
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Reforms in India Railway
- 2 National Multidimensional Poverty Index
- 3 Tax Challenges arising from the digitisation of the Economy
- 4 Industrial Concentration in India
- 5 Small Modular Reactors
- 6 Fusion of rock art at Rudragiri Hillock
- 7 Digital time voucher system for political parties
- 8 Nawab Wajid Ali Shah (1822 –1887)
- 9 RBI’s SOPs to Banks for Rupee Trade
- 10 Steel Slag Road
- 11 DPT3 vaccine (diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus) Vaccine Immunisation coverage
- 12 Cicada species
- 13 Gambusia
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 14.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 14.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 14.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 14.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 14.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 15 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Reforms in India Railway
Tag: GS-3 Economy, Infrastructure Development
In News:
Recently, introduction of Vande Bharat trains has garnered significant attention, there remains a need for comprehensive enhancements in railway services.
About
The history of Indian Railways dates back to the British colonial era when the first passenger train journey took place in 1853 between Mumbai and Thane. Over the years, the railways have played a crucial role in shaping India’s socio-economic fabric and have witnessed significant milestones in its journey.
Indian Railways boasts an extensive network that spans over 68,000 kilometers (track length of 99,235 kms), covering almost every corner of the country. From bustling metropolises to remote villages, the railway lines traverse through diverse landscapes, providing essential connectivity to even the most remote regions.
The development of railways in India is hindered by several challenges:
- Congested networks: The infrastructure is overstretched, with over 60% of routes being more than 100% utilized, causing a decline in the average speed of trains for passengers and freight.
- Inefficiency: The railways face low efficiency in terms of human resources and capacity, impacting their overall performance.
- Decline in revenue generation: There has been a slowdown in internal revenue generation, leading the railways to heavily rely on budgetary support and borrowings from the central government.
- Centralized decision-making: Decision-making in the railways is centralized, with the Railway Board holding powers of policy-making, operations, and regulation. This limits the autonomy of railway zones in raising their own revenue and contributing effectively to improving overall revenue.
- Safety and service quality issues: The railways have faced accidents and safety concerns, impacting public trust. Additionally, poor cleanliness, delays in bookings and arrivals, and ticketing issues have affected service quality.
- Competition from aviation industry: Increasing personal disposable income and lifestyle changes have led to stiff competition from airlines, as people opt for air travel over railways.
- Vicious cycle of poor finances: Insufficient finances result in low investment in infrastructure, leading to compromised services, reduced speed, delays, and safety concerns. As a consequence, the railways lose remunerative business, further deteriorating their financial situation.
Measures Taken by Indian Railway
- The Special Freight Train Operations Scheme enables private enterprises to operate freight trains from their own terminals, leading to more efficient transportation of cargo.
- With the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme, stations will be equipped with facilities inspired by major station upgrades like New Delhi and Ahmedabad, but at a reduced cost.
- The Indian Railway Management Service (IRMS) represents a significant shift in the management of Indian Railways, aiming to streamline the top-heavy bureaucracy.
- Mission Raftaar’s objective is to increase the average speed of freight trains twofold and raise the average speed of Superfast/Mail/Express trains by 25 kmph.
- The Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) is a domestically developed system that aims to minimize accidents caused by human error.
- To expedite project commissioning, measures include securing finances through extra-budgetary resources for throughput enhancement works, emphasizing proper project preparation, advanced land acquisition, utilizing EPC contracts, mechanization in construction, and intensive project monitoring.
- The introduction of New Trains like Vande Bharat promotes local manufacturing and enhances the overall travel experience for passengers.
- Vistadome Trains, operating on the most scenic routes, boost tourism and offer travelers an improved sightseeing experience.

Source: Business Standard
National Multidimensional Poverty Index
Tags: GS – 2: Social Justice (Issues related to poverty and hunger), GS – 3: Indian Economy (Growth and development)
Why in News:
Recently, NITI Aayog has released the ‘National Multidimensional Poverty Index: A Progress Review 2023’.
National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI):
- MPI measures Poverty across its multiple dimensions and in effect complements existing poverty statistics based on per capita consumption expenditure.
- It considers three equally weighted dimensions – Health, Education, and Standard of living.
- These three dimensions are measured by 12 indicators such as nutrition, child and adolescent mortality, maternal health, years of schooling, school attendance, cooking fuel, sanitation, drinking water, electricity, housing, assets, and bank accounts.
- The first edition of MPI was released in 2021.
Key Highlights of MPI 2023:
- It is the 2nd edition of the National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) and has been prepared based on the latest National Family Health Survey-5 (2019-21).
- India’s population living in multidimensional poverty decreased from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-21.
- The rural areas of India registered the fastest decline in poverty, with the poverty rate dropping from 32.59% to 19.28%.
- Uttar Pradesh registered the largest decline in the number of poor individuals, with 3.43 crore (34.3 million) people escaping multidimensional poverty.
- Bihar saw the fastest reduction in MPI value in absolute terms with the proportion of multidimensional poor reducing from 51.89% to 33.76% followed by Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- Except for Bihar, no other state in India has more than one-third of its population living in multidimensional poverty.
- Number of states with less than 10% of people living in multidimensional poverty has doubled between 2016 and 2021 from 7 (Mizoram, HP, Punjab, Sikkim, TN, Goa, and Kerala) to 14 (Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Manipur, and Uttarakhand).
Reasons for Multidimensional Poverty:
- Within Health Category, Lack of proper nutrition contributed almost 30% in the overall calculation of MPI of India.
- Within Education category, lack of years of schooling, inadequate access to maternal health services and less-than-desired school attendance did not show much decline.
- Within the Standard of Living Category, ~44% of India’s population is still deprived of access to cooking fuel, 30% of the population deprived of sanitation services.
Government’s Initiatives:
- Health and Nutrition: Poshan Abhiyan and Anaemia Mukt Bharat
- Sanitation: Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)
- Cooking fuel: PM Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- Other initiatives: Saubhagya (electricity), PM Awas Yojana (housing), PM Jan Dhan Yojana (banking), and Samagra Shiksha (education).
Source: Indian Express
Tax Challenges arising from the digitisation of the Economy
Tags: GS – 3: Economy (Taxation)
Why in News:
138 members of OECD-G20 Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) have joined a new two-pillar plan to reform international taxation rules.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD):
- It is an intergovernmental economic organisation, founded to stimulate economic progress and world trade.
- Most OECD members are high-income economies and are regarded as developed countries. Members and key partners represent 80% of the World Trade.
Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS):
- It refers to corporate tax planning strategies used by multinationals to shift profits from higher-tax jurisdictions to lower or no-tax jurisdictions.
- It is done to minimize the corporation tax that is payable overall.
- The OECD defines BEPS strategies as exploiting gaps and mismatches in tax rules.
- As developing countries have a higher reliance on corporate income tax, they suffer from BEPS disproportionately.
Two Pillar Solution or Global Anti-Base Erosion (GloBE) Rules:
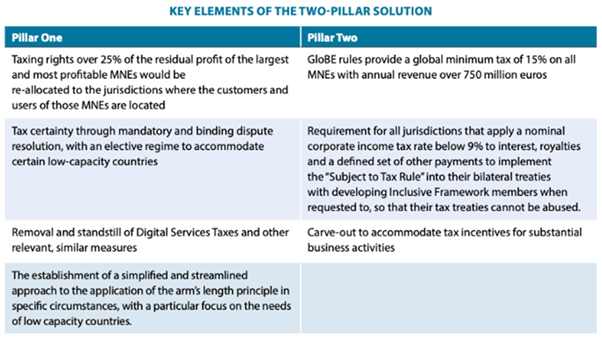
Significance of the solution:
- It will define the multinational enterprises (MNEs) within the scope of the minimum tax and will set out a mechanism for calculating an MNE’s effective tax rate on a jurisdictional basis.
- It will provide much-needed support to governments needing to raise necessary revenues to repair their budgets and their balance sheets while investing in essential public services.
- It will provide stability for the international tax system, making it fairer and work better in an increasingly digitalised and globalised world economy.
Impact on India:
- India will have to roll back the equalisation levy that it imposes on companies such as Google, Amazon and Facebook when the global tax regime is implemented.
- India is in favour of a consensus solution which is simple to implement and simple to comply with.
- The Two Pillar Plan justifies India’s stand for a greater share of profits for the markets and consideration of demand side factors in profit allocation.
Source: OECD
Industrial Concentration in India
Tag: GS-3 Effects of Liberalisation on the Economy, Changes in Industrial Policy
In News:
According to the report of a former RBI deputy governor’s report the assets of the Big 5 business groups in non-financial sectors have almost doubled whereas the share of the next five has halved, since liberalisation..
About concentration of wealth:
- The advance and growth of few large companies such as Adani, Reliance, Tatas, Birlas etc. have been spectacular and even negative reports such as Hindenburg Research, have not halted their progress.
- However small and medium scale firms along with a large mass of informal enterprises have not been able to do well and are yet to recover their COVID-19-inflicted losses.
- This reflects that the business environment overall has not been supportive for all segments and unhindered growth of large corporations have inherent advantages of differential power among economic agents.
Concerns due to rapid rise in industrial concentration:
- Industrial concentration feeds on itself by using market power to stifle competition.
- It results in profit inflation or profiteering, through the manipulation of costs and prices
- Industrial concentration leads to extreme asset and income inequality.
- Large corporations with huge assets influence institutions of democracy.
- They can capture media and dilute the role of civil society as a countervailing power.
- It can also result in lobbying by influence over political processes and the formulation of policy.
Trends that signal narrowing of political distance between state and big business:
- Embrace the idea of Neoliberalism: Neoliberalists, both inside and outside the government view the role of state not as a regulator of private capital but a facilitator of growth for all round economic progress.
- However the argument that competition fostered by liberalisation would prevent concentration has proved otherwise, as seen in the telecommunication and aviation sector.
- Propagation of the view that states must assist in strengthening domestic big business to not just compete against giant global competitors, but to step beyond Indian shores. Thus state policy and public resources were used to strengthen large corporations.
- Increased influence of money in politics as policies have been changed to legitimise corporate donations to political parties, including through the infamous electoral bonds scheme.
Source: The Hindu
Small Modular Reactors
Tag: GS-3 Indigenization of Technology & Developing New Technology
In News:
India’s shift towards smaller nuclear plants such as Small Modular Reactors(SMR) to harness nuclear energy, is being seen as a strategic move towards energy security.
About India’s Nuclear Energy mix:
- Nuclear power represents 1.7% of India’s total installed power capacity as of March 2022. But by 2032, nuclear power is predicted to constitute 2.2% of capacity and 4.4% of gross generation.
- India aims to raise nuclear power to 10% of its energy mix by 2035, requiring a significant increase in nuclear capacity.
What are Small Modular Reactors?
- Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors. SMRs, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity, are:
- Benefits of SMR:
- Cogeneration SMR systems have potential to complement variable renewables through flexible operations.
- SMRs can also be installed in remote off-grid locations and help in achieving energy transition goals.
- SMR can be manufactured in a controlled factory environment and then transported to project site, thus optimising time & cost of project.
- Deployment advantages like reduced size of Emergency Planning Zone (EPZ) and passive safety system.
India’s strategy for nuclear energy transition
- Switching to small reactors which are simpler, safer, and more cost-effective, since hydropower projects and thermal projects are not environmentally sustainable and have lower efficiency.
- Private sector involvement in this initiative is crucial as they bring capital and technology in the power sector.
- Future targets of raising nuclear power to 10% of India’s energy mix by 2035 would require increasing nuclear capacity to approximately 90 GW. This target may be achieved through the development of SMRs.
Major suggestions given by NITI Aayog for SMR:
- Encouraging private sector participation through public-private partnerships (PPPs), which would offer shared responsibilities and benefits.
- Regulatory changes creating a comprehensive regulatory regime with stringent safety standards and regular monitoring to ensure the safe operation of SMRs.
- Modifying foreign investment policies to enable both domestic and foreign private companies to participate in the country’s SMR development.
Source: Business Standard
Fusion of rock art at Rudragiri Hillock
Tags: GS-I: Art and Culture
In News:
Archaeologists deliberates on fascinating fusion of Rock Art at Rudragiri Hillock
About Fusion of rock art at Rudragiri Hillock:
- Rudragiri boasts five naturally formed rock shelters at its foothills, facing westward, which served as living quarters during the Mesolithic age around 5000 B.C.
- These rock shelters bear luminous rock paintings from the prehistoric era, offering valuable insights into ancient artistic expressions.
- Two natural caves at the southern end of the hillock showcase exceptional murals from the Kakatiya kingdom, dating back to the 13th century A.D.
- These paintings depict captivating scenes from the epic Ramayana and utilize colors derived from white kaolin and various pigments.
- The First Cave presents a narrative mural illustrating the intense battle between the Vanara brothers, Vali and Sugriva, from the Ramayana.
- The Middle Cave features a grand sketch of Hanuman carrying the Sanjivani hill in his right hand, symbolizing his mission to save Lakshmana’s life.
- It has sacred symbols of the conch (Sankha) and the fire altar (Yagna Vedi) accompany Hanuman’s depiction.
- The Third Cave houses the prehistoric rock paintings from the Mesolithic era, coexisting harmoniously with the Kakatiya-era murals.
- It showcases superimposed figure of Hanuman in a unique ‘Anjali’ posture, folding his hands in a divine offering.
Rudragiri hillock
- Rudragiri hillock is located in the village of Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh which holds a rich historical and artistic legacy.
- It features a unique combination of prehistoric rock paintings from the Mesolithic period and exquisite artwork from the Kakatiya dynasty.
- Its rock shelter frescoes suggests that the Ramayana scenes depicted at Rudragiri might have drawn inspiration from the artworks at Muppavaram.
- Ganapati Deva Maharaja (1199-1262 AD), the founder of Muppavaram temple and a prominent figure of the Kakatiya dynasty, likely patronized the mural heritage found at Rudragiri.
Source: The Hindu
Digital time voucher system for political parties
Tags: GS-II: ECI
In News:
Election Commission introduces Digital Time Vouchers for political parties’ campaigning on Doordarshan & All India Radio
About Digital Time Voucher System for Political Parties:
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) has introduced a digital time voucher system for political parties during elections.
- The system aims to leverage technology to replace the traditional physical collection of time vouchers from ECI/CEO Offices.
- The scheme was initially notified in 1998 under Section 39A of the Representation of Peoples Act, 1951.
- Important features:
- It provides equitable access to government-owned electronic media for campaigning to recognized National and State Parties during elections.
- Each party receives a base time on Doordarshan (DD) and All India Radio (AIR), with additional time based on past poll performance.
- It will operate through an Information Technology (IT) platform where political parties will be issued digital time vouchers through the online system.
- The new system eliminates the need for physical visits to ECI/CEO Offices for voucher collection streamlining the process of allotting time vouchers to parties.
- Political parties can access the vouchers online from anywhere which will reduce the administrative burden for both parties and election officials.
- Overall, digital time voucher system is a progressive step by the ECI towards leveraging technology for the betterment of the electoral process.
Source: PIB Gov.
Nawab Wajid Ali Shah (1822 –1887)
Tags: General Studies –1 Art & Culture
Why in news?
An exhibition, heritage walk, and talk will be held in Kolkata to commemorate the bicentenary year of Nawab Wajid Ali Shah, the last king of Awadh.
About:
- Mirza Wajid Ali Shah was the eleventh and final King of Awadh, reigning from 13 February 1847 to 11 February 1856.
- The British East India Company annexed Awadh on 11 February 1856, just two days before the ninth anniversary of Wajid Ali Shah’s coronation. He was subsequently exiled to Garden Reach in Metiabruz, near Kolkata, living on a pension.
Major Contributions:
- He is remembered as a poet, playwright, dancer, and patron of the arts who made significant contributions during his rule.
- Dance
- A classical Indian dance form, Kathak, was introduced by him as a court dance.
- His Kathak teacher was Thakur Prasad ji.
- He provided artistic guidance, financial assistance to make this dance form achieve greater heights and a definite form.
- He is also believed to start two distinct forms of dance called Rahas and Raas.
- Music
- He patronized a light classical form of thumri music.
- Most famous is bhairavi thumri “Babul Mora Naihar Chhooto Jaay”
- He also supported and encourages ragas like Tilak, pilu, sendura, khammach, bhairvi and jhanjhauti.
- As a gifted musician he composed various musical compositions such as poems, prose and thumris, under a pseudonym Akhtarpiya.
- Gazhals: Diwan-i-Akhtar and Husn-i-Akhtar
- Ragas: Jogi, Juhi, Shah-Pasand
- Hindustani theatre
- Establishment of Parikhaana – a place to teach music and dance to beautiful and talented girls by expert trainers.
- By staging Rasleela he promoted this theatre art form.
- Some historians and experts believe his to be the first playwright of the Hindustani theatre.
- Playwright
- Radha Kanhaiyya Ka Qissa;
- Darya-i-Tashsq;
- Bhahar-i-Ulfat etc.
- Poetry
- He was known to use a poetic takhallus, a pen name used by poets, Qaisar.
- Works in poetry
- Sawat-ul-Qalub;
- Huzn-i-Akhtar
- He also patronized the famous poet Mirza Ghalib.
Source: PIB Gov.
RBI’s SOPs to Banks for Rupee Trade
Tags: General Studies –3 Economy
Why in news?
Recently, The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to issue a standard operating procedure (SOP) to banks in order to expedite the issuance of proofs of inward remittances for exporters.
About:
- FIRC (Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate) is a document that acts as a testimonial for all the inward remittances entering India.
- Most of the statutory authorities accept this document as proof that an individual or a business, such as a limited company, partnership firm, sole proprietorship firm and others, has received a payment in foreign currency from outside the country.
- Issues with FIRC
- The issue with Foreign Inward Remittance Certificates (FIRC) arises when the certificate from one bank is not being sent to another, which hampers the generation of electronic bank realisation certificates (e-BRCs).
- This creates a problem for exporters as e-BRCs serve as proof of payment for their exports and make them eligible for benefits under the Foreign Trade Policy.
Electronic Bank Realization Certificate(e-BRC):
- An Electronic Bank Realization Certificate(e-BRC) is a vital digital certificate for export businesses.
- A bank issues the e-BRC to confirm that the buyer made payment to the exporter against the export of services or goods.
- The BRC is the proof of realization of payment against exports.
Source: The Hindu
Steel Slag Road
Tags: General Studies –2 Government Policies & Intervention
Why in news?
Recently, India has developed the world’s latest Steel Road technology by using steel slag.
About:
- Steel slag is a byproduct of steelmaking and is produced during the separation of molten steel from impurities in steel-making furnaces.
- Steel slag roads are roads constructed using steel slag. Instead of discarding this waste material, it is processed and used as an aggregate in road construction.
- The steel slag is mixed with other materials and technologies to create a durable and sustainable road surface.
- The technology, pioneered by CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI), allows for the large-scale utilization of waste steel slag from steel plants in road construction.
- It is part of the “Waste to Wealth” initiative and addresses environmental degradation caused by waste steel slag.
- Steel slag roads are well-suited to India’s terrain, offering cost savings of 30% and three times the lifespan of traditional roads.
- It is resistant to weather conditions.
- The success of steel slag roads has been demonstrated in various projects, including in Surat, Arunachal Pradesh, and on National Highway NH-66.
Source: PIB Gov.
DPT3 vaccine (diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus) Vaccine Immunisation coverage
Tags: General Studies –3 Health
Why in news?
Recently, according to the WHO and UNICEF estimates for national immunization coverage for 2022, the coverage rate for DPT3, the third dose of diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus vaccines, in India rose to an all-time of 93% in 2022.
About:
- The DPT vaccine is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious diseases in humans: diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus.
- Diphtheria
- It is an infectious disease caused by Corynebacterium diphtheria, a bacterium.
- It can lead to difficulty breathing, heart failure, paralysis, or death.
- Tetanus
- It is an infection caused by bacteria called Clostridium tetani.
- It causes painful stiffening of the muscles.
- Tetanus can lead to serious health problems, including being unable to open the mouth, having trouble swallowing and breathing, or death.
- Pertussis
- It is also known as whooping cough.
- It is a very contagious respiratory illness caused by a type of bacteria called Bordetella pertussis.
- It can cause uncontrollable, violent coughing that makes it hard to breathe, eat, or drink.
- Pertussis can be extremely serious especially in babies and young children, causing pneumonia, convulsions, brain damage, or death.
- In teens and adults, it can cause weight loss, loss of bladder control, passing out, and rib fractures from severe coughing.
Key Findings:
- The coverage rate for DPT3 vaccines (diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus) in India reached an all-time high of 93% in 2022, surpassing the pre-pandemic record of 91% in 2019.
- This significant increase from the 85% coverage in 2021 was reported by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The region also witnessed improvements in the coverage of the measles vaccine, which rose to 92% in 2022 from 86% in 2021.
- The number of zero-dose children (those who haven’t received any dose of the DPT vaccine) halved to 2.3 million in 2022 from 4.6 million in 2021, while the number of partially vaccinated children decreased to 650,000 in 2022 from 1.3 million in 2021.
- India and Indonesia were credited for the region’s strong immunization recoveries, as they made significant efforts to improve vaccination rates.
- The report highlighted the importance of closing gaps in immunization coverage at the subnational level to prevent outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Source: The Hindu
Cicada species
Tags: General Studies – 3 Conservation, Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Why in news?
Recently, a cicada species commonly found in several parts of South India has been identified as a new species and named Purana cheeveeda (after its Malayalam name Cheeveedu).
About:
- Previously, it was mistaken for Purana tigrina, a species described in Malaysia in 1850.
- The Association for Advancement in Entomology has corrected this long-standing error in taxonomic identification, distinguishing Purana cheeveeda from the Malaysian species.
- The team noticed differences in the structure of the male genitalia and operculum, leading to the reclassification.
Cicadas:
- Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Hemipteran insects, also called true bugs, have mouthparts used for piercing and sucking and have two pairs of wings.
- They have large eyes, transparent wings and loud calls that are produced by special organs called tymbals.
- Cicadas are mostly herbivorous and feed on plant sap using their piercing and sucking mouthparts.
- Habitat:
- Most cicadas are canopy dwellers and are found in natural forests with large trees; found in every continent except Antarctica.
- The generic diversity of cicadas in India and Bangladesh ranks the highest in the world, followed by China.
- Significance:
- Cicadas are important for biodiversity because they provide food for many predators, pollinate flowers, aerate the soil, recycle nutrients and indicate environmental health.
Source: The Hindu
Gambusia
Tags: General Studies –1 Environment, Conservation
Why in news?
Recently, The Andhra Pradesh government has released approximately 10 million Gambusia fish into the state’s water bodies to combat mosquito-borne diseases like malaria and dengue.
About:
- Gambusia Fish is also known as mosquito fish, is widely used as a biological agent for controlling mosquito larvae.
- Gambusia fish are known for their high breeding capacity and adaptability, allowing them to survive in diverse environments.
- It is native to the waters of the south-eastern United States.
- It has been a part of mosquito-control strategies for over a century in various parts of the world, including India.
- The fish is used as a biological agent to control mosquito larvae and has been part of mosquito-control strategies in India since 1928.
- A single full-grown fish eats about 100 to 300 mosquito larvae per day.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature declare Gambusia one of the 100 worst invasive alien species in the world.
Source: Down to Earth
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

