Uttar Pradesh (62.3 µg), Rajasthan (60.4 µg).
- Another analysis carried out by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), the rural population suffers more than its urban counterpart when it comes to the length of losing life span due to exposure to the toxic pollutant.
- Villagers, on average, lose over five years and two months of lifespan due to air pollution exposure, while city dwellers lose about four years and five months.
- Loss of over eight years of lifespan was recorded for rural residents in Uttar Pradesh, villagers of Bihar and Haryana villagers lose over seven years on average.
- 47% of the population lives outside the air quality monitoring network and 62% of the population do not have access to daily alerts on the local air quality index.
About National Clean Air Plan:
- NCAP was launched in 2019, with a tentative national level target of 20-30% reduction of PM 2.5 and PM 10 concentration by 2024.
- So far it has released around Rs 9,000 crores mainly for 131 cities, called non-attainment cities, which consistently go above the national air pollution limits.
- However, most rural areas do not have even any on-ground pollution measuring mechanism. Massive investment to combat urban air pollution is not contributing in any way to tackle country’s rural pollution
Measures to tackle air pollution comprehensively:
- Instead of selected cities, an airshade arrangement model needs to be pursued. Prioritisation in highly dense urban areas is understandable, there is a need to formulate policy and action in rural India as well.
- A larger network of high-spatial-resolution systematic, robust and continuous air pollutants monitoring over the rural and non-urban regions is the need of the hour.
Source: Down to Earth
Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour
Tag: GS-2 International Relations
In News:
French President Emmanuel Macron conferred France’s highest honour, the Grand Cross of the Legion of Honor, upon the Indian Prime Minister who is visiting France to attend the Bastille Day celebrations.
About the Grand Cross of the Legion of Honor
- The National Order of the Legion of Honor, is the highest French decoration, both civil and military, and is one of the most famous national honours in the world.

- Established in 1802 by Napoleon Bonaparte, The Legion of Honour is divided into five classes (lower to higher)– Knight, Officer, Commander, Grand Officer and Grand Cross. The PM was awarded the fifth honour.
- The colour of the ribbon is red and the badge is a five-armed Maltese asterisk hung on an oak and laurel wreath. On the obverse is the effigy of the Republic and on the reverse two tricolour flags surrounded by the motto ‘Honour and Fatherland’ written in French.
- Although the membership to the award is restricted to French nationals, foreign nationals who serve France or uphold its ideals may also be given a distinction of the Legion.
- Indian Prime Minister joins the ranks of other prominent world leaders like Nelson Mandela, King Charles, Angela Merkel.
- The PM announced the opening of a new Indian consulate in Marseille in France and said that Indian students doing masters in European countries will now get five-year-long post-study work visas.
- Describing people-to-people connect as a key foundation of the India-France partnership, he also asked the diaspora members to invest in India.
Other Awards conferred to the Indian Prime Minister:
- Order of the Nile by Egypt in June 2023
- Companion of the Order of Logohu by Papua New Guinea in May 2023
- Companion of the Order of Fiji in May 2023
- Ebakl Award by the Republic of Palau in May 2023
- Order of the Druk Gyalpo by Bhutan in 2021
- Legion of Merit by the US Government in 2020
- King Hamad Order of the Renaissance by Bahrain in 2019
- Order of the Distinguished Rule of Nishan Izzuddin by Maldives in 2019.
- Grand Collar of the State of Palestine Award in 2018
- Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud from Saudi Arabia in 2016.
Source:: PIB Gov.
National Human Rights Commission and UN Human Rights Council
Tags: GS-II: IR
In news:
In U.N. Human Rights Council vote, India stands against desecration of Quran
About National Human Rights Commission and UN Human Rights Council:
- The UN Human Rights Council has recently adopted the resolution ‘Countering religious hatred constituting incitement to discrimination, hostility or violence’ in the aftermath of recent acts of desecration of the Holy Quran.
NHRC:
- The NHRC is an independent statutory body established by the government of a particular country.
- The NHRC in India is an independent statutory body established under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993 passed by the Indian Parliament.
- These operates at the national level and is responsible for safeguarding human rights within that country.
- It investigates complaints of human rights violations, conducts inquiries, and recommends remedial measures.
- It also promotes awareness about human rights and educates the public on their rights and responsibilities and addressing violations within the country.
UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The UNHRC is a global intergovernmental body within the United Nations system consisting of 47 member states elected by the UN General Assembly.
- It addresses human rights issues and violations on a global scale by reviewing the human rights records of member states through the Universal Periodic Review (UPR) mechanism.
- It also receives and investigates allegations of human rights abuses and adopts resolutions to address them.
- Overall, NHRC and UNHRC are essential institutions whose collaboration and cooperation can contribute to the advancement of human rights worldwide.
Source: The Hindu
Welfare Schemes and Brain Development
Tags: GS-III: Health
In News:
Anti-poverty schemes may help poor children’s brains grow normally
About Welfare Schemes and Brain Development:
- Researchers in US have recently used data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) from the brain scans of over 10,000 children aged 9-11 years from 17 U.S. states.
- The study has shown a correlation between low-income families and lower brain development in children born out of poverty.
Major findings:
- The research suggests that anti-poverty policies can reduce the risk of smaller hippocampal volumes.
- Generous cash assistance programs and affordable healthcare can positively influence brain development.
- Children from higher-income families had larger hippocampal volumes and family income correlated with lower incidence of psychopathologies in children.
- More generous policies can reduce chronic stressors associated with low income, benefiting brain development.
- Access to financial resources allows families to make decisions that reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- However, the study’s findings may not directly apply to all regions due to varying economic conditions such as systemic discrimination, such as racism.
- Previously, In the 1960s, neuroscientists found evidence of impaired brain development in rats growing up in impoverished environments.
- Overall, addressing poverty and providing necessary support through welfare schemes can contribute to better cognitive and mental health outcomes for vulnerable populations.
Source: The Hindu
GSI survey of the Siachen
Tags: General Studies –1 Geography
Why in news?
The first Geological Survey of India (GSI) expedition to the Siachen glacier took place in June 1958, led by V. K. Raina, an Indian geologist.
About:
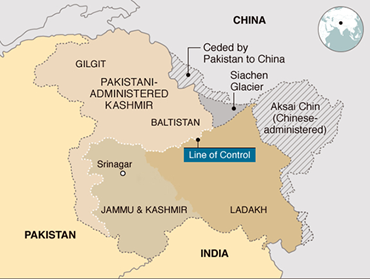
- Significance: This event is of historical and geostrategic significance as it puts to rest all myths to the effect that Pakistan was in control of the glacier since the beginning.
Siachen Glacier
- The Siachen Glacier is located in the Eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas, just northeast of Point NJ9842 where the LOC between India and Pakistan ends.
- Nubra River originates from Siachen glacier.
- Nubra Valley acts as the gateway to strategically important Siachen Glacier and Karakoram Pass.
- The Siachen has been an important bone of contention between India and Pakistan since 1984 when the Indian Army launched Operation Meghdoot to take control of the entire Siachen glacier.
- It is the highest battleground on Earth.
- It is the Second-Longest glacier in the World’s Non-Polar areas after Fedchenko Glacier in Tajikistan.
- The Siachen Glacier lies immediately south of the great drainage divide that separates the Eurasian Plate from the Indian subcontinent in the extensively glaciated portion of the Karakoram sometimes called the “Third Pole”.
- The glacier’s melting waters are the main source of the Nubra River in the Indian region of Ladakh which drains into the Shyok River. The Shyok in turn joins the Indus River which flows through Pakistan.
- Siachen Glacier also boasts of the world’s highest helipad and telephone booth built by India.
- The name Siachen refers to a land with an abundance of roses.
Source: The Hindu
Right to Remain Silent
Tags: General Studies –2 Indian Polity and Governance
Why in news?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) Stated that all accused have a ‘Right to silence’ and investigators cannot force them to speak up or admit guilt.
About:
- The right to silence is a legal principle which guarantees any individual the right to refuse to answer questions from law enforcement officers or court officials.
- It is a fundamental right under part III of the Indian Constitution.
- Article 20 of the Indian Constitution ensures a fair trial and lawful arrest of a person.
- The right to remain silent is guaranteed under Article 20(3) of the Indian Constitution.
Supreme Court’s observations:
- The court clarified that cooperation with an investigation should not be seen as an admission of guilt. Remaining silent cannot be considered non-cooperation, as individuals have the right to choose not to speak.
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 20: It grants protection against arbitrary and excessive punishment to an accused person, whether a citizen or foreigner or legal person like a company or a corporation. It contains three provisions in that direction:
- No ex-post-facto law, No double jeopardy, No self-incrimination.
- No self-incrimination: No person accused of any offence shall be compelled to be a witness against himself.
- The protection against self-incrimination extends to both oral evidence and documentary evidence.
- Article 20(3): The Right to silence emanates from Article 20(3) of the Indian Constitution, “which states that no one can be compelled to be a witness against himself.”
- The provision gives an accused the right against self-incrimination, a fundamental canon of law.
- Further, it extends only to criminal proceedings and not to civil proceedings. Therefore, under civil proceedings, a person cannot refuse to answer a question using the defence of Article 20(3).
Source: Hindustan Times
National Asset Reconstruction Company (NARCL)
Tags: General Studies –3 Economy, Banking Sector & NBFCs
Why in news?
Recently, the government has finally renewed its federal guarantee to the National Asset Reconstruction Company (NARCL), making it easier for the entity to acquire bad loans from lenders.
About:
- NARCL has been set up by banks as a strategic initiative to clean up the legacy stressed assets with an exposure of Rs 500 crore and above in the Indian Banking system.
- It has been incorporated under the Companies Act and registered with RBI as an Asset Reconstruction Company under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002.
- Public Sector Banks maintain 51% ownership in NARCL.
- The main purpose behind the formation of the NARCL is to acquire bad loans from banks and sell them to buyers who are looking for Non-Performing Assets (NPAs).
- The organisation itself will also decide the price of these NPAs.
- NPA refers to a classification for loans or advances that are in default or in arrears.
Source: Economic Times
France
Tags: General Studies –1 Geography
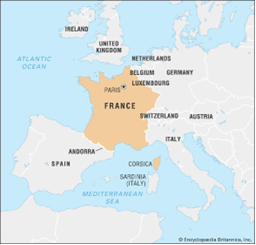
Why in news?
Indian PM will be the Guest of Honour at France’s Bastille Day parade in Paris. The visit coincides with 25 years of strategic partnerships with France.
About:
- France is a country located in Western Europe.
- It is bordered by Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Monaco, Andorra, Spain, and the English Channel.
- Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, the Alps and the Pyrenees.
- The capital of France is Paris.
Source: The Hindu
Sanipreneurs
Tags: General Studies –2,3 Government Policies & Interventions, Health
Why in news?
Recently, The Chennai Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board (CMWSSB) told the Madras High Court that it had decided to convert the sanitary workers involved in manual scavenging into ‘sanipreneurs’ (sanitary entrepreneurs) by awarding them the tender for maintenance of the sewer system, using machines.
About:
- The submission was made at the hearing of a 2017 public interest litigation petition filed by Safai Karamchari Andolan to put an end to manual scavenging.
- This initiative aims to provide workers with safe and dignified self-employment opportunities for a period of seven years.
- The CMWSSB has entered into a partnership with the Dalit Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (DICCI) to train and mentor the ‘sanipreneurs’.
- The DICCI would also assist the ‘sanipreneurs’ in obtaining loans sanctioned under Central and State government schemes.
Source: The Hindu
Phosphate Discovery in Norway
Tags: General Studies –1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, a government organization in Norway, has unearthed extensive deposits of phosphate rocks within the country.
About:

- phosphate rock is the natural source of phosphorous, an element that provides nutrients to plants for their growth and development.
- It is a sedimentary rock formed millions of years ago by the accumulation of organic matter on the ocean floor.
- Around 90% of mined phosphate is used to produce fertiliser for the agriculture industry.
- Previously, the largest amount of phosphate rock was found in Morocco’s western Sahara region, with approximately 50 billion tonnes. China (the largest phosphate producer in the world) and Egypt also have significant phosphate reserves.
- Recently, A huge deposit of phosphate, which can be used to power electric cars and solar panels, has been discovered in Norway.
- There are up to 70 billion tonnes of phosphorus in the deposit, enough to meet demand for the next 50 years.
India:
- Phosphate rocks are also considered a significant and secondary resource of uranium.
- Phosphate rocks are majorly produced only from two States in India, namely Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
- Rock phosphate is the key raw material for DAP and NPK fertilizers. Currently, India is 90% dependent on imports for this raw material.
Source: Down to Earth
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

