Fold mountain systems are predominantly situated along the margins of continents due to the dynamic processes of plate tectonics. The convergence of tectonic plates leads to the formation of these majestic geological features. When continental plates collide, immense pressure forces them to buckle and fold, creating mountain ranges such as the Himalayas and the Andes. This association between fold mountains and plate boundaries explains their global distribution along continental margins. Moreover, the collision of tectonic plates also generates seismic activity, resulting in earthquakes. Volcanic activity often accompanies these processes, as the intense pressure and heat beneath the Earth’s surface lead to the eruption of molten rock. Therefore, the presence of fold mountains is closely linked to the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanoes, illustrating the interconnectedness of geological phenomena along plate boundaries.
Tag: Salient features of the world’s physical geography.
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In Introduction, try to give a brief introduction of Fold Mountains.
- In Body,
- Provide reasons why world’s fold mountain systems are located along the margins of continents.
- Depict the association between the global distribution of fold mountains and the earthquakes, and with the volcanoes as well.
- Conclude with the significance of fold mountains and by giving some examples of fold mountains.
Answer:
World’s fold mountains are located on the margins of the continents because fold mountains are formed from the folding of crust and uprising of the sediments accumulated by rivers along the margins of the continents by the collision of two continental plates or a continental plate and an oceanic plate. An example of fold mountains formed by converging of two continental plates are Himalayas mountains and fold mountains formed by convergence of a continental plate and an oceanic plate are Andes mountains, Appalachians mountains etc.
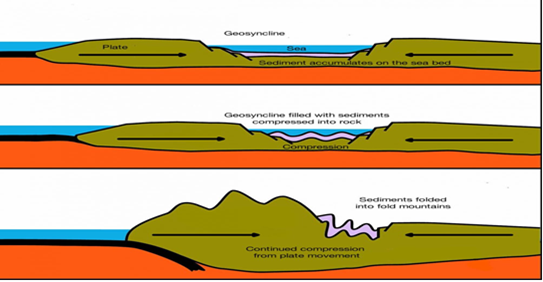
Reasons Why World’s Fold Mountain Systems Located Along the Margins of Continents:
- Fold mountains are often associated with continental crust. They are created at convergent plate boundaries, sometimes called continental collision zones or compression zones.
- Convergent plate boundaries are sites of collisions, where tectonic plates crash into each other. Compression describes a set of stresses directed at one point in a rock or rock formation.
- At a compression zone, tectonic activity forces crustal compression at the leading edge of the crust formation. For this reason, most fold mountains are found on the edge or former edge of continental plate boundaries.
- Rocks on the edge of continental crust are often weaker and less stable than rocks found in the continental interior. This can make them more susceptible to folding and warping. Most fold mountains are composed primarily of sedimentary rock and metamorphic rock formed under high pressure and relatively low temperatures.
Association Between the Global Distribution of Fold Mountains and the Earthquakes:
- When Earth’s tectonic plates grind past one another, enormous amounts of energy can be released in the form of earthquakes.
- Typically, convergent plate boundary can result in one tectonic plate diving underneath another. This process, called “subduction,” involves an older, denser tectonic plate being forced deep into the planet underneath a younger, less-dense tectonic plate.
- When this process occurs in the ocean, an ocean trench can form. These trenches are some of the deepest places in the ocean, and they are often the sites of strong earthquakes.
Association Between the Global Distribution of Fold Mountains and the Volcanoes.
- Volcanoes are also often found near convergent plate boundaries because molten rock from deep within Earth called magma can travel upward at these intersections between plates.
- When subduction occurs, a chain of volcanoes often develops near the convergent plate boundary.
- One such chain of volcanoes can be found on the western coast of the United States, spanning across the states of California, Oregon, and Washington.
Fold mountains are the most common type of mountain in the world. The rugged, soaring heights of the Himalayas, the Andes, and the Alps are all active fold mountains. The Himalayas stretch through the borders of China, Bhutan, Nepal, India, and Pakistan. The Andes are the world’s longest mountain chain. They stretch along the entire west coast of South America, from Colombia in the north and through Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina to the south and the Alps roughly mark the top of the “boot” of the Italian Peninsula.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


