The eastern states of India, a region rich in natural resources, cultural diversity, and historical significance, have played a pivotal role in the nation’s development. From the fertile plains of Assam to the mineral-rich lands of Jharkhand, these states have contributed significantly to India’s economic growth, social progress, and cultural tapestry. Despite facing unique challenges, such as geographical isolation and historical neglect, the eastern states have demonstrated remarkable resilience and potential for future development. This exploration will delve into the key factors driving the growth of these regions, the challenges they confront, and the strategies being implemented to ensure their continued prosperity.

Tags: GS – 2 ,Federalism – Cooperative Federalism, – 3, Industrial Policy– Industrial Growth– Infrastructure– Inclusive Growth
For Prelims: Aspirational Districts Programme, Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR), Skill Development, Ayushman Bharat scheme, Budget 2024-25, Purvodaya, Inclusive Growth.
For Mains: Significance of Government Policies & Interventions in Economic Development, Mobilization of Resources and Addressing Regional Disparity.
Contents
- 0.1 Context:
- 0.2 Challenges Limiting Development of Eastern States
- 0.3 Current Economic Landscape of the Eastern States
- 0.4 Government Initiatives for the Development of Eastern States:
- 0.5 Strategies for Developing Eastern States:
- 0.6 Conclusion
- 1 UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 2 FAQs
- 2.1 1. What are the key challenges faced by the eastern states in India’s development?
- 2.2 2. What are some of the key initiatives taken by the government to address the development challenges in the eastern states?
- 2.3 3. How have the eastern states contributed to India’s overall development?
- 2.4 4. What are the prospects for future development in the eastern states?
- 2.5 5. What role can the private sector play in the development of the eastern states?
- 3 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context:
- India’s goal of becoming a developed nation by 2047 heavily depends on the progress of its eastern states—Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Odisha, Bihar, and Jharkhand.
- Despite their mineral wealth and strategic locations, these states have lagged in economic growth, contrary to the theory of beta convergence, which suggests that poorer regions should grow faster.
- This gap underscores the need for targeted policies. For India to become a global economic powerhouse, the development of these states is crucial to ensure balanced growth and reduce disparities.
- Tapping into their agricultural, mineral, and industrial potential while addressing poverty, low literacy, and inadequate infrastructure is key.
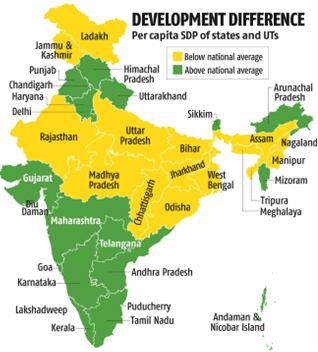
Challenges Limiting Development of Eastern States
- Economic Factors:
- Underdeveloped Industrial Sector: Historical neglect and poor infrastructure have prevented a robust industrial base, limiting formal jobs and economic diversification.
- Freight Equalisation Policy (1952): Reduced incentives to establish industries near mining areas, adversely affecting economic prospects.
- Low Social Progress: SPI ranks Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, and Odisha in Tiers 4 and 5, while Bihar and Jharkhand are in Tier 6, indicating low social progress.
- Aspirational Districts: Many districts in Bihar and Jharkhand rank among the bottom 20 of 112 Aspirational Districts, highlighting severe socio-economic challenges.
- Labor Market Issues: Bihar’s LFPR is 50.9%, and 83% of the workforce in these states is semi-skilled, limiting productivity.
- Agriculture Dependence: High reliance on low-productivity agriculture hinders economic growth and stability.
- Social & Human Development Issues:
- Low Literacy Rates: Particularly in Bihar and Jharkhand, low literacy rates impede skill development and workforce quality.
- High Poverty Rates: Persistent poverty traps large populations in cycles of low education and limited economic opportunities.
- NITI Aayog SDG India Index 2023-24: Bihar scored 57 points, the lowest, followed by Jharkhand with 62, indicating poor performance.
- Historical & Geographical Factors:
- Colonial Legacy: Exploitative policies left a legacy of economic backwardness.
- Geographical Isolation: Challenging terrain and poor connectivity limit market access.
- Vulnerability to Natural Disasters: Frequent cyclones (e.g., Amphan in 2020) and floods disrupt development efforts.
- Governance & Political Challenges:
- Political Instability: Frequent government changes disrupt long-term planning.
- Competitive Federalism: Richer states attract more investment, widening inequalities.
- Corruption and Bureaucratic Inefficiency: These issues divert resources and deter private investment.
- Naxalite Insurgency: Ongoing conflict in some areas disrupts governance and development, deterring investment.
Current Economic Landscape of the Eastern States
- GDP:
- The combined GDP of the eastern region reached USD 579 billion in 2022-23, a significant increase from USD 185 billion in 2011-12. However, the region’s share of India’s total GDP has remained stagnant at around 17% during this period.
- This growth rate is insufficient to propel India towards its development goals, indicating the need for enhanced economic performance.
- Growth Projections:
- If the eastern region grows at an annual rate of 9%, it could achieve an output of around USD 5 trillion by 2047.
- Conversely, if the growth rate remains at a modest 5%, its GDP would only reach about USD 1.8 trillion by 2047.
- This disparity underscores the urgency for policy changes to align the region’s growth trajectory with national aspirations.
Government Initiatives for the Development of Eastern States:
- Purvodaya – Development of the Eastern Region:
- Industrial Development: The Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor includes creating an industrial hub in Gaya, blending cultural heritage with economic development under the “Vikas bhi Virasat bhi” (Development along with Heritage) model.
- Road Connectivity Projects: Key projects include the Patna-Purnea Expressway, Buxar-Bhagalpur Expressway, and spurs to Bodhgaya, Rajgir, Vaishali, and Darbhanga. Additionally, a new 2-lane bridge over the Ganga at Buxar will be constructed.
- Power and Infrastructure Projects: Major investments include a new 2400 MW power plant at Pirpainti in Bihar, alongside new airports, medical colleges, and sports facilities.
- Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act:
- The government is committed to the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, with significant budget allocations in 2024-25:
- Capital Development Aid: Rs 15,000 crore in financial aid for capital development through multilateral agencies.
- Polavaram Irrigation Project: Completion of this project to support farmers and enhance food security.
- Infrastructure Investments: Development in the Kopparthy and Orvakal nodes of industrial corridors, with grants for Rayalaseema, Prakasam, and North Coastal Andhra regions.
- The government is committed to the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, with significant budget allocations in 2024-25:
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan:
- This initiative aims to improve socio-economic conditions for over 5 crore tribal people across 63,000 villages in tribal-majority areas, including aspirational districts in the eastern states.
- Bringing Green Revolution to Eastern India (BGREI):
- A sub-scheme of Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), BGREI supports farmers in seven eastern states with rice and wheat demonstrations, seed production, soil management, pest control, farm machinery, and irrigation.
- Urja Ganga Gas Pipeline Project:
- This project aims to provide clean fuel to the people of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Odisha, enhancing energy security and environmental sustainability in the region.
- Controlling Naxalism:
- Through the effective implementation of the SAMADHAN Doctrine and the Rehabilitation Policy, left-wing extremism-related violent incidents have decreased by 76% in 2022 compared to 2010, contributing to enhanced security and stability.
Strategies for Developing Eastern States:
- Economic Growth Initiatives:
- Target investments in infrastructure to boost connectivity and economic activities.
- Promote industrialization, especially in mineral-rich states like Odisha and Jharkhand, by establishing value-added industries near mining areas.
- Develop projects like the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor to reduce transportation costs and attract industrial investments.
- Social Development Focus:
- Implement skill development programs to enhance workforce quality, with a focus on health and education.
- Expand initiatives like Ayushman Bharat and Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan to improve health and education outcomes.
- Labor Market Improvements:
- Increase labour force participation, especially among women, through programs like microfinance and Start-Up India.
- Support small businesses and entrepreneurship to create employment opportunities, as seen in successful models in West Bengal and Bihar.
- Cooperative Federalism:
- Strengthen collaboration between central and state governments to address regional disparities.
- Share resources and expertise for effective policy implementation and socio-economic development.
- Governance and Policy:
- Enhance local governance to ensure efficient execution of development programs.
- Adopt successful models like Odisha’s KALIA scheme and West Bengal’s Kanyashree Prakalpa to support agriculture and empower disadvantaged groups.
- Addressing Regional Disparities:
- Focus on equitable development through targeted policies that improve social indicators and economic growth.
- Continue efforts like Bihar’s Vikas Mission to boost education and healthcare in the region.
- Realising Potential:
- Leverage the eastern states’ mineral resources, strategic locations, and untapped potential to contribute to India’s industrial and economic growth.
- Develop industries like steel, aluminium, and cement in Jharkhand and Odisha.
- Boosting MSMEs:
- Enhance access to financing, credit, technology, and skills for MSMEs.
- Create a conducive business environment with streamlined regulations and improved infrastructure.
Conclusion
Prioritising the development of eastern states is crucial for India’s balanced and sustainable growth. With vast resources and strategic advantages, these states have the potential to drive the nation’s economic transformation. The next few decades are pivotal for bridging the development gap and aligning their growth with national objectives, making their success a cornerstone of India’s journey toward developed nation status.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q:1 Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character? (2021)
- The independence of the judiciary is safeguarded.
- The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units.
- The Union Cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties.
- The Fundamental Rights are enforceable by Courts of Law.
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q:1 The concept of cooperative federalism has been increasingly emphasised in recent years. Highlight the drawbacks in the existing structure and the extent to which cooperative federalism would answer the shortcomings. (2015)
Source: LM
FAQs
1. What are the key challenges faced by the eastern states in India’s development?
- Infrastructure: Lack of adequate infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and ports, hinders economic growth and connectivity.
- Geographical Disadvantage: Many eastern states are prone to natural disasters like floods, cyclones, and earthquakes, which disrupt development efforts.
- Poverty and Inequality: High levels of poverty and inequality persist in these regions, limiting human capital development and economic opportunities.
- Lack of Industrialization: The eastern states have lagged behind in industrialization compared to western India, leading to a dependence on agriculture and a limited industrial base.
- Educational Disparity: Educational disparities exist between urban and rural areas, as well as between different social groups, hindering human capital development.
2. What are some of the key initiatives taken by the government to address the development challenges in the eastern states?
- National Eastern Region Development Initiative (NERD): This initiative aims to promote balanced regional development by investing in infrastructure, industry, agriculture, and education.
- Act East Policy: This policy seeks to strengthen India’s economic and cultural ties with countries in Southeast Asia and the Pacific region, providing new opportunities for the eastern states.
- Infrastructure Development: The government has invested significantly in infrastructure projects, such as highways, railways, and ports, to improve connectivity and facilitate economic growth.
- Industrial Corridors: The government has established industrial corridors in the eastern states to attract investments and create jobs.
- Skill Development Initiatives: Various programs have been launched to enhance the skills of the workforce and make them more employable.
3. How have the eastern states contributed to India’s overall development?
- Natural Resources: The eastern states are rich in natural resources, such as coal, minerals, and forests, which have contributed to the country’s industrial development.
- Agriculture: Agriculture remains a major economic activity in the eastern states, contributing to food security and rural livelihoods.
- Tourism: The region’s diverse cultural heritage, natural beauty, and historical sites attract tourists, boosting the tourism industry.
- Strategic Location: The eastern states’ proximity to Southeast Asia and the Pacific region has made them important gateways for trade and investment.
4. What are the prospects for future development in the eastern states?
- Infrastructure Improvements: Ongoing infrastructure development projects are expected to enhance connectivity and attract investments.
- Industrial Growth: The establishment of industrial corridors and the focus on skill development are likely to drive industrial growth and create jobs.
- Tourism Potential: The region’s tourism sector has significant potential for growth, given its diverse attractions and increasing accessibility.
- Renewable Energy: The eastern states have abundant renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind power, which can contribute to sustainable development.
- Regional Cooperation: Increased regional cooperation with neighboring countries can provide new opportunities for trade, investment, and development.
5. What role can the private sector play in the development of the eastern states?
- Investment: Private sector investments in infrastructure, manufacturing, and services are crucial for driving economic growth and creating jobs.
- Innovation: The private sector can play a key role in promoting innovation and technological advancements.
- Skill Development: Companies can collaborate with educational institutions to provide vocational training and skill development programs.
- Social Responsibility: Private sector businesses can contribute to the development of the region by undertaking corporate social responsibility initiatives.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

