“The String of Pearls” is a geopolitical concept that refers to China’s strategy of developing a network of military and commercial facilities in the Indian Ocean region, extending from the Chinese mainland to the Middle East. This term implies that China aims to establish a series of naval bases, ports, and infrastructure projects along critical maritime routes, resembling a string of pearls encircling India. The impact of this strategy on India is multifaceted and significant. Firstly, it poses a potential threat to India’s maritime security by enhancing China’s naval presence in proximity to India’s shores, potentially challenging its dominance in the Indian Ocean. Additionally, it could undermine India’s influence in neighboring countries by fostering closer economic and strategic ties with China.
In response to “The String of Pearls,” India has undertaken several measures to safeguard its interests and counterbalance China’s growing influence in the region. Firstly, India has strengthened its naval capabilities through modernization and expansion of its fleet, enhancing maritime surveillance, and conducting joint military exercises with other regional powers. Secondly, India has pursued closer partnerships with countries like the United States, Japan, Australia, and various Southeast Asian nations to foster a collective security architecture in the Indo-Pacific region. Furthermore, India has engaged in infrastructure development projects in neighboring countries to counter China’s economic influence and enhance regional connectivity on its own terms. Overall, India’s response to “The String of Pearls” underscores its commitment to protecting its strategic interests and maintaining stability in the Indian Ocean region.
Tag: Bilateral relationships involving India and/or affecting India’s interests including India and East and West Asian Nations, African Nations, Europe, and the Americas.
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In the Introduction, try to write about string of pearls theory.
- In Body,
- The first part explains China’s string of pearls theory.
- In the second part, discuss How it impacts India and then write about India’s steps taken to counter it.
- Try to conclude the answer by writing about India’s approach to balance China in Indian Ocean Region.
Answer:
The String of Pearls is a strategy deployed by China, by building a network of commercial and military bases and ports in many countries. This strategy has been deployed by China to protect its trade interests, as a major chunk of its trade passes through the Indian Ocean and various choke points like Strait of Hormuz, Strait of Malacca and Lombok Strait.
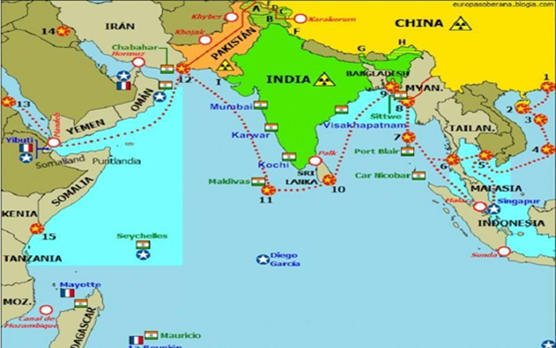
String of Pearl’s impact on India:
- It endangers Indian maritime security: China is developing more firepower with more submarines, destroyers, vessels, and ships. Their presence will pose a threat to India’s security through the water.
- Impact on the Indian economy: Indian resources will be diverted towards defense and security. Thus, the economy will not reach its potential hampering economic growth. This may further lead to instability in India and the whole east and southeast region.
- The strategic clout of India which it enjoys today in the Indian ocean will be reduced. China doesn’t have any openings in the Indian ocean, the Strings of pearls will lead to China surrounding India and it will be able to dominate it. Countries that today consider India as a partner in response to China may end up in the lap of China.

India’s Plan to Counter China:
India’s Act East Policy, which was launched as an effort to integrate India’s economy with South-East Asian nations. It has been used to make important military and strategic agreements with Vietnam, Japan, the Philippines, South Korea, Indonesia, Singapore, and Thailand helping India to counter China.
Building & Accessing Ports –
- India is developing Chabahar port in Iran, opening a new land-sea route to Central Asian countries by-passing Pakistan. It is strategically located close to the Chinese Gwadar Port in Pakistan and is close to the Strait of Hormuz. Chhabahar gives India a strategic position since it overlooks the Gulf of Oman, a very strategic oil supply route.
- Indonesia – India is building a deep-sea Port in Indonesia, a place named Sabang. It has strategic significance as it is close to the Strait of Malacca and India’s Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- Myanmar – India built a deep water port in Sittwe in 2016.
- Bangladesh – India would help Bangladesh modernize Sea Port in Mongla. India can also use the Chittagong port in Bangladesh.
- Oman – India has signed agreements to access strategically located Naval facilities of Oman. This facility is close to the Strait of Hormuz. More than 30% of oil exports pass through the Strait of Hormuz.
- Singapore – India has signed an agreement to access Changi Naval Base of Singapore, which is strategically located close to the Strait of Malacca.
Military and Naval relationships: To upgrade and train its navy, India has developed a strategic naval relationship with Myanmar which gives India an increased footprint in the area. It has also made agreements for military cooperation in the region with Japan, Australia and the USA. The four countries carry out joint military exercises in the IOR region and are known as the ‘Quad’
Building Coastal Radar Networks
- Bangladesh – India has recently signed an agreement with Bangladesh to install 20 Coastal Surveillance Radar Systems along the coastline of Bangladesh. This will help India to monitor Chinese Warships which have been frequently visiting the Bay of Bengal.
- The Maldives – India will install 10 Coastal Radar Systems in the Maldives. These radars will relay live images, videos, location information of Ships moving in the Indian Ocean Region. The project is implemented by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL). As of 2019, 7 are completed, there were small hiccups in the project due to the Government of Maldives. Once a Government that is favourable to India came to power, the project is moving with full speed.
- Sri Lanka – 6 Coastal Surveillance Radars (CSR) have been installed in Sri Lanka. As per some reports, India is planning to set up at least 10 more CSR in Sri Lanka. There are constant ongoing efforts by the Governments of India and Sri Lanka to solidify India- Sri Lanka ties.
- Mauritius – 8 Coastal Surveillance Radars have been installed in Mauritius.
- Seychelles – 1 Coastal Surveillance Radar (CSR) have been Installed in Seychelles. The 1st Coastal Surveillance Radar in Seychelles became operational in 2015. It was commissioned on the main island of Mahe. More Coastal Surveillance Radar will be installed in the small islands of Astove, Assumption and Farquhar. There are plans for 32 more Coastal Surveillance Radar Systems in Seychelles.
- India – BEL had set up 46 Coastal Radar stations and 16 command and control systems in 2015 in India. In the next phase, 38 more Coastal Radar stations and 5 command and control systems will be set up.
China is encircling India through its string of pearls theory and BRI projects, but India has been taking all the necessary steps to counter China effectively on every front. But there are some issues such as a stable political regime in Myanmar, Bangladesh, Maldives, and opposition parties in these countries are more or less favourable towards China. Therefore, if India wants to become a sole security provider, and become a blue water economy, it needs to build a strong navy which should be based on the Blue Water Navy Concept.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


