In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
Green Credit Programme
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News
Recently, the government unveiled an innovative and voluntary Green Credit program designed to reward and incentivize individuals and entities for their positive environmental contributions.
About Green Credit
- Green Credit represents a form of incentive granted to individuals and organizations participating in endeavors that have a positive impact on the environment.
- It constitutes a voluntary initiative established by the government to motivate a diverse range of stakeholders to actively engage in actions that promote environmental conservation and sustainable practices.
- This program is an integral component of the Mission ‘LiFE’ campaign (Lifestyle for Environment), aiming to promote and acknowledge voluntary efforts that foster a more environmentally responsible way of life.
Covered Activities
The Green Credit program encompasses eight key types of activities aimed at enhancing environmental sustainability:
- Afforestation: The act of planting trees to enhance greenery and combat deforestation.
- Water Resource Conservation: The application of techniques to efficiently manage and preserve water resources.
- Eco-Friendly Farming: The promotion of agricultural methods that are both environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Waste Control: The implementation of efficient waste management systems to mitigate environmental pollution.
- Air Quality Enhancement: Initiatives aimed at diminishing air pollution and improving the overall quality of the air.
- Mangrove Protection and Revival: Activities focused on safeguarding and reviving mangrove ecosystems to maintain ecological equilibrium.
Earning and Calculation of Green Credit
- To accumulate Green Credits, individuals and entities are required to officially record their environmentally beneficial actions via a dedicated website. Based on the agency’s report, the administrator will grant the applicant a certificate of Green Credit.
- The quantification of Green Credits is contingent on various factors, including the resource needs, scale, extent, magnitude, and other pertinent criteria essential for accomplishing the intended environmental results.
Green Credit Registry and Trading Platform
- Establishment of a Green Credit Registry, which will help track and manage earned credits.
- Administrator will create and maintain a trading platform, enabling the trading of Green Credits on a domestic market.
Independence from Carbon Credits
- GCP operates independently of the carbon credits provided under the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, 2023, which is governed by the Energy Conservation Act of 2001.
- An environmental activity generating Green Credits may have climate co-benefits, such as reducing or removing carbon emissions, which can potentially lead to the acquisition of carbon credits in addition to Green Credits.
- Verification and Validation Complexity:
- The process of verifying and validating environmentally beneficial actions can be intricate and time-intensive.
- This raises concerns about the administrative burden placed on both participants and regulatory authorities.
- Risk of Greenwashing:
- There is a legitimate concern that some participants may engage in greenwashing, which involves making false claims of environmentally friendly activities to earn Green Credits without genuinely contributing to environmental preservation.
- Compatibility with Carbon Credits:
- Despite the program’s intent to remain separate from carbon credits, there are concerns about potential overlaps and the complexity of evaluating and distinguishing between these two types of environmental credits.
- Accounting for Regional Differences:
- The program may encounter difficulties in accommodating regional disparities in environmental impact, making it challenging to establish uniform credit values for diverse geographical areas.
| UPSC CSE Previous Year Question (PYQ) Prelims Q1. The concept of carbon credit originated from which one of the following? (2009) (a) Earth Summit, Rio de Janeiro (b) Kyoto Protocol (c) Montreal Protocol (d) G-8 Summit, Heiligendamm Answer: (b) Q2. Regarding “carbon credits”, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2021) (a) The carbon credit system was ratified in conjunction with the Kyoto Protocol (b) Carbon credits are awarded to countries or groups that have reduced greenhouse gases below their emission quota (c) The goal of the carbon credit system is to limit the increase of carbon dioxide emission (d) Carbon credits are traded at a price fixed from time to time by the United Nations Environment Programme. Answer: (d) Mains Q1. Should the pursuit of carbon credits and clean development mechanisms set up under UNFCCC be maintained even though there has been a massive slide in the value of a carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth. (2014) Q2. Discuss global warming and mention its effects on the global climate. Explain the control measures to bring down the level of greenhouse gases that cause global warming, in the light of the Kyoto Protocol, 1997. (2022) |
SC to Hear Challenge on Designation of Bills as Money Bills
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Parliament)
In News
Recently, a seven-judge Supreme Court bench headed by Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud said it will “take a call” on petitioners’ request to give precedence to a reference regarding how the Centre was able to enact significant amendments in the Parliament as Money Bills.
Money Bill
- A money bill is a form of financial legislation that only includes issues pertaining to revenue, taxation, spending, and borrowing by the government.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 110(1) provides that a Bill is deemed to be a money Bill if it deals only with matters specified in Article 110 (1) (a) to (g) — taxation, borrowing by the government, and appropriation of money from the Consolidated Fund of India, among others.
- Article 110 (3) provides that when any question arises whether a Bill is a Money Bill or not, the decision of the Speaker of the House of the People thereon shall be final.
- Passage of Money Bill:
- Money Bill can be introduced in Lok Sabha (Lower House) only. It cannot be introduced in the Rajya Sabha (Upper House).
- The Rajya Sabha does not have the power to amend or reject it. It can only make recommendations on a Money Bill and these recommendations are not binding on the Lok Sabha.
- President can either accept or reject a money bill but cannot return it for reconsideration.
- There is no provision for Joint sitting in case of Money Bill.
Amendments passed as Money Bill and which have been Challenged
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) Amendments:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) was amended starting in 2015, giving the Enforcement Directorate a wide range of powers, including the ability to make arrests and carry out raids.
- The main issue is the approval of these modifications as Money Bills, which raises doubts regarding their constitutionality and legality.
- Legal professionals and petitioners query whether the traditional legislative procedure including both chambers of Parliament should have been used for these important reforms.
- Aadhaar Act, 2016:
- In 2018, the Supreme Court upheld the government’s position and declared the Aadhaar Act to be a legitimate money bill in accordance with Article 110 of the Constitution.
- The government had maintained that the bill is properly categorised as a Money Bill since the subsidies received through Aadhaar come from the Consolidated Fund of India, raising both legal and procedural issues.
- Finance Act of 2017:
- The Finance Act of 2017 was classified as a Money Bill and approved as such, which raises questions regarding how this legislative process should be used.
- There are claims that the Act intended to change the appointments to 19 important judicial tribunals, including the Central Administrative Tribunal and the National Green Tribunal.
- There have been claims that the 2017 Act’s classification as a money bill was an intentional attempt to increase executive authority over these tribunals.
| UPSC CSE Previous Years Questions Prelims Q1. Regarding the Money Bill, which of the following statements is not correct? (2018) A bill shall be deemed to be a Money Bill if it contains only provisions relating to the imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of any tax. A Money Bill has provisions for the custody of the Consolidated Fund of India or the Contingency Fund of India. A Money Bill is concerned with the appropriation of money out of the Contingency Fund of India. A Money Bill deals with the regulation of borrowing of money or giving of any guarantee by the Government of India. Answer: (c) Q2. What will follow if a Money Bill is substantially amended by the Rajya Sabha? (2013) The Lok Sabha may still proceed with the Bill, accepting or not accepting the recommendations of the Rajya Sabha. The Lok Sabha cannot consider the Bill further. The Lok Sabha may send the Bill to the Rajya Sabha for reconsideration. The President may call a joint sitting for passing the Bill. Answer: (a) |
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act
Tags: GS – 2: Governance (Non-Governmental Organisations)
In News
A worrying trend regarding the registration of non-governmental organisations (NGOs) in India under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010, has been shown by recent statistics from the Ministry of Home Affairs. The data indicates that NGOs are engaged in activities that deviate from their declared purposes and do not adequately describe their operational regions in their FCRA registrations.
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA)
- Because of worries about foreign meddling in India’s politics through financial backing for independent organisations, the FCRA was passed in 1976 during the Emergency era. The FCRA was created to control foreign donations to people and organisations and make sure they adhere to the principles of a sovereign democratic republic.
- The 2010 Amendment Act was passed to codify the laws governing the acceptance and use of foreign contributions by certain people or organisations and to outlaw the acceptance and use of foreign contributions for any purposes that are harmful to the interests of the country.
- The 2020 Amendment Act includes provisions that forbid the transfer of foreign contributions to any other person or organisation and reduce the 50% to 20% cap on the amount that can be used for administrative costs.
- Receiving foreign donations in India requires registration under the FCRA. It is given to people or organisations working in a variety of fields, such as social, cultural, educational, or economic initiatives. In these specified sectors, the FCRA restricts foreign donations to guarantee accountability and legal observance.
- In order to receive the foreign funds, applicants have to open a bank account at a particular State Bank of India branch in New Delhi.
- The MHA made updates to the FCRA regulations in July 2022. These adjustments included an increase from 7 to 12 in the number of compoundable violations. The laws also extended the window for notifying the opening of bank accounts and increased the maximum for donations from relatives abroad that do not require government notification from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 10 lakhs.
- FCRA registration is valid for five years, and NGOs are required to apply for renewal within six months of the registration’s expiry.
- The government has the authority to cancel an NGO’s FCRA registration for various reasons, including violations of the Act or a lack of reasonable activity in their chosen field for two consecutive years. Once cancelled, an NGO is ineligible for re-registration for three years.
Activities Prohibited Under FCRA Registration
- No fictitious entities may be represented by the applicant.
- The candidate shouldn’t have taken part, either directly or indirectly, in religious conversion operations.
- The candidate shouldn’t have a history of prosecutions related to communal tension or disharmony.
- The applicant cannot be involved in any sedition-related activity.
- The FCRA forbids politicians, journalists, media outlets, judges, public officials, and political organisations from accepting foreign donations.
Concerns of NGOs Regarding the FCRA
- For NGOs, the FCRA registration procedure can be difficult since it necessitates extensive documentation and rigorous compliance.
- Long administrative processes for FCRA renewal and registration impede NGOs’ access to funding and operations.
- Some NGOs have come under criticism for using foreign funding obtained under the FCRA in an opaque manner.
- Organisations have difficulties as a result of the difficult FCRA registration process, which has a high denial rate that limits their capacity to accept contributions from abroad.
- Politics may have an impact on whether FCRA registrations are approved or denied, according to those who have expressed worries about political interference in the registration and regulation process.
Way Forward
- In order to safeguard against any potential abuse of foreign contributions, strengthen the supervision systems.
- To encourage increased access to financing for genuine NGOs, streamline and accelerate the FCRA registration procedure.
- Make sure that the FCRA registration and regulatory procedures are unbiased and free from political interference.
- NGOs should be encouraged to provide transparent and thorough reports on the use of foreign donations, making sure that the objectives and recipients are made known.
Quantum Engine
Tag: Gs-3 Science and Technology
In News
New ‘quantum engine’ does work by flipping the identity of atoms.
About
- A groundbreaking achievement in the field of quantum mechanics involves the creation of a quantum engine known as the ‘Pauli engine.’ This remarkable invention can efficiently convert the energy differential between two quantum states within a cluster of atoms into practical, usable work.
- This breakthrough has the potential to significantly enhance our comprehension of quantum thermodynamics, opening the door to applications that could lead to the development of more effective quantum computers.
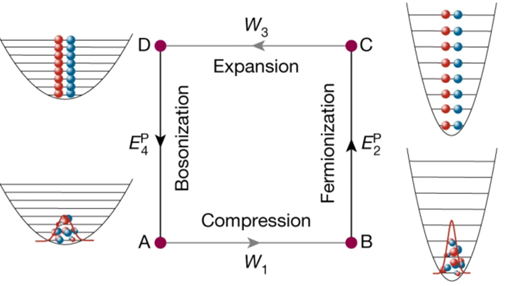
Quantum Engine
- The quantum engine or Pauli’s engine consists of a gas of lithium-6 atoms that are trapped in a combined optical and magnetic trap. The gas can be tuned to behave like bosons or fermions by changing the magnetic field around it.
- This is possible because the atoms can pair up into bosonic molecules or dissociate into individual fermionic atoms depending on the strength of the magnetic field.
- The engine operates in a four-step cycle and it opens up new possibilities for studying quantum thermodynamics and its implications for other fields of physics.
IndiaSkills 2023-24
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship has recently inaugurated IndiaSkills 2023-24 and extended their congratulations to the champions of the World Skills Competition (WSC) 2022.
About
IndiaSkills 2023-24 aims to foster and enhance the skills of individuals in various domains, preparing them for national and international skill competitions.
IndiaSkills is the precursor to the WorldSkills competition.
Key Objectives
- Promotion of Employable Skills: This program prioritizes the development of employable skills that are in harmony with the requirements of the job market. Its goal is to enhance the employability of the workforce and ensure that they are well-suited for various industries.
- Addressing Skill Gaps: An essential objective is to recognize and bridge skill gaps. This involves a focus on identifying the specific skills demanded by industries and minimizing the mismatch between academic qualifications and practical skills.
- Integration of Competencies and Knowledge: The program places equal emphasis on developing competencies, practical knowledge, and hands-on training. The aim is to equip individuals with the capabilities and expertise needed to excel in the 21st century, preparing them for effective leadership in their respective fields.
Rafah Crossing
Tag: GS-2 International Relation
In News
The Rafah border crossing in southern Gaza has attracted worldwide attention due to the efforts of Palestinians trying to depart Gaza in anticipation of a potential Israeli military action, which is part of the continuing Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
About
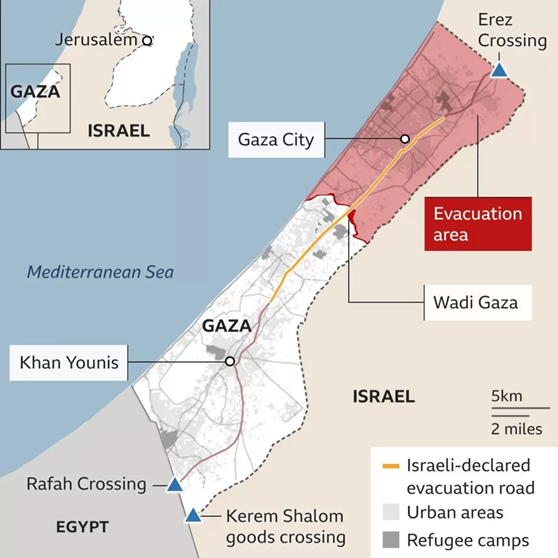
- The Rafah crossing is the southernmost exit point from the Gaza Strip, and it shares a border with Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula. The crossing is controlled by Egypt.
- It is the only exit that does not lead to Israeli territory.
| Two other border crossings in and out of Gaza |
| Erez is located in the north and is used by people in Israel. Kerem Shalom, in the south, which is exclusively for commercial goods. Erez and Kerem Shalom are controlled by Israel. |
Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula
Tag: GS-2 International Relation
In News
Egypt rejects displacement of Palestinians into Sinai.
About
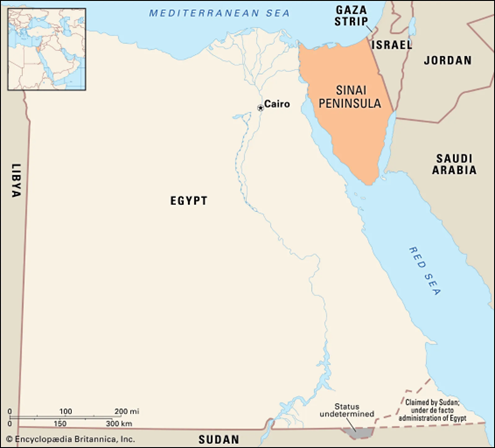
- The Sinai Peninsula is a triangular peninsula in Egypt linking Africa with Asia and occupying an area of 23,500 square miles.
- It is separated by the Gulf of Suez and the Suez Canal from the Eastern Desert of Egypt, but it continues eastward into the Negev desert without marked change of relief.
- It’s located in the northeastern part of the country.
- The peninsula is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Red Sea to the south, and the Gulf of Aqaba to the east.
- The peninsula includes the Suez Canal, which is a man-made waterway that connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


