
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 How are cheetahs faring in India?
- 2 SDG 1.2 Target
- 3 National Research Foundation
- 4 Senior advocates in the Supreme Court
- 5 Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) Mechanism
- 6 Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS)
- 7 Universe Expansion Dispute
- 8 Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) virus
- 9 Low-cost perovskite solar cells
- 10 Ghaggar River
- 11 Kerch Bridge (Crimea)
- 12 Advancements in Smart Windows
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 13.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 13.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 13.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 13.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 14 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
How are cheetahs faring in India?
Tags: GS – 3: Environment (Biodiversity Conservation)
Why in News:
Five of the relocated cheetahs and three out of four cubs born have died in four months in Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh. It has created a serious cause of concern for the authorities.
Project Cheetah:
- It is an initiative of Indian Government to relocate cheetahs.
- The objective is to introduce 5-10 cheetahs each year for the next ten years, with the goal of establishing a self-sustaining population of approximately 35 cheetahs.
- In South Africa and Namibia cheetahs inhabit enclosed reserves whereas in India they are allowed to thrive in natural, wilderness settings.
- At present, 11 of the relocated cheetahs are in the true wild, while four are being kept in specialized enclosures.
Issues with the Project Cheetah:
- Kuno National Park has too little space and prey for 20 cheetahs.
- It has three cheetahs per 100 sq. km compared to one cheetah per 100 sq. km in Africa.
- A cheetah’s home range is over 1,600 sq. km of unfenced territory. Whereas area of Kuno is 750 sq. km.
- The prolonged confinement of cheetahs in quarantine has had adverse effects on their ability to adapt and has led to psychological adjustment issues.
- Unlike tigers and leopards, cheetahs are comparatively fragile creatures and are more prone to sustaining fatal injuries in the wild. At present, Indian cheetahs do not encounter competition from similar predators like lions and leopards.
Need for a medical examination of the death of cheetahs:
- One of the dead cheetahs had a wound on its neck. He was infected with maggots. There was a chance that chafing from the collar is responsible for infection.
- Radio collars pose obstructions for cheetahs. The animal is unable to lick itself. It is compounded by the moisture generated by monsoon.
- The cheetahs may have been exposed to parasites that they are not immune to.
- Three out of four cubs passed away due to heat and malnourishment, while an adult female succumbed to injuries sustained during a conflict among the animals.
Way Forward:
- An expert committee charged with managing the Project Cheetah programme has recommended that all animals undergo a thorough medical review.
- The committee has also recommended that all surviving cheetahs be subject to a thorough physical examination. This will involve removing their collars, taking tissue samples and checking for parasites.
Source: The Hindu
SDG 1.2 Target
Tags: GS – 2: Social Justice (Issues related to poverty and hunger), GS – 3: Indian Economy (Growth and Development)
Why in News:
Recently, NITI Aayog has released the Report “National Multidimensional Poverty Index: A Progress Review 2023”.
National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI):
- Its first edition was released in 2021. Its aim is to deconstruct the Global MPI and create a globally aligned MPI customised for India.
- Its larger goal is improving India’s position in the Global MPI rankings.
- NITI Aayog is the nodal agency for the National MPI, ranking States and UTs based on their performance.
- The 2023 report has been prepared based on the latest National Family Health Survey-5 (2019-21) and is the 2nd edition of MPI.
- It has three equally weighted dimensions – Health, Education, and Standard of living. These three dimensions are represented by 12 indicators such as nutrition, child and adolescent mortality, maternal health, years of schooling, school attendance, cooking fuel, sanitation, drinking water, electricity, housing, assets, and bank accounts.
Key Highlights of MPI report 2023:
- The number of multidimensionally poor has been decreased from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-2021.
- Around 13.5 crore people moved out of multidimensional poverty during this period.
- The rural areas of India experienced the fastest decline in poverty, with the poverty rate dropping from 32.59% to 19.28%.
- Number of states with less than 10% of people living in multidimensional poverty Doubled between 2016 and 2021 from 7 (Mizoram, HP, Punjab, Sikkim, TN, Goa, and Kerala) to 14 (Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Manipur, and Uttarakhand).
- Except for Bihar, no other state in India has more than one-third of its population living in multidimensional poverty. It recorded the fastest reduction in MPI value in absolute terms with the proportion of multidimensional poor reducing from 51.89% to 33.76% in 2019-21 followed by Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- Uttar Pradesh saw the largest decline in the number of poor individuals, with 3.43 crore (34.3 million) people escaping multidimensional poverty.
Comparison with SDG Targets:
- The MPI value for India has nearly halved from 0.117 to 0.066 between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- The intensity of poverty has reduced from 47% to 44%, indicating that India is on track to achieve SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Target 1.2 (reducing multidimensional poverty by at least half) ahead of the stipulated timeline of 2030.
Government Initiatives:
- Health and Nutrition: Poshan Abhiyan and Anaemia Mukt Bharat have contributed to reduced deprivations in health.
- Sanitation: Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) have improved sanitation across the country.
- Cooking fuel: PM Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) has positively transformed lives.
- Other initiatives: Saubhagya (electricity), PM Awas Yojana (housing), PM Jan Dhan Yojana (banking), and Samagra Shiksha (education).
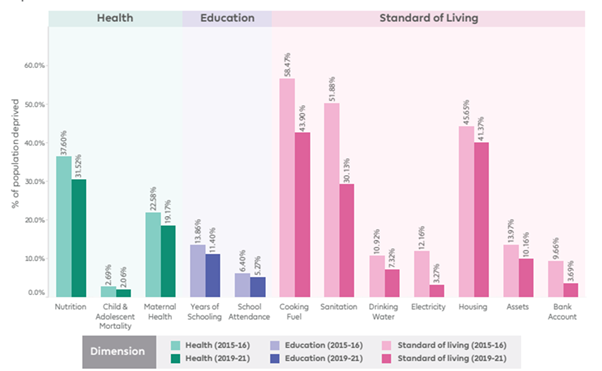
Source: The Times of India
National Research Foundation
Tag: GS-2 Statutory Bodies/Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services Relating to Education
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the introduction of the National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill in Parliament, which was one of the key recommendations of the National Education Policy 2020.
About National Research Foundation:
- NRF is a proposed entity that will replace the Science and Engineering Research Board of India (SERB) and catalyse and channel interdisciplinary research for accelerating India’s ambitious development agenda, through impactful knowledge creation and translation.
- Objectives of NRF
- NRF intends to act as a coordinating agency between researchers, various government bodies and industry, thus bringing industry into the mainstream of research.
- NRF is slated to provide research grants to individuals.
- NRF also plans to seed, grow and facilitate research in India’s universities, especially State universities, by funding research infrastructure and researchers.
- NRF will operate with a budget of Rs 50,000 crore for five years, of which 28% (Rs 14,000 crore) will be the government’s share, and the remaining 72% (Rs 36,000 crore) will come from the private sector.
- It will be governed by a board consisting of the Prime Minister, who will be the ex-officio President of the Board and the Union Minister of S&T and Union Minister of Education, who will be the ex-officio Vice-Presidents. The governing body will also consist of eminent researchers and professionals across disciplines.
How can NRF facilitate Ease of Doing Research?
- Reducing time between application and release of funds preferably within 6 months and timely release of money.
- Digitised process of application which does not require sending paperwork in hard copies to the NRF.
- All finance-related queries, paperwork, approval, and acceptance need to be between the NRF and the finance department of the university/research institution keeping the scientist free to focus on research.
- The NRF needs explicit spending guidelines away from the General Financial Rules (GFR) and the government’s e-Marketplace (GeM) usage.
Source: Hindustan Times
Senior advocates in the Supreme Court
Tag: GS 2 Indian Judiciary
In News:
The Supreme Court (SC) has published new guidelines for the designation of senior advocates practising mainly in the Apex Court. These guidelines were issued after the Indira Jaising vs. Union of India case in 2017 ruling.
About Senior Advocates:
- These are Advocates who are designated as Senior Advocates by the Supreme Court or by any High Court.
- A Senior Advocate is not entitled to appear without an Advocate-on-Record in the SC or without a junior in any other court or tribunal in India.
- He is also not entitled to accept instructions to draw pleadings or affidavits, advise on evidence or do any drafting work of an analogous kind in any court or tribunal in India.
About the New guidelines
- Indira Jaising, India’s first woman Senior Advocate, challenged the existing process as “opaque”, “arbitrary” and “fraught with nepotism.” Thus, the SC in 2017 decided to lay down guidelines for itself and all HCs on the process of designating senior advocates.
- Since the SC acknowledged that the 2017 guidelines were not exhaustive, in February 2023 the Central Government sought to change guidelines for the designation of senior lawyers.
- The new guidelines prescribe the minimum age as 45 years to apply for the ‘senior advocate’. However this age limit may be relaxed by the Committee, the Chief Justice of India, or a Supreme Court judge if they have recommended an advocate’s name.
- The new guidelines assign only 5 marks for “publication of academic articles, experience of teaching assignments in the field of law,” and “guest lectures delivered in law schools and professional institutions connected with law” combined, which earlier used to be 15.
- Weightage given to reported and unreported judgements, excluding orders that do not lay down any principle of law, has increased from 40 to 50 points in the new guidelines
Why were the new guidelines proposed?
- The centre claimed that 40% weightage to publications, personality, and suitability gauged through the interview is subjective, ineffective, and dilutes the esteem and dignity of the honour of the title.
- The centre pointed towards rampant circulation of “bogus” and “sham” journals where people could publish their articles without any academic evaluation.
- Centre also argued that current requirements are “extraneous” and have resulted in “ousting otherwise eligible candidates”.
Source: Indian Express
Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) Mechanism
Tags: GS-II: IR
In News:
Indian External Affairs Minister meets Myanmar Counterpart at Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) Mechanism meeting hosted in Bangkok
About Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) Mechanism
- Mekong Ganga Cooperation is a regional cooperation framework that fosters ties between six countries in South and Southeast Asia.
- It was established in 2000 with an aim to strengthen cultural, economic, and political relations among member states.
- It has six participating countries are India and five Mekong River basin countries: Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- The cooperation mechanism is named after the two iconic rivers, the Mekong River and the Ganges River (Ganga).
- It focuses on areas including cultural exchanges, tourism, education, trade, investment, agriculture, and water resource management.
- The mechanism encourages dialogue and collaboration in various sectors to promote mutual understanding and friendship.
- MGC facilitates people-to-people contact, academic exchanges, and cultural events to enhance cultural connectivity.
- It seeks to leverage the historical and cultural ties between the participating countries to deepen bilateral and regional engagement.
- Overall, Mekong Cooperation will go a long way to help India bolster its “Act East” policy and strengthen its engagement with Southeast Asian nations.
Source: Economic Times
Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS)
Tags: GS-II: IR
In News:
India and the UAE signed a memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to create a Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS) for INR (Indian rupee) and AED (UAE Dirham) transactions.
About Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS)
- The Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS) is a framework aimed at promoting the use of local currencies for cross-border transactions between countries.
- Its primary goal of LCSS is to enable exporters and importers to invoice and pay in their respective domestic currencies, reducing reliance on foreign currencies like the US dollar.
- It aims to enhance bilateral trade, investment, and economic cooperation between participating nations by facilitating transactions in local currencies.
- It covers various types of transactions, including current account transactions (trade of goods and services) and capital account transactions (foreign direct investment, portfolio investment etc.,
- The mechanism encourages the development of local foreign exchange markets for the involved currencies, promoting stability and liquidity.
- Importance:
- Implementing LCSS can optimize transaction costs and settlement times, leading to more efficient cross-border trade and remittances.
- It helps in reducing exchange rate risks for businesses engaged in cross-border trade, as they can avoid exposure to volatile foreign exchange rates.
- It provides an avenue to diversify their currency exposure and reduce dependence on the dollar for countries that are heavily reliant on the US dollar for international trade.
- The system facilitates better economic integration and financial connectivity among participating nations, fostering stronger economic ties.
- It can play a crucial role in supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) by easing foreign trade processes and reducing currency-related complexities.
- In the long run, by encouraging the use of local currencies, LCSS can help in internationalization of national currencies, promoting their acceptance in the global market.
- As more countries explore the adoption of LCSS, it has the potential to reshape global trade dynamics and strengthen regional economic partnerships.
Source: Indian Express
Universe Expansion Dispute
Tags: GS –3 Science and Technology
Why in news?
Recently, Researchers from the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences (ICTS), Bengaluru, the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune, and the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), have proposed a new method to determine the Hubble constant.
About:
Hubble Constant
- The Hubble constant is a unit that describes how fast the universe is expanding at different distances from a particular point in space.
- It is one of the keystones in our understanding of the universe’s evolution.
- It gets its name from Edwin Hubble who was first to calculate the constant from his measurements of stars in 1929.
Universe:
- The universe, born from the Big Bang around 13.8 billion years ago, has been expanding, with its expansion rate initially rapid and then slowing down.
- However, about five to six billion years ago, dark energy caused the universe’s expansion to accelerate again.
Universe Expansion Dispute
- The dispute surrounding the expansion of the universe centres on determining the precise rate at which it is expanding, known as the Hubble constant. Multiple methods have been used to calculate this constant, including analyzing the brightness of supernovae, studying the cosmic microwave background, and observing gravitational waves.
- However, these methods have provided conflicting results, with some measurements reporting higher values than others. This discrepancy has led to a crisis in cosmology, as scientists seek to reconcile these differing measurements and understand the true rate of expansion.
New method
- In an effort to address this dispute, researchers from various institutions have proposed new methods, such as using lensed gravitational waves, to independently estimate the Hubble constant.
- Gravitational lensing is when massive objects in space can warp spacetime. This bends all kinds of waves that travel near the objects, distorting them. The phenomenon is typically used to describe when light waves are bent.
- As we have seen before, sometimes, extreme lensing of some objects can make them visually appear as multiple objects in the sky. Just like that, lensing can produce multiple copies of the same gravitational signal that can reach Earth at different times.
- The researchers believe that the delays between the signals could be used to calculate the universe’s expansion rate.
Source: The Hindu
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) virus
Tags: GS – 3 Health
Why in news?
As Europe reels under a heat wave and wildfires, the rising temperatures have also raised fears of spread of viral haemorrhagic fever generally not found in colder climates.
About:
- Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral disease transmitted by ticks (Hyalomma ticks).
- It can also be contracted through contact with viraemic animal tissues (animal tissue where the virus has entered the bloodstream) during and immediately post-slaughter of animals.
- The disease was first detected among soldiers in the Crimean Peninsula (near the Black Sea) in 1944.
- In 1969, it was found that an ailment identified in the Congo Basin was caused by the same pathogen. Thus, the disease was named the Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever.
- Threat: CCHF outbreaks pose a public health threat, as the virus can lead to epidemics and has a high case fatality ratio (10–40%).
- Symptoms: It includes fever, muscle ache, headache, and bleeding.
- Vaccine: There is currently no vaccine for CCHF, and treatment involves managing symptoms and using antiviral drugs in some cases.
- Region: It is endemic to Africa, the Balkan countries, the Middle East, and parts of Asia.
Source: Indian Express
Low-cost perovskite solar cells
Tags: GS – 3 Science and Technology, Scientific Innovations & Discoveries
Why in news?
Recently, Indian scientists have indigenously developed highly stable, low-cost Carbon-based perovskite solar cells with superior thermal and moisture stability.
About:
- It is the first indigenous perovskite-powered niche product developed in India and can pave the way for futuristic stable perovskite solar cells.
Perovskite solar cells
- Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are a type of solar cell that utilizes perovskite materials as the light-harvesting active layer to convert sunlight into electricity.
- The most commonly used perovskite material in solar cells is methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3).
- Perovskite Solar Cells (PSC) offer a promising alternative to traditional silicon solar cells as they have higher efficiencies and very low production costs.
- Issues with PSCs: However, Perovskite solar cells face the problem of degradation during operation when they come in contact with heat, moisture, light, and other environmental factors. This long-duration stability is a major hindrance in the large-scale commercialisation of the product.
- Solution: The scientists engineered MaPbI3 to enhance thermal stability by incorporating Guanidinium iodide (GuI) and moisture stability by using 5-amino valeric acid iodide (5-AVAI) for surface passivation. This breakthrough can resolve stability concerns and reduce fabrication costs, potentially accelerating the commercialization of perovskite-based niche products.
Source: DST Gov.
Ghaggar River
Tags: GS –1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, the Ghaggar River and its tributaries caused havoc after reclaiming their floodplains in Haryana.
About:
- The Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season.
- It originates in the village of Dagshai in the Shivalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh and flows through Punjab and Haryana states into Rajasthan.
- The main tributaries of the Ghaggar are the Kaushalya River, Markanda, Sarsuti, Tangri and Chautang.
- The river is known as Ghaggar in India, before the Ottu barrage, and as the Hakra in Pakistan, downstream of the barrage.
- It eventually dries up in the Great Indian (Thar) Desert.
- In pre-Harappan times the Ghaggar was a tributary of the Sutlej.
More Information:
- Ghaggar, Tangri, Markanda and others are considered dead rivers in the state and heavily encraoched upon but in this monsoon season they reclaimed their floodplains and caused heavy losses.
Source: Down to Earth
Kerch Bridge (Crimea)
Tags: GS –1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, Recently, the Crimea bridge suffered damage when one of its sections was blown up.
About:
- The Kerch Bridge, also known as Crimea Bridge, is the only direct link between the transport network of Russia and the Crimean Peninsula.
- The bridge that passes over the Kerch Strait was inaugurated in 2018, four years following Russia’s annexation of Crimea.
- The bridge is a pair of parallel bridges, one for a four-lane road and one for a double-track railway, spanning the Kerch Strait between the Taman Peninsula of Krasnodar Krai in Russia and the Kerch Peninsula of Crimea.
| About Kerch Strait: |
| The Kerch Strait is located in Eastern Europe. It serves as a waterway that connects the Black Sea with the Sea of Azov. This strait acts as a natural boundary, separating the Kerch Peninsula in Crimea from the Taman Peninsula in Russia. Its name is derived from the Crimean city of Kerch. |
Source: BBC News
Advancements in Smart Windows
Tags: GS – 3 Scientific Innovations & Discoveries
Why in news?
Researchers at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Science in Bengaluru have introduced a new dimension to smart window technology by combining hierarchical double network polymers with liquid crystals.
About:
- Hierarchical Double Networks of Polymers are a type of interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs).
- Polymers are large molecules composed of smaller molecules called monomers, which are linked together in a chain-like structure. Examples of polymers include common materials like plastic and rubber.
- Interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) are soft matter systems that combine different polymer networks to optimize various properties.
- IPNs have potential applications in fields like smart windows, and sensors.
- Hierarchical Double Networks combine rigid and soft networks to achieve desired thermal, electrical, and optical properties.
- They can be tailored to specific requirements, such as mechanical, optical, and electrical properties.
Source: PIB Gov.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

