
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill 2021
- 2 Opium Wars
- 3 Manual for Disaster Management Plan (DMP)
- 4 No Confidence Motion
- 5 UNESCO endorses banning smartphones from schools
- 6 PM DevINE
- 7 Mangrove Mitra Programme (Odisha)
- 8 Constitution (STs) Order (5th Amendment) Bill
- 9 Novel features spotted in radiation emitted from black holes due to atoms falling
- 10 Ocular Burns in Children
- 11 STARFIRE Algorithm
- 12 National Coal Index
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 13.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 13.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 13.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 13.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 14 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
The Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill 2021
Tag: GS-2 Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors and Issues arising out of their Design and Implementation; GS-3 Environment and Conservation
In News:
The Lok Sabha passed the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021, which aims to amend the Biological Diversity Act, 2002
About Biological Diversity Act 2002:
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 was framed to give effect to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), 1992, that strives for sustainable, fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilisation of biological resources and associated traditional knowledge. India became a signatory to CBD in 1994.
- The CBD recognises sovereign rights over biological resources and permits countries to regulate access to these resources as per their national legislation.
- The Biodiversity Act, 2002, enacted by India, regulates access to biological resources and associated traditional knowledge.
- It specifies distinct frameworks for regulating access by foreign and domestic entities.
- It formulates a three-tier structure consisting of
- National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) at the national level,
- State Biodiversity Boards (SBBs) at the State level and
- Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) at local body levels.
- The primary responsibility of the BMCs is to document local biodiversity and associated knowledge in the form of a People’s Biodiversity Register.
Key Amendments Proposed by the bill:
| Provisions | Biological Diversity Act 2002 | Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill 2021 |
| Access to Biological Resources | It requires anyone seeking to access biological resources or associated knowledge in India to obtain prior approval or inform the regulatory authority | Bill amends the classification of entities and activities that require intimation, while also introducing exemptions to certain cases. |
| Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) | The Act currently demands NBA’s approval before applying for IPR related to biological resources from India. | The Bill suggests that approval will be required before the actual grant of the IPR, not during the application process. |
| Exemption for AYUSH Practitioners | Earlier, only use by local people and communities including growers and cultivators of biodiversity were exempted. | It seeks to exempt registered AYUSH medical practitioners and people accessing codified traditional knowledge, , from giving prior intimation to State biodiversity boards for accessing biological resource. |
| Benefit Sharing | The Act mandates benefit sharing, which involves sharing both monetary and non-monetary benefits with those who conserve biodiversity or hold traditional knowledge associated with it. | The Bill removes the applicability of benefit sharing requirements from research, bio-survey, and bio-utilisation. |
| Criminal Penalties | The Act imposes criminal penalties, including imprisonment, for offenses such as not obtaining approval or intimation for specific activities. | The Bill, on the other hand, decriminalises these offences and introduces fines ranging from one lakh to fifty lakh rupees instead. |
Major Concerns with the Bill:
- Favours Industries over Conservation of Biodiversity as easing of certain provisions like reduction of compliance burden, decriminalisation of violations etc. make the biodiversity more vulnerable to exploitations.
- Decriminalisation of Violations along with removal of the power of NBA to file FIRs against parties that do not comply with regulations, further weakens the enforcement of biodiversity protection laws.
- Exemption of AYUSH manufacturing companies from requiring approvals from the NBA, will go against one of the core provisions of the Act and open the law for abuse.
- Limited Benefit Sharing as the inclusion of “codified traditional knowledge” exempts certain users, including practitioners of Indian systems of medicine, from the need to share benefits. This may lead to profiteering by domestic companies.
Way Forward
- There is a need to maintain balance between the interests of industries and practitioners of traditional medicine and interests of communities which preserve traditional knowledge.
- The public consultations and concerns of stakeholders should be carefully evaluated and incorporated into the bill.
Source: The Hindu
Opium Wars
Tags: GS – 1: World History
Why in News:
Amitav Ghosh’s new book “Smoke and Ashes” explores the historical significance of opium as a powerful agent that has shaped and continues to shape the world’s history.
The Opium Wars:
- Due to increasing consumption of tea by Britain, there was a trade deficit with China.
- To address this trade deficit, the British East India Company promoted the opium trade. They increase the opium production in India for export to China.
- Due to increasing addiction of opium in China, there was a severe socio-economic crisis. This weakened the Qing dynasty’s governance.
- In order to stop the opium smuggling, the conflict between Chinese and the British started which led to the two Opium Wars.
First Opium War (1839-42):
- The conflict escalated when British authorities refused to comply with Chinese demands to end the opium trade.
- In response, the Chinese attempted to enforce their laws, leading to a military confrontation.
- The British, with their advanced military technology defeated the Chinese and forced them to sign the Treaty of Nanking in 1842.
- This treaty opened several Chinese ports for trade, ceded Hong Kong to Britain, and granted extraterritorial rights to British citizens in China.
Second Opium War (1856-1860):
- The Treaty of Nanking did not fully address all the issues between China and Britain, and tensions continued to simmer.
- The Second Opium War ensued when British and French forces clashed with the Chinese again.
- The conflict resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Tientsin in 1858 and Treaty of Peking in 1860, which further opened China to foreign trade and allowed for the establishment of foreign diplomatic missions in Beijing.
Impacts on India:
- Increased Opium Cultivation: This led to the exploitation of Indian farmers and increased dependence on opium cultivation, often to the detriment of other crops.
- Economic Repercussions: It diverted resources and labour away from other productive activities.
- Social Consequences: The addiction and widespread use of opium within certain regions of India, leading to social problems and health issues.
- Consolidation of British policies: The revenue generated from the opium trade financed the maintenance of their military and administrative apparatus.
Acts passed during that time:
- Charter Act of 1813: It granted a monopoly of the opium trade to the British East India Company.
- Charter Act of 1833: The company’s monopoly on the production and sale of opium in India and export to China continued.
- Charter Act of 1853: The Company still retained control over opium cultivation and trade in India during this period.
Source: Indian Express
Manual for Disaster Management Plan (DMP)
Tags: GS – 3: Disaster Management
Why in News:
Recently, Union Minister for Jal Shakti has released the Manual for Disaster Management Plan (DMP).
Manual for Disaster Management Plan (MDP):
- The manual has been developed by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti, based on the Advisory issued by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), under the Disaster Management Act 2005.
- Its aim is to ensure safety, uninterrupted supply and minimum loss of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) assets and services involving stakeholders at national, state, district and village level.
- The plan aligns with the two-flagship programmes on WASH implemented by the Department namely the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) and Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin (SBM-G).
- The plan includes Gender-based vulnerabilities, and issues concerning SC/ST, elderly, children and people with disabilities.
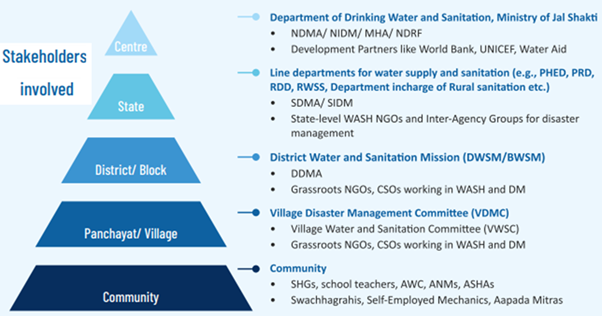
- The plan explores the Disaster Management (DM) Cycle in four stages:
- Preparedness: Preparing WASH assets and services for disasters includes ensuring that the system is geared to respond swiftly and effectively to a disaster.
- Response: It includes emergency services provided during or immediately after a disaster to save lives, reduce health impacts, ensure public safety and meet the basic needs.
- Recovery and Reconstruction: It includes the restoration and improvement of the facilities, livelihoods and living conditions of the affected communities.
- Mitigation: It includes the steps taken to minimize the vulnerability of WASH infrastructure and services to future disasters.
- Three kinds of assessment need to be conducted:
- Before the disaster: A Hazard-Vulnerability-Capacity mapping to guide the preparedness activities most needed.
- During Response: A Rapid Needs Assessment (RNA) which can be completed in a day and point out the immediate needs of the affected population.
- During Recovery & Reconstruction: A detailed Post-Disaster Needs Assessment (PDNA) which highlights the long-term needs of the community and helps the administration “build back better” the damaged infrastructure and update the service delivery mechanisms to mitigate against future disasters.
Other Best Practices – Disaster Response in Odisha:
- Sneha Abhiyaan: Under this, self-help groups (SHGs) in the village are entrusted with managing cyclone shelters, including the distribution of cooked food.
- Mamta Gruhas: These safe spaces provide comprehensive care for women, children and other vulnerable sections of society.
- Training and capacity building of frontline workers (ASHAs, SHGs): SDRF provides training in first aid, shelter management, rescue operations, government regulations concerning trafficking and compensation norms.
Source: PIB Gov.
No Confidence Motion
Tags: GS – 2: Indian Polity (Parliament)
Why in News:
Recently, Lok Sabha Speaker accepted the Opposition’s no confidence motion against the Government.
No Confidence Motion:
- In a parliamentary democracy such as India, a government can be in power only if it commands a majority in the directly elected House, i.e., the Lok Sabha in case of India.
- Article 75(3) of the Constitution embodies this rule by specifying that the Council of Ministers are collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha.
- For testing this collective responsibility, the rules of Lok Sabha provide a particular mechanism – a motion of no-confidence. The Constitution does not mention either a Confidence or a No Confidence Motion.
- There have been 27 no-confidence motions introduced in the Lok Sabha since independence.
Reason for introducing No Confidence Motion:
- In recent time, due to the cases of violence in Manipur, the opposition parties have been demanding that Prime Minister Narendra Modi make a statement in Parliament.
- After several days of protests and washouts, the opposition gave two separate notices to move motions of no-confidence against the government.
Procedure for passing No Confidence Motion:
- Any Lok Sabha MP, with the support of 50 colleagues can at any point of time, introduce a motion of no-confidence against the Council of Ministers.
- It can be moved only in the Lok Sabha. It cannot be moved in the Rajya Sabha.
- It is moved in writing and must be signed by the member moving it, the motion is submitted to the Speaker of Lok Sabha.
- The Speaker will decide whether to admit the motion for discussion and debate. If the motion is admitted, the Speaker will decide on the date and time for discussion.
- The motion will be debated in the Lok Sabha and it will be moved by the member who submitted it.
- After the debate, the Lok Sabha will vote on the motion, it will be passed if it is supported by the majority of the members of the House.
- If a no-confidence motion is passed, the government must resign.
Other types of Motions used in Parliament:
- Adjournment Motion: It is moved to discuss a definite matter of urgent public importance and must be of immediate concern, with the Speaker’s consent.
- Closure Motion: It is moved by a member to cut short the debate on a matter before the House.
- Short Duration Discussion: It allows MPs to discuss a specific issue of public importance without voting on it.
- Confidence Motion: It is passed when the governments formed with wafer-thin majority have been called upon by the President to prove their majority on the floor of the House.
- Privilege Motion: A member can initiate this motion when they believe a minister has violated the privileges of the House or its members by withholding crucial information about a case or providing inaccurate and manipulated facts.
- Motion of Thanks: It is a parliamentary procedure to express gratitude for the President’s Address at the commencement of Lok Sabha.
- Cut Motion: It is proposed to reduce the amount of a demand in the budget.
Source: Indian Express
UNESCO endorses banning smartphones from schools
Tags: GS-III: Important Reports
In News:
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) report cautions on use of technology in education
About UNESCO Endorses Banning Smartphones from Schools:
- UNESCO has recently released a report on Global Education Monitoring 2023 titled “Technology in Education: A Tool on Whose Terms”
- The report endorses banning smartphones in schools if technology integration doesn’t improve learning or worsens well-being.
- UNESCO warns against uncritical rush towards digital products in educational settings as there is little robust evidence on digital technology’s added value in education.
- The report finds negative link between excessive screen time and a child’s educational performance and emotional stability.
- Key findings:
- Research shows banning smartphones improves academic performance, especially for low-performing students.
- Higher screen time associated with poorer well-being, less curiosity, self-control, and emotional stability in young people aged 2 to 17.
- Higher costs of digital infrastructure delivery for basic education risks worsening unequal access to education in low-income countries.
- Only 16% of countries explicitly guarantee data privacy in education by law as nearly 39 of 42 governments providing online education during the pandemic risked or infringed on children’s rights.
Overall, there is need for government to prioritize learners when making decisions on digital technology use besides securing child data protection and accountability for infringements.
Source: The Hindu
PM DevINE
Tags: GS-II: Government Schemes
In News:
Government of India launches schemes for development of North Eastern region
About PM DevINE
- PM-DevINE or Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North Eastern Region is a new Central Sector scheme for the development of North Eastern Region (NER).
- NER are a group of eight states including Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura located in the northeastern part of the country
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 with 100% Central funding for an outlay of Rs. 6,600 crores for the period 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The scheme aims to fund infrastructure convergently, in the spirit of multi-modal infrastructure connectivity grid of PM GatiShakti.
- It will also support social development projects based on the needs of the North Eastern Region.
- Major Projects approved in FY 2022-23
- NECTAR Livelihood Improvement Project for utilization of Banana Pseudo Stem for Value-Added Products
- Promoting Scientific Organic Agriculture in North-East including Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur.
- Pilot project for the construction of Bamboo Link Roads at different locations in various districts in the State of Mizoram.
- Overall, PM-DevINE will help enable livelihood activities for youth and women and fill the development gaps in various sectors.
Source: PIB GOV.
Mangrove Mitra Programme (Odisha)
Tags: General Studies –3 Environment & Ecology
Why in news?
Recently, over 25 acres of land near Bhitarkanika National Park (BNP) in Odisha’s coastal Kendrapara district have been given by at least 25 families for the planting of mangroves.
About:
- The park has 82 mangrove species, but the expansion of aquaculture and agriculture has degraded the mangrove habitats in the region.
- The land donation is aimed at regenerating mangrove forests during the monsoon season.
- Mangroves are spread over 258 square km in Odisha and are mostly concentrated in BNP.
- The Bhitarkanika mangrove ecosystem is India’s second largest, but it has suffered losses due to deforestation caused by resettlement and human activities. Activists emphasize that mangrove forests offer the best insurance against such natural calamities.
Fact for mains:
- The 2021 Forest Survey of India report said the mangrove forest cover in the country increased by 17 square km over the previous two years. Odisha accounted for 8.34 square km of the increase.
Source: Hindustan Times
Constitution (STs) Order (5th Amendment) Bill
Tags: General Studies – 2 Polity and Governance
Why in news?
Recently, Parliament passes Constitution (STs) Order (5th Amendment) Bill to include some communities in the STs category in Chhattisgarh.
About:
- The Bill seeks to amend the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order 1950. The Bill includes the Dhanuhar, Dhanuwar, Kisan, Saunra, Saonra, and Binjhia communities in the list of Scheduled Tribes in Chhattisgarh.
- The Bill seeks to include Bhuinya, Bhuiyan, and Bhuyan communities as synonyms of the Bharia Bhumia community.
- It also includes three Devanagari versions of the name of the Pando community.
Source: News O Nair
Novel features spotted in radiation emitted from black holes due to atoms falling
Tags: General Studies – 3 Science and Technology
Why in news?
Recently, Novel features spotted in radiation emitted from black holes due to atoms falling into it could help understand the unification of quantum theory with gravity.
About:
- It could throw new light on the efforts of scientists towards the unification of quantum mechanics which plays out at the smallest scales of matter and the general theory of relatively propounded by Einstein which is applicable at the largest cosmological scales.
- Quantum theory describes the microscopic behavior of fundamental particles whereas the general theory of relativity accurately describes the motion of objects or particles around a massive object which is the exact mathematical description of the theory of gravitation at the classical level.
- General relativity theory by Einstein states that the laws of nature remain the same if an experiment is done in a small enough region in the presence of a gravitational field compared to the same experiment done in the absence of gravity. This is called the principle of equivalence which is completely classical.
- A fundamental consequence of the general theory of relativity is the existence of a black hole. This astrophysical object is characterized by something known as the event horizon.
Source: PIB Gov.
Ocular Burns in Children
Tags: General Studies – 3 Science and Technology
Why in news?
Recently, Ocular burns due to household chemicals are a tragic and avoidable cause of ocular morbidity, even vision loss, among children.
About:
- Slaked lime is an alkali compound widely used as a binding agent, along with betel nut and other ingredients, to make paan in the Indian subcontinent.
- A new study has found that chuna is a major cause of ocular burns among children, along with household chemicals and fireworks.
- Indian paan has slaked lime, or chuna smeared onto a betel leaf and is chewed along with areca nut. Tobacco is also added to the paan and the alkali quickens its absorption.
- An exploding packet of chuna can deliver the alkali straight into a person’s eye, with the chemical lodging itself inside the eyelid and coating the cornea, the outer transparent layer of the eye. Alkali chemically burns through the delicate tissue, causing extensive damage.
- The rim of the cornea, called the corneal limbus, is home to specialized stem cells that replenish the cornea. Chemical burns can destroy the limbus, in turn compromising the cornea’s ability to repair itself.
- Household cleaning agents like toilet cleaners and other acids, as well as fireworks and even super-glue in tubes, are all liable to cause ocular injury.
About Slaked Lime
- Slaked lime (Ca (OH)2), is obtained by mixing quicklime (calcium oxide) with water, resulting in a chemical reaction that produces calcium hydroxide.
- The process of slaking quicklime with water is highly exothermic, generating a significant amount of heat.
- It has a high pH value, making it highly alkaline and caustic.
- Slaked lime has been used for various applications throughout history, including in construction and agriculture.
Source: The Hindu
STARFIRE Algorithm
Tags: General Studies – 3 Science and Technology
Why in news?
Recently, an algorithm called STARFIRE has been created by scientists at the Raman Research Institute (RRI), an autonomous institution under the Department of Science and Technology.
About:
- The Simulation of Terrestrial Radio Frequency Interference in Orbits around Earth (STARFIRE) is an advanced algorithm engineered to effectively estimate and map unwanted RFI signals in the space environment.
- By employing STARFIRE, researchers can accurately gauge and identify RFI emissions originating from various sources, such as FM radio stations, Wi-Fi networks, mobile towers, radar systems, satellites, and communication devices.
- This groundbreaking algorithm holds immense potential for transforming space-based astronomy missions by enhancing the quality of data obtained from such missions in the future.
- To develop STARFIRE, scientists collected data on FM transmitter stations from six different countries, namely Canada, the USA, Japan, Australia, Germany, and South Africa.
Source: PIB Gov.
National Coal Index
Tags: General Studies – 3 Economy
Why in news?
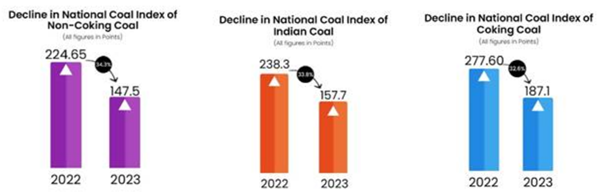
Recently, National Coal Index declines by 33.8% Impressive Coal Stock Ensures Sufficient Supply to Various Sectors.
About:
- The National Coal Index (NCI) is a price index that combines coal prices from all sales channels, including notified prices, auction prices, and import prices.
- National Coal Index established with the base year as the fiscal year 2017-18, it serves as a reliable indicator of market dynamics, providing valuable insights into coal price fluctuations.
- The downward trend in the NCI signifies a more balanced market, aligning supply and demand.
- With sufficient coal availability, the nation can not only meet the growing demand but also support its long-term energy requirements, thus building a more resilient and sustainable coal industry.
Source: PIB Gov.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

