
Sustainable Land Management (SLM) stands as a pivotal approach in addressing the intricate interplay between environmental preservation, economic development, and social well-being. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, and social inequalities, SLM emerges as a holistic framework that seeks to harmonize these often conflicting goals. By integrating environmentally conscious practices, promoting economic viability, and fostering social inclusivity, SLM endeavors to create a synergistic relationship among these fundamental aspects. This discussion delves into the ways in which Sustainable Land Management can effectively navigate the complex terrain of environmental, economic, and social dynamics, offering a nuanced perspective on how these complimentary goals can be aligned for the benefit of both present and future generations.
Contents
Answer
The United Nations defines sustainable land management (SLM) as “the use of land resources, including soils, water, animals and plants, for the production of goods to meet changing human needs, while simultaneously ensuring the long-term productive potential of these resources and the maintenance of their environmental functions”.
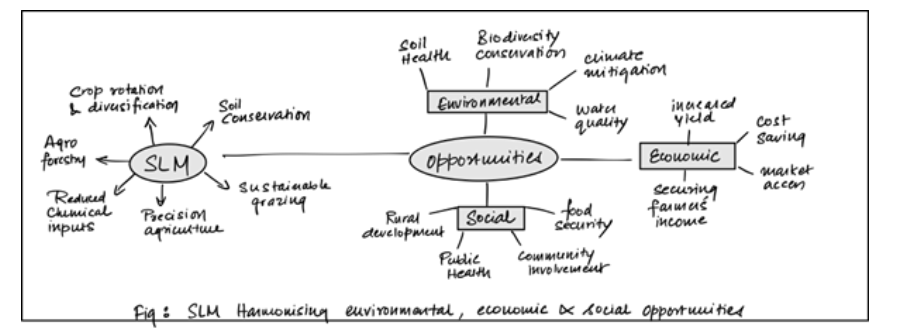
SLM harmonizing Environmental Opportunities:
- Soil Health: preserving soil quality through SLM practices like crop rotation, reduced chemical inputs, and organic farming. Eg- Restoration of China’s Loess Plateau
- Climate Mitigation: Practices like agroforestry and reforestation sequester carbon and reverse
desertification(SDG 15) Eg- The Great Green Wall Initiative involves reforestation of the Sahel Region - Water Quality: SLM minimizes runoff and pollution, protecting water quality in rivers and aquifers. Eg- Conservation efforts in the Chesapeake Bay watershed in the US
- Biodiversity: SLM practices safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem services. Eg- Polyculture in
Andes.

SLM Harmonising Economic Opportunities:
- Increased Yields: SLM techniques enhance crop yields and livestock productivity, thus increasing farmer’s income.
- Cost Savings: Reduced chemical inputs, optimized resource use, and resilient farming practices lowers production costs.
| Case Study Organic farming in Sikkim has significantly reduced the input cost of farmers to negligible amount as the farmer’s could now make their own organic inputs and had to no longer depend on market |
- Market Access: Sustainable products fetch premium prices in global markets, providing economic incentives for sustainable practices. Eg- Coffee producers who adhere to organic and fair-trade standards often receive higher prices for their products.
- Securing farmer’s income: SLM practices make farming more resilient to environmental shocks, such as droughts and floods, protecting livelihoods.
SLM Harmonising Social Opportunities:
- Food Security: SLM contributes to food security by maintaining soil fertility and preserving water resources.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in SLM decisions fosters social cohesion and empowers them ensuring their needs are considered.
| Case study Empowering ST communities by giving them political representation under PESA Act has increased canopy cover by 3%, reducing land degradation (Global Forest Cover Report) |
- Health Benefits: Reduced exposure to harmful chemicals in food and water improves public health.
- Rural Development: Sustainable agriculture can create employment opportunities in rural areas, reducing urban migration.
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture, PM Krishi Sinchai Yojna, and the Soil Health Card Scheme are some of the government’s initiatives to promote SLM practices in India. Apart from this, India also aims to promote south-south cooperation in SLM practices through initiatives like the Sustainable Land and Ecosystem Management Programme (India and GEF), Centre of Excellence on Sustainable Land Management (est. Under COP14, UNCCD).
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

