
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 UAPA Designates Hurriyat Chief’s Organization as an Unlawful Association
- 2 PM JANMAN Scheme: A Support for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups
- 3 MGNREGS Scheme
- 4 Dark Energy
- 5 Pantoea Tagorei
- 6 Sensor for Formalin Detection in Fish
- 7 Palna Scheme
- 8 National Legal Services Authority (NALSA)
- 9 Wang’s Garden Lizard
- 10 Eurasian Otter
- 11 Case Study of the Day – “Sikkim man keeps 12,406 ft. lake litter-free for over a decade.”
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 12.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 12.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 12.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 12.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 13 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
UAPA Designates Hurriyat Chief’s Organization as an Unlawful Association
Tag: GS-3 Defence and Security
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) announces the unlawful status of the Muslim League Jammu Kashmir (Masarat Alam faction).

Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967: An Overview
Introduction
- Enacted in 1967, the UAPA serves as India’s primary counter-terrorism legislation, aimed at curbing unlawful and terrorist activities that threaten the nation’s integrity and sovereignty.
Prohibited Activities
- The UAPA targets various activities, including aiding and abetting terrorists, funding terrorism, inciting anti-national sentiments, and engaging in other unlawful acts against the state.
Key Provisions
- Granting extensive powers to the Central Government, the UAPA allows for the designation of organizations as terrorist entities and prescribes penalties for involvement in their activities.
- Notably, these provisions apply to both Indian and foreign nationals, even if offenses occur outside India.
Timeline and Special Court
- The UAPA stipulates a maximum of 180 days for filing a charge sheet after arrests, with investigations to be completed within 90 days.
- Failure to meet this deadline grants the accused eligibility for default bail. The act establishes special courts to conduct trials.
Sanction to Prosecute
- Section 45 mandates that no court can take cognizance of UAPA offenses without prior sanction from the central or state government or an authorized officer.
- The sanction must be granted within a specified time after an independent review of evidence by the competent authority.
Crucial Sections
- Several sections of the UAPA, including Section 13 (Punishment for unlawful activities), Section 16 (Punishment for terrorist acts), Section 17 (Punishment for raising funds for terrorist acts), Section 18 (Punishment for organizing terrorist camps), and Section 22 (Punishment for threatening witnesses), outline specific offenses and corresponding penalties.
2019 Amendment
- The UAPA underwent amendments in 2019, expanding its scope.
- Changes included empowering the government to designate individuals as terrorists, requiring NIA approval for property seizure in NIA-led investigations, and adding the International Convention for Suppression of Acts of Nuclear Terrorism (2005) to the list of treaties.
Masarat Alam: Who is He?
- Masarat Alam, successor to the late Syed Ali Shah Geelani and current chairman of the Hurriyat Conference, leads the Muslim League Jammu Kashmir. Notably, Alam played a prominent role in organizing anti-India protests in the Valley in 2010.
- Arrested under the Jammu and Kashmir Public Safety Act (PSA), he was released in 2015 but has remained in detention for almost 13 years.
Source: TH
PM JANMAN Scheme: A Support for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups
Tag: GS-1 Social Issues
In News:
On November 29, the Union Cabinet gave its nod to the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN).
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs): Overview
Introduction
- PVTGs represent the most vulnerable segment among tribal groups, initially identified as “Primitive Tribal Groups” (PTG) by the Dhebar Commission in 1960-61.
- The category was later renamed Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in 2006.
Numbers and Distribution
- In 1975, the Government of India designated 52 tribal groups as PVTGs based on the Dhebar Commission’s recommendations.
- Presently, there are 75 such groups spread across 22,544 villages in 18 states and one Union Territory, totaling approximately 28 lakh individuals.
- Odisha has the highest concentration, exceeding 2.5 lakh PVTG members.
Distinct Characteristics
- PVTGs share common characteristics, including stagnant or declining populations, pre-agricultural technology, extremely low literacy levels, and economies at a subsistence level.
- Population sizes vary significantly among groups, ranging from under 1,000 to over 1 lakh.
Challenges in Development
- Severely marginalized due to isolation and distinct socio-economic and cultural traits, PVTGs face challenges such as limited access to basic services, social discrimination, vulnerability to displacement, and inadequate political representation.
- Mainstream society often overlooks their traditional knowledge, and stereotypes persist.
Government Schemes for PVTGs
- Government initiatives, including the PVTG Development Plan, Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM), and others, aim for holistic tribal area development.
- These schemes focus on education, healthcare, livelihood opportunities, and the preservation of traditional knowledge.
Other Measures
- Various measures, such as Eklavya Model Residential Schools, Forest Rights Act 2006 for land titles, and support through the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act 1989, contribute to education, self-governance, and protection against discrimination.
PM-JANMAN: A Different Approach
Proper Identification and Recognition
- Criticism of outdated criteria for identifying PVTGs led to the government’s initiative to create a Human Development Index specifically for them.
- The participatory bottom-up approach abandons a one-size-fits-all strategy, involving PVTGs in decision-making.
Livelihood Promotion
- The scheme emphasizes customized strategies, providing skills training, and resources, and implementing the Forest Rights Act to secure access to forest resources.
- Traditional technologies are encouraged for sustainable development.
Health, Nutrition, and Education
- Outreach strategies, such as Mobile Medical Health Units, are crucial for healthcare in remote areas. Education accessibility is enhanced by incorporating culture and language into the curriculum and training teachers about PVTG cultural contexts.
Infrastructure Development
- Guidelines for infrastructure schemes have been relaxed to accommodate the unique habitation patterns of PVTGs, ensuring improved access to housing, water, sanitation, electricity, and connectivity.
Source: IE
MGNREGS Scheme
Tag: GS-2 Government policies and interventions, poverty and development
In News:
In the fiscal year 2023-24, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) has experienced a notable increase in women’s involvement, reaching an unprecedented high.
Women’s Participation Trends in MGNREGA: An Analysis
Women Participation Trends
- Gradual Increase
- Over the last decade, women’s participation in MGNREGA has steadily risen, reaching 59.25% from 53.19% during the 2020-21 Covid-19 outbreak.
- Regional Disparities
- Southern states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and Goa exhibit high women’s involvement, exceeding 70%, while northern states such as Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh lag at around 40%.
- Recent Improvements
- Despite historical disparities, states like Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Lakshadweep have shown recent improvements in women’s participation rates in the ongoing financial year.
Rural Labor Force Trends
- Beyond MGNREGS
- The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) indicates a substantial surge in the Female Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in rural areas, rising from 18.2% in 2017-18 to 30.5% in 2022-23.
- Female unemployment rates have concurrently decreased from 3.8% to 1.8% during the same period.
MGNREGA Scheme Overview
- Introduction
- MGNREGA, initiated in 2005 by the Ministry of Rural Development, is one of the world’s largest work guarantee programs.
- Legal Guarantee
- It provides a legal guarantee of 100 days of employment in every financial year to adult members of rural households willing to engage in unskilled manual work at the minimum wage.
- Active Workers
- As of 2023-24, there are 14.32 crore active workers.
Major Features
- Legal Guarantee
- The cornerstone of MGNREGA ensures that rural adults can request and must receive work within 15 days; otherwise, an “unemployment allowance” is mandated.
- Priority for Women
- The scheme prioritizes women, aiming for at least one-third of beneficiaries to be women who have registered and requested work.
- Social Audit
- Section 17 mandates a social audit of all works executed under MGNREGA.
Implementation Agency
- Monitoring
- The Ministry of Rural Development, in collaboration with state governments, monitors the entire implementation of the scheme.
Objective
- Poverty Alleviation
- MGNREGA aims to improve the purchasing power of rural people, offering semi or unskilled work to those below the poverty line and bridging the gap between the rich and poor.
Achievements of 2022-23
- Households Employed
- In 2022-23, 11.37 crore households availed employment.
- Person-Days Generated
- A total of 289.24 crore person-days employment was generated, with significant proportions for women, Scheduled Castes (SCs), and Scheduled Tribes (STs).
Challenges with Scheme Implementation
- Funds Dispersal
- Delays and insufficiency in funds dispersal, leading to delays in wage payments, have impacted the effectiveness of MGNREGA.
- Caste-Based Segregation
- Significant variations in delays by caste, with SC and ST workers facing more challenges than non-SC/ST workers.
- Ineffective Role of PRI
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) lack autonomy, hindering the effective implementation of MGNREGA.
- Incomplete Works
- There is a delay in completing works, irregular inspection of projects, and concerns about the quality of work and asset creation.
- Fabrication of Job Cards
- Issues related to fake job cards, inclusion of fictitious names, missing entries, and delays in making entries pose challenges.
Way Forward
- Consistent Fund Flow
- Ensuring a consistent fund flow to states and implementing agencies while leveraging digital tools for transparent, timely wage payments.
- Focus on Exclusion Errors
- Identifying areas where marginalized SC and ST families are missing out on MGNREGA benefits.
- Empower Councils
- Empowering State and Central Employment Guarantee Councils for informed decisions, incorporating public participation through assemblies, civil society, and worker unions.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2011) Q. Among the following who are eligible to benefit from the “Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act”? (a) Adult members of only the scheduled caste and scheduled tribe households (b) Adult members of below poverty line (BPL) households. (c) Adult members of households of all backward communities (d) Adult members of any household Ans: (d) Exp: Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee (MGNREGA), which is the largest work guarantee program in the world, was enacted in 2005 with the primary objective of guaranteeing 100 days of wage employment per year to every household whose adult members volunteer to do unskilled manual work. It aims at addressing the causes of chronic poverty through the ‘works’ (projects) that are undertaken, thus ensuring sustainable development. There is also an emphasis on strengthening the process of decentralization by giving a significant role to Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in planning and implementing these works. Therefore, option D is the correct answer. |
Source: IE
Dark Energy
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech.
In News:
A fragile equilibrium exists in the composition of the universe’s energy, with various forms of matter and radiation intricately balanced.
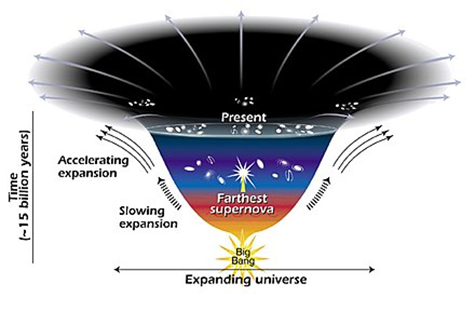
Understanding Dark Energy in the Universe: An Overview
About Dark Energy
- Dark energy, a mysterious and elusive form of energy, constitutes a significant portion of the universe’s total energy content.
- It plays a crucial role in the observed accelerated expansion of the cosmos, with approximately 68% of the universe attributed to dark energy, while dark matter makes up around 27%.
- In contrast, all observable matter on Earth constitutes less than 5%.
Key Characteristics of Dark Energy
Invisible Force Driving Expansion
- Dark energy serves as an unseen force responsible for the universe’s accelerated expansion.
- Unlike gravity, which pulls objects together, dark energy acts as a repulsive force, pushing galaxies away from each other.
Space Dynamics
- Dark energy challenges the idea of space as a void, presenting it as a dynamic, stretchable medium that responds to the presence of energy.
Unique Contributions to Expansion
- Different forms of energy, including matter, radiation, and dark energy, contribute uniquely to the non-uniform expansion of the universe.
Balancing Act
- Dark energy dominates the universe’s energy budget, influencing the overall rate at which space expands.
- Maintaining a delicate balance with other forms of energy is essential for cosmic stability.
Implications of Dark Energy
Significance for the Observable Universe
- The amount of dark energy holds significant implications for the observable universe.
- An excess of positive energy could result in galaxies moving away faster than light, limiting visibility to nearby regions.
- Conversely, excessive negative energy might lead to a universe collapse.
Diluteness Across the Universe
- Despite its dominance, dark energy is incredibly dilute across the vastness of the universe, posing questions about its nature and distribution.
Possible Explanations for Dark Energy
Property of Space
- Einstein’s gravity theory suggests that “space” can possess its energy, not diluted as space expands, causing accelerated expansion.
Quantum Theory of Matter
- The quantum theory of matter proposes that “space” is filled with temporary particles, forming and disappearing continually.
Fifth Fundamental Force
- Speculative theories suggest a fifth fundamental force, termed “quintessence,” to explain dark energy.
- However, none of these theories have been conclusively proven, rendering dark energy the “most profound mystery in all of science.”
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2012) Q. Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidence for the continued expansion of the universe? Detection of microwaves in space Observation of redshift phenomenon in space Movement of asteroids in space Occurrence of supernova explosions in space Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) None of the above can be cited as evidence Ans: (a) Exp: Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson in 1963 found mysterious microwaves coming equally from all directions. The radiation called the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation was the radiation predicted years earlier by Gamow, Herman, and Alpher. This convinced most astronomers that the Big Bang theory was correct and provided an evidential base for the continued expansion of the universe. Hence, 1 is correct. Edwin Hubble in 1929 measured the redshifts of several distant galaxies. On plotting redshift against relative distance, the redshift of distant galaxies increased as a linear function of their distance. Astronomers measure the movement of objects relative to us using the Doppler shift. Light from distant objects in the universe is redshifted (shift in the frequency of light towards red color), which tells us that the objects are all receding away from us. Hence, 2 is correct. The movement of an asteroid in space may provide information regarding the type of material in the early universe, but as such no evidence regarding the expanding universe is provided. Hence, 3 is not correct. The supernova explosion occurs when there is a change in the core, or center, of a star. It happens in either a binary star system or at the end of a single star’s lifetime. It helps in studying the distribution of elements throughout the universe. These elements travel on to form new stars, planets, and everything else in the universe. However, it does not provide evidence for an expanding universe. Hence, 4 is not correct. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer. |
Source: TH
Pantoea Tagorei
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech.
In News:
A groundbreaking discovery by researchers at Visva-Bharati University unveils a novel bacterial species, Pantoea Tagorei, with the potential to revolutionize agricultural methods.
Unlocking Agricultural Potential: Pantoea Tagorei’s Role as a Biofertilizer
Overview
- Pantoea Tagorei bacteria, belonging to the genus Pantoea within the Enterobacteriaceae family, have notable characteristics and applications.
Habitat and Isolation
- Pantoea bacteria, including Pantoea Tagorei, can be found in diverse environments such as water, soil, humans, animals, and plants.
Plant Growth-Promoting Abilities
- Described as a plant growth-promoting bacteria, Pantoea Tagorei exhibits impressive capabilities in enhancing the cultivation of various crops, including paddy, pea, and chili.
Nutrient Extraction and Solubilization
- The bacteria efficiently extract potassium from the soil, contributing to enhanced plant growth.
- Additionally, it facilitates the solubilization of both potassium and phosphorus, nitrogen fixation, and overall nutrient availability for plants.
Impact on Crop Yield and Food Security
- The positive effects on plant growth suggest the potential for increased crop yield, addressing critical issues related to food security.
Reducing Dependency on Commercial Fertilizers
- Pantoea Tagorei plays a crucial role in enhancing soil nutrient availability, potentially reducing the reliance on commercial fertilizers.
- This aspect makes it a cost-effective approach to sustainable agriculture, positioning it as a potential biofertilizer.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2021) Q. Concerning Madanapalle of Andhra Pradesh, which one of the following statements is correct? (a) Pingali Venkayya designed the tricolor Indian National Flag here. (b) Pattabhi Sitaramaiah led the Quit India Movement of the Andhra region from here. (c) Rabindranath Tagore translated the National Anthem from Bengali to English here. (d) Madame Blavatsky and Colonel Olcott set up the headquarters of the Theosophical Society first here. Ans: (c) The original song ‘Jana Gana Mana’ (National Anthem) was written in Bengali but in a Sanskritized dialect known as Sadhu Bhasha. The idea of translating the song from Bengali to English came to Rabindranath Tagore while he was visiting the Besant Theosophical College at the invitation of Irish poet James H. Cousins. He penned down the English translation during his stay at Madanapalle, a small town in the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh. Jana Gana Mana was officially proclaimed as India’s National Anthem by the Constituent Assembly of India on 24th January 24, 1950. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer. Prelims (2010) Q. Which feature of some species of blue-green algae helps promote them as bio-fertilizers? (a) They convert atmospheric methane into ammonia which the crop plants can absorb readily (b) They induce the crop plants to produce the enzymes that help convert atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates (c) They have the mechanism to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that the crop plants can absorb readily (d) They induce the roots of the crop plants to absorb the soil nitrates in larger quantities Ans: (c) Exp: Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae is an example of a bio-fertilizer, a type of organic fertilizer that contains living organisms and harnesses naturally occurring inputs like solar energy, nitrogen, and water to ensure soil fertility and plant growth Blue-green algae are photoautotrophic microbes. They have specialized cells which utilise solar energy to reduce atmospheric N2 into Ammonia. Ammonia is used by plants for growth and increased production. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer. |
Source: TH
Sensor for Formalin Detection in Fish
Tag: GS-3 Environment and Science and Tech.
In News:
Researchers at Guwahati University, Assam, have innovated a novel sensor comprising a metal oxide-reduced graphene oxide (metal oxide-rGO) composite.
Key Facts About the Metal Oxide-rGO Sensor
Overview
- The sensor utilizes a composite of Graphene Oxide (GO) and tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2) to detect formalin in adulterated fishes, offering a low-cost, non-invasive, and selective solution to prevent food adulteration.
Need for Innovation
- Traditional formalin sensors for fish either rely on expensive electrochemical-based methods or less costly but invasive colorimetric-based approaches.
- These methods often struggle with issues related to low-level and selective detection.
Working Procedure
Challenges with GO
- The oxidized form of graphene, GO, initially poses challenges due to low electrical conductivity.
Enhanced Composite
- Scientists addressed GO’s limitations by developing a composite, tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2), with improved properties.
Composite Benefits
- rGO provides high solution processability and ease of chemical modification, while tin oxide contributes high stability and sensitivity to low concentrations of formaldehyde.
Effective Sensing
- The sensor, crafted from tin oxide (SnO2) decorated Reduced graphene oxide (rGO), demonstrates effective sensing of formaldehyde vapor at room temperature.
Optimized Combination
- Leveraging the strengths of rGO in detecting toxic gases and SnO2 in formaldehyde detection, the combination maximizes their capabilities.
Breakthrough in Food Adulteration Prevention
- The ongoing lab process for designing the prototype marks a potential breakthrough in preventing food adulteration, showcasing the sensor’s significance in ensuring food safety for consumers.
Source: PIB
Palna Scheme
Tag: GS-2 Women Empowerment
In News:
Under the ‘Palna’ scheme, the Ministry of Women and Child Development aims to establish 17,000 creches within Anganwadi centers throughout India
About Palna Scheme
- This undertaking seeks to offer secure daycare facilities, fostering the cognitive, nutritional, and health advancement of children.
- With a rising women workforce participation rate, reaching 37% in 2022, the expansion of creches reflects a dedicated endeavor to bolster women’s support while nurturing the development of upcoming generations.
- In July 2022, the Ministry of Women and Child Development overhauled the National Creche Scheme, rebranding it as the Palna Scheme under ‘Mission Shakti.’
- This transformation introduced Anganwadi cum Creches and reclassified existing creches from the previous scheme as Stand Alone Creches.
Source: PIB
National Legal Services Authority (NALSA)
Tag: GS-2 Polity and Governance
In News:
The Executive Chairperson of the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) has been nominated by the President, with the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court, Justice Sanjiv Khanna, selected for the position.
About the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA)
Introduction
- NALSA, established under the Legal Services Authorities Act, of 1987, is dedicated to offering free legal services to the marginalized sections of society and facilitating Lok Adalats for amicable dispute resolution.
Primary Objective
- The paramount goal of NALSA is the expeditious disposal of cases to alleviate the burden on the judiciary.
Leadership
- The Chief Justice of India serves as the patron-in-chief of NALSA.
- The second senior-most judge of the Supreme Court of India assumes the role of the Executive Chairman.
- NALSA is headquartered at the Supreme Court of India in New Delhi.
Organizational Structure
- In each State, a State Legal Services Authority exists.
- In every High Court, a High Court Legal Services Committee is constituted.
- District Legal Services Authorities and Taluk Legal Services Committees are established at the district and taluk levels, aligning with NALSA’s policies and directions.
Legal Literacy Programs
NALSA, through State Legal Services Authorities, conducts legal literacy programs to enhance legal awareness.
Free Legal Services
The spectrum of free legal services includes:
- Payment of court fees and related charges in legal proceedings.
- Provision of legal representation in court.
- Obtaining certified
- copies of orders and documents.
- Preparation of appeals and related documents in legal proceedings.
Eligibility for Free Legal Services
- Women and children
- SC/ST members
- Industrial workmen
- Victims of mass disasters, violence, natural calamities, and industrial disasters.
- Disabled individuals
- Persons in custody
- Those with an annual income not exceeding Rs. 1 lakh (Rs. 5,00,000 for the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee).
- Victims of human trafficking or begging.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 39A emphasizes free legal aid for the economically weaker sections.
- Articles 14 and 22(1) obligate the State to ensure equality and justice.
Key Facts about Lok Adalats
- An alternative dispute resolution mechanism.
- Settles or compromises disputes pending in court or at the pre-litigation stage.
- Conducted by NALSA and other legal services institutions.
- Holds statutory status under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987.
Appeal and Fees
- The Lok Adalat’s decision is deemed a decree, final and binding.
- No appeal lies against the Lok Adalat’s award.
- No court fee is payable for matters filed in Lok Adalats.
Nature of Cases for Lok Adalats
- Any pending case before any court.
- Disputes not presented before any court but likely for future litigation.
- Matters related to non-compoundable offenses are not settled in Lok Adalats.
Source: TI
Wang’s Garden Lizard
Tag: GS-3 Science and Tech.
In News:
China has recently identified a new reptile species, naming it Wang’s Garden Lizard.

About Wang’s Garden Lizard
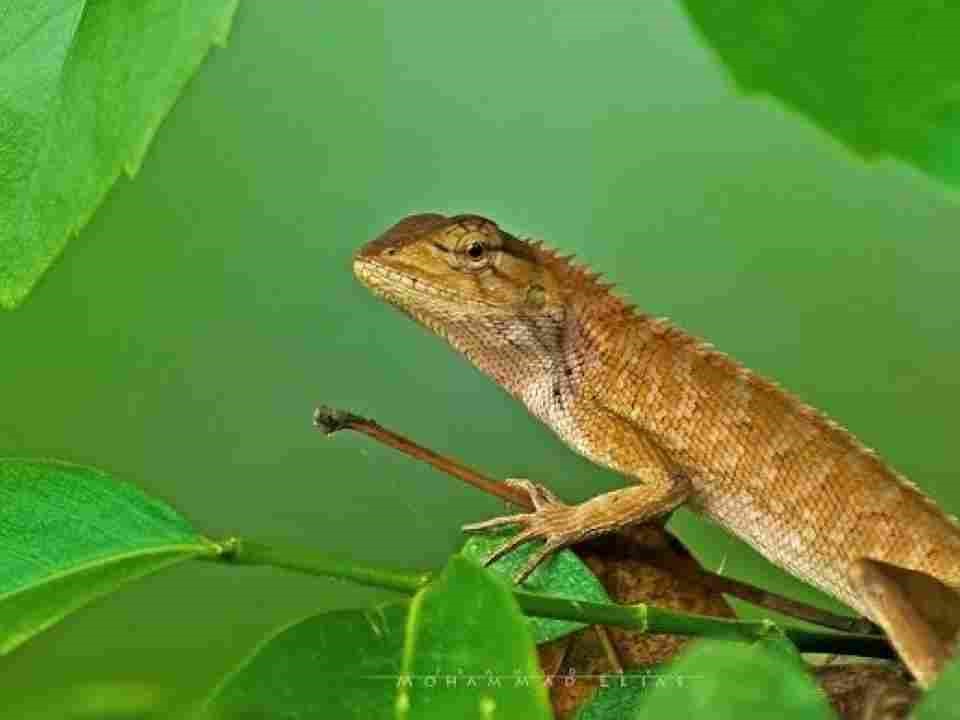
Species Identification
- Wang’s Garden Lizard is a newly identified species of iguana.
- Scientific Name: Calotes wangi
Distribution
- Found in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests and tropical monsoon forests in southern China and northern Vietnam.
- Primarily located in mountainous areas, hills, plains on forest edges, arable land, shrublands, and urban green belts.
Conservation Status
- Currently not considered threatened, but certain areas face habitat fragmentation.
Distinctive Features
- Measures less than 9 cm in length.
- Notable feature includes an orange tongue.
- Active at the forest edge, demonstrating a tendency to rush into bushes or climb tree trunks when endangered.
- During the night, it rests on sloping shrub branches, sleeping close to the branches.
Diet and Activity
- Consumes a diverse range of insects, spiders, and other arthropods.
- Active from April to October annually, extending to March to November or longer in tropical regions.
Cultural Significance
- Apart from their ecological role, their bodies are utilized for medicinal purposes, and the lizards are also consumed as food.
Source: SN
Eurasian Otter
Tag: GS-3 Environment and Ecology
In News:
In a noteworthy discovery, a team of researchers recently identified the presence of a Eurasian otter in the Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary in Idukki, marking the first recorded instance in Kerala.
About the Eurasian Otter
Species Classification
- The Eurasian Otter is a semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal native to Eurasia.
- Scientific Name: Lutra lutra
Geographical Distribution
- Among Palearctic mammals, it boasts one of the broadest distributions, ranging from Ireland to China and extending south to Southeast Asia.
- Populations are found throughout Europe, North Africa, and Asia.
- In India, it is present in northern, northeastern, and southern regions.
Habitat Variety
- Inhabits diverse environments such as streams, rivers, lakes, freshwater and peat swamp forests, ocean shores, rice fields, fjords, caves, and terrestrial habitats near waterways.
- In the Indian subcontinent, it thrives in cold hills and mountain streams.
Physical Features
- Possesses a lengthy body with a thick tail and short legs.
- Exhibits a brown upper coat and cream-colored underbelly.
- Sensitive whiskers around the snout aid in prey detection.
- Dual layers of fur include a dense, waterproof outer coat and a warm inner layer.
- Displays acute senses of sight, smell, and hearing.
- Primarily an elusive, solitary otter, but occasional sightings of family groups, comprising a mother and her offspring, occur.
Diet Diversity
- Maintains a varied diet encompassing fish, crustaceans, amphibians, and occasionally reptiles, birds, eggs, insects, and worms.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Status: Near Threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II
- CITES Listing: Appendix I
Source: TH
Case Study of the Day – “Sikkim man keeps 12,406 ft. lake litter-free for over a decade.”
Sangay Lama, a resident of Thegu village in Sikkim, has dedicated over a decade to maintaining the cleanliness of Tsomgo Lake and its environs. In 2008, at the age of 37, he established the Tsomgo Pokhri Sanrakshan Samiti, a lake conservation committee comprising representatives from various entities such as the state forest department, the World Wide Fund, environment, and wildlife management officials, a drivers’ association, shop owners’ association, and gram panchayats, to preserve this oval-shaped water body, also known as Changu. Situated at an altitude of 12,406 feet, approximately 40 km from Gangtok and 16 km from the Nathu La pass connecting Sikkim to China’s Tibet Autonomous Region.
Lama explained, “All waste generated in the vicinity is gathered in designated bins and segregated at the source. Waste collection trucks operate twice daily, at 8 am and 4 pm, catering to the 52 shops selling food items, handicrafts, and other goods, each contributing around 4 kilos of dry waste and 2 kilos of wet waste. The collected waste is then disposed of at the 32, Martam Dumping and Recovery Centre.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

