In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Climate Change and the Indian Dairy Sector
- 2 India’s GDP measurement and its limitations
- 2.1 In News:
- 2.2 Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- 2.3 Types of GDP:
- 2.4 Calculation of GDP:
- 2.5 Limitations Of GDP:
- 2.6 Concerns with the current calculation of GDP:
- 2.7 Way Forward:
- 2.8 World Coffee Conference
- 2.9 Why in News:
- 2.10 Key highlights of the 5th World Coffee Conference (WCC):
- 2.11 Conditions required for Coffee Plantation:
- 2.12 Coffee Production:
- 2.13 Coffee Varieties in India:
- 2.14 International Coffee Organization (ICO):
- 3 Gita Mittal Committee
- 4 Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan
- 5 Foreign Contribution Regulations Act
- 6 Indian Standards on Biofuel to Aid GBA’s Clean Energy Goals
- 7 Kole wetlands
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 8.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 8.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 8.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 8.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 8.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
Climate Change and the Indian Dairy Sector
Tag: GS-3 Economics: Animal Rearing, Inflation
In News:
India, the world’s largest milk producer for over half a century, is struggling with runaway milk prices. Despite producing a quarter of global milk production, milk prices are at an all-time high. Average retail price of milk has increased by 18 % in the past two years.
Causes of Inflation in prices of milk:
- Infectious lumpy skin disease: The viral pox disease LSD is novel to the country and has infected 3.2 million cattle and buffaloes across the country in the past year and killed over 0.2 million animals.
- Milk production of the surviving animals has dropped by 20 to 50%,
- Rebound in consumer demand: During COVID the demand and production of milk took hit. However post COVID increased demand for milk and milk products were witnessed, leading to increase in price. .
- Missing 17 million Cattles: According to an estimates the country has likely missed 16.84 million artificial inseminations and have led to stagnation in the number of high-yield dairy cattle and buffaloes between 2020 and 2022.
- This led to double burden of milk loss and incurring additional maintenance cost till the animal enters the next oestrus cycle.
- Fodder Inflation: Farmers faced an acute shortage of dry fodder (wheat straw, along with other items) in 2022, and have been facing a steady fodder inflation since then. The shortage was fuelled by fall in wheat stocks due to an unusually hot March 2022.
What is Artificial Insemination?
- In artificial insemination technology, semen is collected from a bull with proven superior genetic merits and is stored at ultra-low temperatures (known as cryopreservation) at the country’s more than 99,000 artificial insemination centers.
- It is then introduced to the reproductive tract of the female cattle at a time when it is ready for conception (also known as oestrus period that coincides once in 21 days).
- The Union government implements the Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme (NAIP), as part of the Rashtriya Gokul Mission scheme for genetic upgradation of all breeds of bovines and enhances their milk productivity using advanced technologies.
Factors affecting the Indian Dairy Sector:
- Climate Impact:
- Milk Productivity: Increasing temperatures could decrease milk production and reproductive success in cattle. Increasing temperatures could reduce milk production in India’s arid and semi-arid regions by 25% by the end of 2085.
- Increased sensitivity to heat stress: Lactating dairy cows have an increased sensitivity to heat stress. Furthermore, higher yielding cows are more challenged by heat stress than lower yielding animals.
- Reproductive success: Heat stress also decreases reproductive success. Elevated temperatures affect the cow’s ability to display natural mating behaviour, as it reduces both the duration and intensity of oestrus expression.
- Exodus of Dairy Farmers: Dairy farmers find the sector is no longer lucrative and that they are incurring huge losses. This is leading to an exodus of farmers from the dairy sector.
- Government Policies:
- Sex-sorted semen production: The policy aims to produce semen of only female calves up to “90% accuracy”. This has been done to enhance milk production and limit stray cattle population. However this policy overlooks the utility of male cattle and could eliminate them slowly.
- Anti-Slaughter rules: There is also the issue of the utility of female animals after they become unproductive, because it has become difficult to sell cows due to the anti-slaughter rules across many States.
India’s GDP measurement and its limitations
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Growth and Development)
In News:
Recently, a number of experts have drawn attention to a disparity in India’s GDP numbers that masks underlying problems including growing inequality.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- GDP is the gross valuation of all the goods and services generated within a country’s borders for a specific period, generally one financial year.
- The GDP of a nation may be utilized to measure its growth and economic advancement.
- India’s GDP is calculated by the Central Statistics Office (CSO), which is part of the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI).
Types of GDP:
- Real GDP:
- Real GDP is an economic metric that is used to describe the economic output of a country within a specific year. It reflects the value of all goods and services produced while factoring inflation into its calculation. At present, the base year for calculating India’s Real GDP is 2011-12.
- Nominal GDP:
- Nominal gross domestic product (GDP) is GDP given in current prices, without adjustment for inflation.
- Nominal GDP is seen by the government as a more realistic indication of economic growth.
Calculation of GDP:
- Expenditure Method:
- This method considers the total expenditure on goods and services made by every individual inside a single economy.
- GDP = Consumption Expenditure (C) + Investment Expenditure (I) + Government Spending (G) + Net Export (Nx)
- Income Method:
- This method takes account of the gross revenue generated inside a nation’s borders by different production factors, such as labor and capital.
- GDP calculated based on this approach is known as GDI or Gross Domestic Income.
- GDP = Wage + Rent + Interest + Profit
- Output Method:
- This approach is used to determine the market value of all the services and products produced within a country.
- This method aids in removing any discrepancy in GDP measurement brought on by fluctuations in pricing levels.
Limitations Of GDP:
- GDP excludes non-market activities including domestic, volunteer, and other participations that have a beneficial effect on productivity. Additionally, goods produced for personal use are not included.
- GDP does not reflect the unequal distribution of income as seen in the case of India.
- The Standard of Living cannot be estimated by GDP, India has a high GDP but the living standards is relatively low in India.
- The Environmental Impact of growth and social well-being are not explained by GDP.
Concerns with the current calculation of GDP:
- The country’s GDP is presently computed with the base year of 2011-12 which is now more than 10 years old. Under normal circumstances, the base should have been revised after five years in 2016-17, with the readiness for another revision for 2021-22.
- GDP estimates based on an outdated base would not adequately capture new activities being undertaken in the economy like large investments in infrastructure, large inflow of foreign investment, value addition due to diversification, adoption of efficient technologies, and increased capacity.
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has not come out with the results of various surveys like the consumer expenditure survey and the annual survey on unincorporated enterprises which are crucial for the base revision exercise.
- There is a need for the introduction of Supply Use Tables (SUTs) which are critical for the validation of national accounts statistics. This would also take care of confusion faced by some of the followers of national account statistics in understanding the “discrepancies” brought out in the estimates as a balancing term on the expenditure side of GDP.
Way Forward:
- MoSPI should initiate the process by constituting an advisory committee on National Accounts Statistics with professional experts from academia, industry and civil society and also set up working groups for the revision of the base year.
- A decision on the new base year should be taken at the highest level after due consideration of data availability and an assessment of whether the year has been normal or not.
- Steps should also be taken to change the base for all relevant price and production indices.
World Coffee Conference
Tags: GS – 3: Indian Economy (Agriculture)
Why in News:
Recently, the International Coffee Organisation (ICO) hosted the 5th World Coffee Conference (WCC) in Bengaluru.
Key highlights of the 5th World Coffee Conference (WCC):
- The ICO focused on highlighting the economic importance of coffee.
- It is being held for the first time in an Asian coffee-producing country.
- “Regenerative agriculture,” a comprehensive agricultural method was one of the main themes covered during the conference.
- Regenerative Agriculture:
- It is a comprehensive agricultural strategy that emphasizes reducing soil disturbance, diversifying crops, utilizing cover crops, and including livestock in order to improve soil health, biodiversity, and sustainability.
- By adhering to concepts like conservation tillage, crop variety, soil cover with cover crops, and livestock integration, it seeks to increase resources rather than depleting them.
Conditions required for Coffee Plantation:
- Climate: Hot and Humid; Dry weather is necessary at the time of ripening of the berries.
- Rainfall: High (150 – 250 cm)
- Ideal Soil Conditions: Well-drained loamy soils, Presence of humus and minerals (iron, calcium), Fertile volcanic red earth, and Deep sandy loam soils.
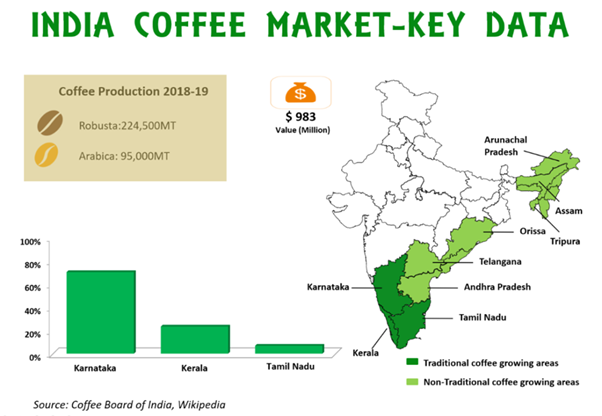
Coffee Production:
- In India:
- Karnataka (Highest) > Kerala > Tamil Nadu > Andhra Pradesh.
- Karnataka accounts for approximately 70% of India’s total coffee production.
- Global Production:
- Brazil is the largest producer.
- India’s position is 6th (65 – 70% of India’s coffee is exported).
Coffee Varieties in India:
- Arabica: Grown at higher altitudes and it has Higher market value due to its aroma.
- Robusta: Known for its strength and used in various blends.
International Coffee Organization (ICO):
- ICO was established in 1963, under the United Nations and is headquartered at London.
- It serves as the only intergovernmental organization for coffee.
- It administers the International Coffee Agreement (ICA), an important instrument for development cooperation.
- Aim to strengthen the coffee sector and promote sustainable growth for the Global Coffee Value Chain (G-CVC).
- It has 43 exporting members (including India) and 6 importing members.
Gita Mittal Committee
Tags: GS – 2 Government Policies & Intervention
In News:
Recently, The Supreme Court of India has informed petitioners involved in the Manipur ethnic violence case that it cannot oversee the administration of the state and encouraged petitioners to place their trust in the Justice Gita Mittal Committee to address the issues raised in the case.
About:
- The Justice Mittal Committee was constituted by the Supreme Court to intervene and monitor relief and rehabilitation, restoration of homesteads, religious places of worship, etc, in Manipur.
- The committee will look into the issues include:
- The distribution of Aadhaar cards and disability certificates to the displaced people of the State,
- distribution of compensation to the families of the dead,
- reconstruction of religious buildings and homes damaged during the violence,
- handling of bodies, and
- the functioning of courts in the state.
SC judgments regarding Manipur violence:
- The State shall appoint a nodal officer in Delhi to guide people who had fled Manipur during the violence by helping them file complaints and petitions with the appropriate authorities in the State.
- The video-conferencing facilities shall be installed in district courts of Manipur within a week, and violation of it may bring the case of “contempt of court” against the State.
Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan
Tags: GS – 3 Economy, Renewable energy
In News:
Recently, The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti has introduced a Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan to streamline the registration of Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) and biogas plants nationwide.
About:
- Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) is an umbrella initiative of the Government of India.
- It aims to transform organic waste, including cattle dung, agricultural residues, and biomass, into valuable resources like biogas, CBG, and organic manure.
- The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti is the coordinating department for GOBARdhan.
- This initiative supports high-value Biogas/CBG production and promotes the use of bio-slurry to improve soil health, carbon content, and water retention.
Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan:
- Anyone who operates or intends to set up a biogas/ CBG/ Bio CNG plant in India can obtain a registration number by registering in this unified registration portal.
- The registration number is required to avail benefits/ support from other Ministries/ Departments.
More information about the news:
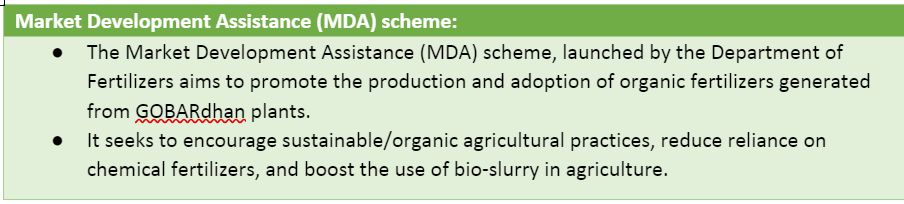
- Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (Nodal Department for GOBARdhan) announced that over 1163 biogas plants and 426 CBG plants have successfully registered on the portal to date.
- These registered CBG/Biogas plants are eligible for assistance under the Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme of the Department of Fertilizers, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
Foreign Contribution Regulations Act
Tags: GS – 2 Polity and Governance, Government Policies & Interventions
In News:
Recently, Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has amended the rules related to the filing of annual returns by Non-Government Organizations (NGOs) registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA).
About:
- These changes involve the requirement for NGOs to provide details about both movable and immovable assets created using foreign funds.
- Significance: The amendment aims to enhance transparency and accountability in the utilization of foreign contributions received by NGOs.
Foreign Contribution Regulations Act (FCRA)
- FCRA was enacted during the Emergency in 1976 amid apprehensions that foreign powers were interfering in India’s affairs by pumping money into the country through independent organisations.
- The law sought to regulate foreign donations to individuals and associations so that they functioned in a manner consistent with the values of a sovereign democratic republic.
- Criteria:
- The FCRA requires every person or NGO seeking to receive foreign donations to be:
- registered under the Act
- to open a bank account for the receipt of foreign funds in the State Bank of India, Delhi
- to utilize those funds only for the purpose for which they have been received and as stipulated in the Act.
- FCRA registrations are granted to individuals or associations that have definite cultural, economic, educational, religious, and social programs.
- The FCRA requires every person or NGO seeking to receive foreign donations to be:
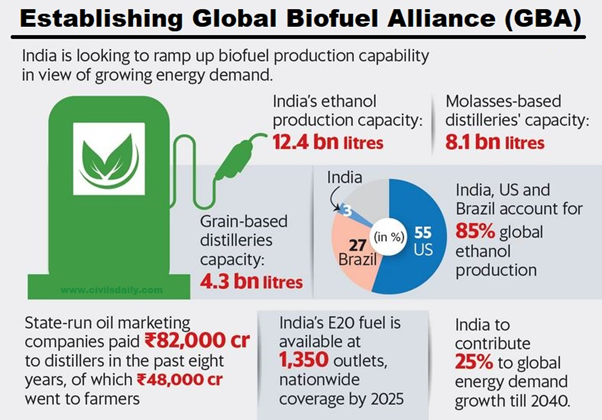
Indian Standards on Biofuel to Aid GBA’s Clean Energy Goals
Tag: GS-3 Economy, Renewable energy
In News:
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the National Standards Body of India commits to complement the green initiatives of the country through the development of relevant standards.
About
- The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has developed nine Indian standards on biofuels, including specifications for anhydrous ethanol, biodiesel, biogas, biodiesel-diesel fuel blends, hydrous ethanol, E85 fuel, E20 fuel, aviation turbine fuel containing synthesized hydrocarbons, and ethanol as a fuel for spark-ignition engine-powered vehicles.
- BIS is working on a standard for paraffinic (green) diesel derived from 2G feedstock.
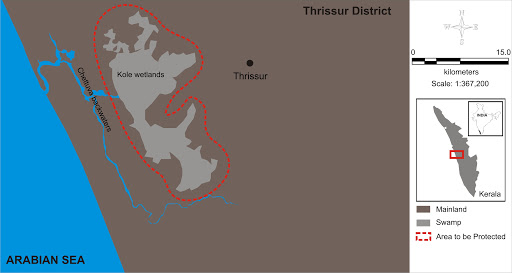
Kole wetlands
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
Kole wetlands of Kerala face the threat of alien plants
About
- The Kole wetlands in Kerala, a Ramsar site of international importance celebrated for its rich biodiversity, are confronting a fresh menace in the form of an invasive alien plant species known as ‘Cabomba furcuta’, commonly referred to as Pink Bloom.
- This species, originally hailing from Central and South America, was initially introduced to Kerala as an aquarium plant but has now emerged as a serious threat to the Kole fields, exacerbating existing challenges posed by invasive species like water hyacinth and Salvinia molesta.
- Despite its visually striking pink flowers, ‘Cabomba furcuta’ presents a substantial risk to the region’s biodiversity and agricultural productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here


