The Later Mughal period witnessed the twilight of one of the most illustrious dynasties in Indian history, marked by a decline in central authority and the rise of regional powers. Concurrently, the arrival of European powers on the Indian subcontinent brought about profound changes in the political and economic landscape, setting the stage for the eventual British conquest of India. This period of transition and transformation holds significant importance in understanding the dynamics of colonialism and its impact on Indian society. In this series of UPSC Prelims topic-wise questions, we embark on a journey through the Later Mughal era, the influx of European powers, and the pivotal events leading to British dominance in India. Through a nuanced exploration of key themes and historical developments, we unravel the complexities of this period, shedding light on its enduring legacy and relevance in the broader context of Indian history and civilization.
Contents
- 1 1. Examine the map given below(1995)
- 2 2. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?(1995)
- 3 3. Hooghly was used as a base for piracy in the Bay of Bengal by (1995)
- 4 4. Who among the following was associated with suppression of Thugs? (1997)
- 5 6. The term imperial preference was applied to the
- 6 7. Who among the following Indian rulers established embassies in foreign countries on modern lines?
- 7 8. With reference to the entry of European powers into India, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2003)
- 8 9. In India, among the following locations, the Dutch established their earliest factory at (2003)
- 9 10. Which of the statement (s) given above is/are correct?
- 10 11. Which of the following is the correct chronological order of the battles fought in India in the 18th century? (2005)
- 11 12. Which one of the following is a correct statement?
- 12 13. In the year 1613, where was the English East India Company given permission to set-up a factory (trading post)? (2006)
- 13 14. Who among the following Europeans, were the last to come to pre-independence India as traders?
- 14 15. What was the immediate reason for Ahmad Shah Abdali to invade India and fight the Third Battle of Panipat? (2010)
- 15 17. With reference to Pondicherry now Puducherry), consider the following statements. (2010)
- 16 17. Consider the following statements. (2011)
- 17 18. Economically, one of the result of the British rule in India in the 19th century was the (2018)
- 18 19. Which one of the following groups of plants was domesticated in the ‘New World’ and introduced into the ‘Old World’? (2019)
- 19 20. Consider the following statements. (2021)
- 20 21. In the first quarter of seventeenth century, in which of the following was/were the factory/factories of the English East India Company located? (2021)
- 21 22. With reference to Indian history, consider the following statements. (2022)
- 22 Frequently Asked Questions
- 23 Q1. What were the significant factors contributing to the decline of the Later Mughals?
- 24 Q2. How did the arrival of European powers impact the political landscape of India during the Mughal period?
- 25 Q3. What were the key events leading to the British conquest of India?
- 26 Q4. How did the British East India Company consolidate its power in India after the Battle of Plassey?
- 27 Q5. What were the long-term consequences of British conquest and colonial rule in India?
- 28 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
1. Examine the map given below(1995)
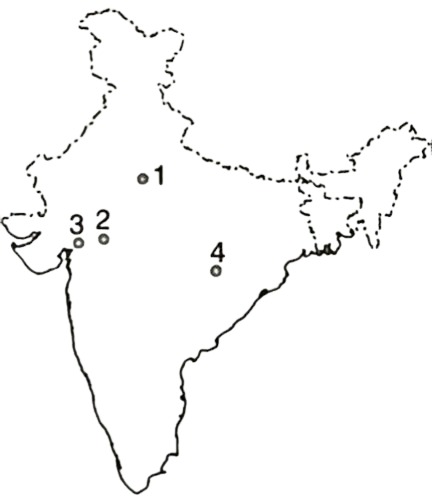
The places marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 were respectively the seats of powers of the
(a) Scindias, Holkars, Gaekwads and Bhonsles
(b) Holkars, Scindias, Gaekwads and Bhonsles
(c) Gaekwads, Bhonsles, Scindias and Holkars
(d) Scindias, Holkars, Bhonsles and Gaekwads
Ans. (a)
Exp. The places marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 are Scindias, Holkars, Gaekwards and Bhonsles respectively. Scindias ruled the Gwalior state in Central India. The holkars were ruled at Indore, Gaekwards at Baroda and Bhonsle at Nagpur.
2. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?(1995)
(a) Battle of Buxar Mir Jafar o/s Clive
(b) Battle of Wandiwash French o/s East India company
(c) Battle of Chillianwala Dalhousie v/s Marathas (d)
(d) Battle of Kharda Nizam v/s East India Company
Ans. (b)
Exp. Only pair (b) is correctly matched. The Battle of Wandiwash or Third Caratic War was fought during 1757 – 1763 between the French (under General Count de Lally) and the British (under Lieutenant General Sir Eyre Coote) East India Company. It took place in Carnatic, South India. In this battle the French army was decisively defeated by the British East India Company.
Pairs (a), (c) and (d) are incorrectly matched as the Battle of Buxar was fought on 22nd October, 1764 between the British East India Company force under the command of Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim Nawab of Bengal till 1764, the Nawab of Awach Shuja-ud-Daula and the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II. Mi Casim, Shuja-ud-Daula and Shah Alam-II lost the battle and Mir Jafar was commemorated as Nawab of Bengal. The Battle of Chillianwala was fought in January 1849 between the British East India Company and the Sikhs in the Chillianwala region of Punjab. As a result at the end of the battle both sides claimed victory. Battle of Kharda took place in March 1795, between Nizan and Maratha Empire, in which Nizam was badly defeated The Battle took place at Khardah which currently lies in Ahmednagar district in the state of Maharashtra.
3. Hooghly was used as a base for piracy in the Bay of Bengal by (1995)
(a) the Portuguese
(b) the French
(c) the Danish
(d) the British
Ans. (a)
Exp. Hooghly was used as a base for piracy in the Bay of Bengal by the Portuguese. It became a center of piracy due to the British East India Company vanishing the influence of Portuguese trade in the region, so dacoits confiscation and capture of goods were increased. The Portuguese merchant sailed from Bay of Bengal to Hooghly to deceive the custom duties and practiced piracy in the region. Finally it was subdued by Qasim Khan, the Governor of Bengal during the reign of Shah Jahan.
4. Who among the following was associated with suppression of Thugs? (1997)
(a) General Henry Prendergast
(b) Captain Sleeman
(c) Alexander Burnes
(d) Captain Robert Pemberton
Ans. (b)
Exp. Sir William Henry Sleeman along with William Bentinck is known for their duty for suppressing the Thugs across the country. In 1835, the ‘Thuggee and Dacoity Dept’ was created by William Bentinck and William Henry Sleema was made its superintendent. He is regarded for capturing Syeed Amir Ali and many other notorious leaders.
5. At a time when empires in Europe were crumbling before the might of Napoleon which one of the following Governors General kept the British flag flying high in India? (1999)
(a) Warren Hastings
(c) Lord Wellesley
(b) Lord Cornwallis
(d) Lord Hastings
Ans. (d)
Exp. At a time when empires in Europe were crumbling before the might of Napoleon, Lord Hastings kept the British flag flying high in India. He served as Governor-General of India from 1813 to 1823. His tenure is known for policy of intervention and war. Two important wars, Gurkha War or the Anglo-Nepalese War and Third Anglo Maratha War occurred during his tenure.
6. The term imperial preference was applied to the
(a) Special privileges on British imports in India (1999)
(b) Racial discrimination by the Britishers
(c) Subordination of Indian interest to that of the British
(d) Preference given to British political agents over Indian
Ans. (a)
Exp. The term imperial preference was applied to the Special privileges on British imports in India. On the basis of this privilege, nominal duty was paid on British imports in India while India exports paid high duty in Britain.
7. Who among the following Indian rulers established embassies in foreign countries on modern lines?
(a) Haider Ali
(b) Mir Qasim
(c) Shah Alam I
(d) Tipu Sultan
Ans. (d)
Exp. Tipu Sultan established embassies in Egypt, France and Turkey on modern lines. Tipu Sultan (1750-1799) was known as the ‘Tiger of Mysore’ and Tipu Sahib. He introduced number of administrative innovations during his rule, including the introduction of a new coinage, a new Mauludi Lunisolar Calendar etc.
8. With reference to the entry of European powers into India, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2003)
(a) The Portuguese captured Goa in 1499
(b) The English opened their first factory in South India at Masulipatnam
(c) In eastern India, the English Company opened its first factory in Orissa in 1633
(d) Under the leadership of Dupleix, the French occupied Madras in 1746
Ans. (a)
Exp. With reference to the entry of European power in India statement (a) is incorrect. The Portuguese conquest of Goa occurred in 1510 and not in 1499. Albuquerque was not ordered to conquer Goa by the Portuguese government. He had been only ordered to capture Hormuz, Adam and Malacca.
9. In India, among the following locations, the Dutch established their earliest factory at (2003)
(a) Surat
(b) Pulicat
(c) Cochin
(d) Cassimbazar
Ans. (b)
Exp. In India, among the following locations, the Dutch established their earliest factory at Pulicat.
However, In India, Dutch East India company established its first factory in Masulipatnam in 1605 AD, followed by Pulicat in 1610 AD, Surat in 1616 AD, Bimilipatam in 1641 AD and Chinsura in 1653 AD. Factory at Pulicat was known as ‘Fort Geldria’. The Dutch East India company was formed in 1602 AD as ‘United East India Company’ and its first permanent trading post was in Indonesia.
10. Which of the statement (s) given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) Only 3
c) 2 and 3
(d) None of the above
Ans. (b)
Exp. Only statement (3) correct.
Mir Jafar served as the commander of Bengali forces under Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, but betrayed him during the Battle of Plassey and succeeded him after the British victory in 1757. Statements (1) and (2) are incorrect becauses the third battle of Panipat took place on 14th January, 1761, between a northern expeditionary force of the Maratha empire and invading forces of Ahmad Shah Abdali. As a result the forces led by Ahmad Shah came out victorious after destroying Marathas. Also, Tipu Sultan was killed in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War.
11. Which of the following is the correct chronological order of the battles fought in India in the 18th century? (2005)
(a) Battle of Wandiwash, Battle of Buxar, Battle of Ambur, Battle of Plassey
(b) Battle of Ambur, Battle of Plassey, Battle of Wandiwash, Battle of Buxar
(c) Battle of Wandiwash, Battle of Plassey, Battle of Ambur, Battle of Buxar
d) Battle of Ambur, Battle of Buxar, Battle of Wandiwash, Battle of Plassey
Ans. (b)
Exp. The correct chronological order is Battle of Ambur, Battle of Plassey, Battle of Wandiwash and Battle of Buxar. Battle of Ambur was the first major battle of the Second Camatic War started on 3rd August, 1749. The battle was initiated by Muzzafar Jung and supported by Joseph Francois Dupleix and led by Chanda Sahib, who sought to overthrow Anwaruddin Muhammed Khan, the Nawab of the Carnatic, for supporting Nasir Jung’s claim to be Nizam of Hyderabad. Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British Bast India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23rd June, 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. Battle of Wandiwash was a battle in India between the French and the British in 1760. The battle was part of the Third Camatic War fought between the French and British colonial empires. Battle of Buxar was fought between 22nd and 23rd October, 1764 between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, led by Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Mir Oasim, (Nawab of Bengal) Shuja-ud-Daula (Nawab of Awadh) and the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II till 1764.
12. Which one of the following is a correct statement?
(2005)
(a) The modern Kochi was a Dutch colony till India’s independence
(b) The Dutch defeated the Portuguese and built Fort Williams in the modern Kochi
(c) The modern Kochi was first a Dutch Colony before the Portuguese took over from them
(d) The modern Kochi never became a part of the British Colony
Ans. (b)
Exp. Statement (b) is correct as in 1663, Dutch under Van Goens defeated the Portuguese and built Fort Williams in modern Kochi. They destroyed the Jesuit College and many Roman Catholic Churches except for St. Francis which they used. On the islands in the backwaters, the Dutch built the Bolgatty Palace and the Dutch Palace at Mattancherry and many other country houses.
13. In the year 1613, where was the English East India Company given permission to set-up a factory (trading post)? (2006)
(a) Bangalore
(c) Masulipatnam
(b) Madras
d) Surat
Ans. (d)
Exp. In the year 1613, in Surat the English East India Company was given permission to set-up a factory (trading post). In 1612, James I instructed Sir Thomas Roe to visit the Mugha Emperor Jahangir and arrange for a commercial treaty that would give the Company exclusive rights to reside and bui factories in Surat and other areas.
14. Who among the following Europeans, were the last to come to pre-independence India as traders?
(a) Dutch
(b) English
(c) French
(d) Portugu
Ans. (c)
Exp. French were the last Europeans to come to India for trading. The French East India Company was established in 1664. They established their first factory in Surat in 1668.
15. What was the immediate reason for Ahmad Shah Abdali to invade India and fight the Third Battle of Panipat? (2010)
(a) He wanted to avenge the expulsion by Marathas of his
Viceroy Timur Shah from Lahore
(b) The frustrated Governor of Jullandhar Adina Beg Khan invited him to invade Punjab
(c) He wanted to punish Mughal administration for nonpayment of the revenues of the Chahar Mahal (Gujarat, Aurangabad, Sialkot and Pasrur)
(d) He wanted to annex all the fertile plains of Punjab upto the borders of Delhi to his kingdom
Ans. (a)
Exp. Statement (a) is correct with regard to Ahmad Shah Abdali invasion. The immediate reason for Ahmad Shah Abdali to invade India and fight the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761 was to avenge the expulsion by Marathas of his Viceroy Timur Shah from Lahore.
17. With reference to Pondicherry now Puducherry), consider the following statements. (2010)
1. The first European power to occupy Pondicherry were the Portuguese.
2. The second European power to occupy Pondicherry were the French.
3. The English never occupied Pondicherry.
Which of the statements) given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) 2 and 3
(c) Only 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (a)
Exp. Statement (1) is correct with reference to Pondicherry. The first European powers to occupy Pondicherry were the Portuguese. After the Portuguese, the second European powers to capture Pondicherry were the Dutch. Statements (2) and (3) are incorrect as the French East India Company set up a trading center at Pondicherry in the year 1674, and this later became the most prominent French settlement in India. Pondicherry (now Puducherry) was occupied several times by the British, but it was ultimately the French who ruled the territory. In 1761, the British captured Pondicherry from the French but later had to return it back to the French under the Treaty of Paris in 1763.
17. Consider the following statements. (2011)
1. Assessment of land revenue on the basis of nature of the soil and the quality of crops.
2. Use of mobile cannons in warfare.
3. Cultivation of tobacco and red chillies.
Which of the above was/were introduced in India by the English?
(a) Only 1
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) None of these
Ans. (d)
Exp. None of the given systems was introduced in India by the English. Assessment of land revenue on the basis of nature of the soil and the quality of crops was prevalent in the medieval period to increase their land revenue collection. Use of mobile cannons in warfare was introduced in India by Babur in the first Battle of Panipat. Tobacco cultivation in India was introduced in India.
18. Economically, one of the result of the British rule in India in the 19th century was the (2018)
(a) increase in the exports of Indian handicrafts
b) growth in the number of Indian owned factories
(c) commercialisation of Indian agriculture
(d) rapid increase in urban population
Ans. (c)
Exp. Commericalisation of Indian agriculture is one of the result of the British rule in India. A major economic impact of the British policies in India was the introduction of a large number of commercial crops such as tea, coffee, indigo, opium, cotton, jute, sugarcane and oilseeds. Exports of handicrafts suffered during British rule. Further, there is no conclusive evidence of growth in the number of Indian owned factories or rapid increase in the urban population.
19. Which one of the following groups of plants was domesticated in the ‘New World’ and introduced into the ‘Old World’? (2019)
(a) Tobacco, cocoa and rubber
(b) Tobacco, cotton and rubber
c) Cotton, coffee and sugarcane
d) Rubber, coffee and wheat
Ans. (a)
Exp. The plants of ‘New World’ (America) including maize, tomato, pineapple, patato, cocoa, tobacco and rubber were native to the New World before 1492 AD and were not found anywhere else at that time. The merchants of Europe, Asia and Africa (Old World) took products of the New World to Europe, Asia and Africa.
20. Consider the following statements. (2021)
1. St. Francis Xavier was one of the founding
members of the Jesuit Order.
2. St. Francis Xavier died in Goa and a church is dedicated to him there.
3. The Feast of St. Francis Xavier is celebrated in Goa each year.
Which of the statements) given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1,2 and 3
Ans. (c)
Exp. Statements, (1) and (3) are correct. St. Francis Xavier, one of the founders of the Society of Jesus, arrived in Goa in 1542 and travelled as far as Thoothukudi and Punnakayal to baptise the converts. Xavier established a network of Jesuit mission centres. Each year, on 3rd December, the anniversary of St Francis Xavier’s death is celebrated, thousands gather at the Basilica of Bom Jesus. This annual festival, known as the Feast of St Francis Xavier is the biggest of all the Christian festivals in Goa. He died on a Chinese Island in 1552.
21. In the first quarter of seventeenth century, in which of the following was/were the factory/factories of the English East India Company located? (2021)
1. Broach
2. Chicacole
3. Trichinopoly
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) Only 1
(b) 1 and 2
(c) Only 3
(d) 2 and 3
Ans. (a)
Exp. By the first quarter of 17th century, English East India Company had established factories at Surat (1613), Masulipatam (1616), Broach (1619), Ahmedabad (1619) and Agra (1619) and First factory in South India was established at Masulipatnam. Kalingapatnam (part of current-day Srikakulam and British era Chicacole) was one of the harbor villages and was a minor port during the East India Company regime.
22. With reference to Indian history, consider the following statements. (2022)
1. The Dutch established their factories/warehouses on the East coast on lands granted to them by Gajapati rulers.
2. Alfonso de Albuquerque captured Goa from the Bijapur Sultanate.
3. The English East India Company established a factory at Madras on a plot of land leased from a representative of the Vijayanagara empire.
Which of the statements) given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (b)
Exp. Statements (2) and (3) are correct with reference to Indian
history. In 1510 AD, Alfonso de Albuquerque captured Goa from the Sultan of Bijapur, Ismail Adil Shah with the help of Krishnadevaraya, ruler of Vijayanagara Empire. In 1611 AD, the British established their first factory in South India at Machilipatnam, but soon the main center of activities shifted to Madras. Francis Day leased Madras in 1639 from Chandragin, the representative of the Vijayanagara Empire. He built a fortified kothi there, which was named ‘Fort St George’. Statement (1) is incorrect as the Gajapati rulers ruled in the region of coastal Odisha and North coastal Andhra Pradesh from 1434 to 1541 AD and the 1st Dutch factory was established at Masulipatnam in 1605.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What were the significant factors contributing to the decline of the Later Mughals?
The decline of the Later Mughals was influenced by various factors, including weak leadership, administrative inefficiency, succession disputes, and external invasions. Economic instability, coupled with the growing influence of regional powers, further exacerbated the decline of the Mughal Empire.
Q2. How did the arrival of European powers impact the political landscape of India during the Mughal period?
The arrival of European powers, notably the Portuguese, Dutch, French, and British, introduced significant changes to the political dynamics of India. European trading companies established footholds in various regions, leading to competition for dominance and eventually contributing to the decline of indigenous powers like the Mughals.
Q3. What were the key events leading to the British conquest of India?
The British conquest of India was a gradual process marked by several pivotal events. The Battle of Plassey in 1757, where the British East India Company defeated the Nawab of Bengal, marked the beginning of British political dominance in India. Subsequent conflicts, treaties, and alliances enabled the British to expand their territorial control and establish supremacy over Indian territories.
Q4. How did the British East India Company consolidate its power in India after the Battle of Plassey?
Following the Battle of Plassey, the British East India Company consolidated its power through a combination of military conquests, alliances with Indian rulers, and administrative reforms. The company expanded its territorial control, established administrative structures, and implemented policies that favored its economic interests, gradually asserting political dominance over vast regions of India.
Q5. What were the long-term consequences of British conquest and colonial rule in India?
The British conquest of India and subsequent colonial rule had profound and lasting consequences for Indian society, economy, and politics. It led to the dismantling of indigenous power structures, economic exploitation, social upheaval, and cultural transformation. The British Raj also laid the groundwork for nationalist movements that eventually culminated in India’s independence in 1947.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

