Today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants explores the latest developments relevant to the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping India’s socio-political and economic landscape. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.

Contents
- 1 Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF)
- 2 The Grave Threat from Antimicrobial Resistance
- 3 Paris Paralympics Games 2024
- 4 Enemy Property Act 1968
- 5 Program of the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- 6 Presbyopia
- 7 Pahadi Korwa Tribe
- 8 INS Malpe and INS Mulki
- 9 Myristica Swamps
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 10.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 10.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 10.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 10.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 11 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF)
Tags: GS-2, Polity & Governance- Govt. scheme & Incentive
Why in the news?
- The inaugural Governing Board meeting of the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), chaired by the Prime Minister of India, was held recently.

Government’s Plan under the PM Professorship Initiative
- The Government plans to engage accomplished retired scientists and professors as mentors for faculty in universities with lower rankings under the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Mentorship will be provided by experts from national laboratories and premier institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs).
- The initiative includes substantial government funding, postdoctoral support, and resources aimed at building research groups in these universities.
- The goal is to enhance research capabilities in higher education institutions.
- Final details of the programme will be presented to the Executive Council for approval.
Another Major Announcement at the ANRF Meeting
- Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) Programme: The PAIR programme aims to create a mentorship environment, promoting research excellence across the nation.
- Urgency: Currently, less than 1% of India’s 40,000 higher education institutions (HEIs) are engaged in research.
Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF)
- Established under the ANRF Act 2023 and aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, ANRF is an apex body designed to guide the strategic direction of scientific research in India.
- The ANRF will:
- Forge collaborations between industry, academia, and government.
- Create mechanisms for the participation of industries and State governments in research initiatives.
- The Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), established in 2008, has been subsumed into the ANRF.
Governing Board and Executive Council of ANRF:
- Governing Board:
- Chaired by the Prime Minister of India, providing strategic direction and overseeing implementation.
- Includes:
- Union Ministers of Science and Technology, and Education as Vice Presidents.
- Principal Scientific Advisor as Member Secretary.
- Secretaries from the Departments of Science and Technology, Biotechnology, and Scientific and Industrial Research.
Conclusion:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation and its initiatives are crucial steps towards strengthening research and innovation in India. By fostering collaborations, providing mentorship, and supporting research-oriented institutions, the ANRF aims to enhance the quality of higher education and contribute to the country’s scientific progress.
Source: PIB
The Grave Threat from Antimicrobial Resistance
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology-
Why in the news?
- Ahead of the UN General Assembly High-Level Meeting on antimicrobial resistance scheduled for September 26, the World Health Organization (WHO) published its first-ever guidance on antibiotic pollution from manufacturing.

Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR):
- History of Antibiotics and Resistance:
- 1928: Penicillin, the first commercialized antibiotic, was discovered by Alexander Fleming.
- Resistance has been recognized alongside the discovery of new antibiotics since then.
- Meaning of AMR:
- Antimicrobials:
- Medicines, including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitic drugs, used to treat infections in humans, animals, and plants.
- Antimicrobials:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR):
- Occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites change over time, becoming unresponsive to medicines.
- This makes infections harder to treat and increases the risk of disease spread, severe illness, and death.
- Causes & Combat of AMR:
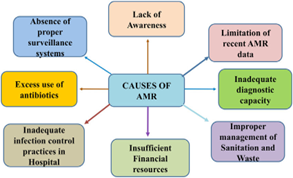
- Resistant Pathogens in India:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): Causes gut infections.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae: Causes pneumonia and urinary tract infections.
- Acinetobacter baumannii: Linked with hospital-acquired infections.
Major Initiatives by India to Combat AMR:
- National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (NAP-AMR):
- Launched in 2017, two years after the WHO’s Global Action Plan on AMR.
- Focuses on six strategic priority areas:
- Awareness and education
- Surveillance of antibiotic resistance
- Infection prevention and control
- Optimized antimicrobial use in health, animal, and food sectors
- AMR-related research
- Strengthened leadership at national and sub-national levels
- The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), New Delhi, is the coordinating body for NAP-AMR implementation.
- Red Line Campaign:
- A government initiative urging people not to use medicines marked with a red vertical line without a doctor’s prescription.
- Aims to reduce the irrational use of antibiotics, helping combat drug resistance for diseases like TB, malaria, and dengue.
Conclusion:
AMR poses a grave threat to global health, making infections harder to treat and leading to severe health risks. Addressing AMR requires coordinated efforts from individuals, policy makers, and the healthcare sector to ensure responsible antimicrobial use and preventive measures.
Source: IR
Paris Paralympics Games 2024
Tags: GS-1, History – Sports
Why in the news?
- India achieved its best-ever performance at the Paris Paralympics 2024, securing a total of 29 medals: 7 gold, 9 silver, and 13 bronze.
- Mascot: The Paralympic Phryge, inspired by the Phrygian cap, symbolizes liberty and freedom.
India’s Performance at the Paris Paralympic Games 2024:
- Medal Count and Ranking: Total medals: 29 (7 gold, 9 silver, 13 bronze). Overall rank: 18th.
- Notable Achievement:
- Gold Medal in Javelin Throw: Navdeep Singh won India’s first gold medal in the men’s javelin throw F41 category, following the disqualification of Iran’s Beit Sayah Sadegh. The F41 category is for field athletes with short stature.
What are the Government Initiatives for Sport Promotion?
- Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS): Focuses on improving the performance of athletes with the potential to win medals at the Olympics by offering training, coaching, and infrastructure support.
- Fit India Movement: Encourages physical activities and sports participation at all levels, including schools and communities, to improve overall health and fitness.
- Khelo India: Aims to identify and nurture young talent through sports competitions, coaching camps, and scholarships for promising athletes.
- National Sports Awards Scheme: Includes awards such as the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna, Padma Bhushan, Padma Shri, and Dronacharya Awards.
- National Sports Development Fund (NSDF): Provides financial assistance for training, research, and enhancement of facilities to promote sports and support athletes at various levels.
Enemy Property Act 1968
Tags: GS- 2, Polity & Governance- Government Policies & Interventions
Why in the news?
- A parcel of land in Uttar Pradesh, once owned by the family of an ex-Pakistani President, is set for auction under the Enemy Property Act, 1968, reigniting discussions on the management of enemy properties in India.

What is the Enemy Property Act?
- Enactment: Passed in 1968 after the 1965 India-Pakistan war, it regulates properties of those classified as “enemy aliens.”
- Definition: Refers to properties left by people who migrated to enemy nations (Pakistan and China) after wars (1965 and 1971 India-Pakistan wars, 1962 Sino-Indian War). These were seized under the 1962 Defence of India Act.
- Tashkent Declaration: India and Pakistan discussed returning these properties in 1966, but Pakistan sold them in 1971. India retained them under the Act.
- Provisions: The Act gives the government control over such properties to ensure they are not used against India.
- Amendment (2017): The 2017 amendment expanded “enemy subject” and “enemy firm” to include legal heirs and successors, ensuring the property remains with the government even if the enemy’s status changes.
- Key Legal Precedents:
- Union of India vs. Raja Mohammad Amir Mohammad Khan (2005): The SC ruled that enemy property cannot be classified as such if the rightful heir is an Indian citizen.
- Lucknow Nagar Nigam vs. Kohli Brothers Colour Lab (2024): The SC held that the Custodian holds enemy property temporarily and that the government doesn’t acquire ownership rights from the original owner.
Program of the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
Tags: GS – 2, Government Policies & Interventions– E-Governance– Issues Related to Children – Issues Related to Women, GS – 3, Cyber Security
Why in the news?
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) is an initiative of the Ministry of Home Affairs established to combat cybercrime in a coordinated and comprehensive manner.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre, he announced plans to train 5,000 cyber commandos in next 5 years and inaugurated platforms and a suspect registry to combat cybercrime.

About I4C:
- Established in January 2020.
- Aims to:
- Enhance coordination between law enforcement agencies and stakeholders.
- Improve India’s overall capability to tackle cybercrime.
- Functions as a nodal point for:
- Curbing cybercrime nationwide.
- Strengthening the fight against cybercrime against women and children.
- Facilitating easy cybercrime complaint filing and identifying trends.
- Acting as an early warning system for proactive cybercrime prevention and detection.
- Raising public awareness on cybercrime prevention.
Major I4C Initiatives:
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP): Allows 24/7 reporting of all cybercrimes through cybercrime.gov.in.
- Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System: Enables immediate reporting of financial cyber frauds.
- National Toll-Free Helpline Number 1930: Provides citizen assistance in lodging online cyber complaints.
- National Cyber Forensic Laboratory (NCFL): A state-of-the-art facility for training and assisting state/UT investigation officers.
- CyTrain Portal (https://cytrain.ncrb.gov.in): Offers Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) on cybercrime investigation, forensics, and prosecution for police and judicial officers.
- CyberDost Social Media Handles: Generate cyber awareness among citizens across various platforms.
Four New I4C Platforms Launched:
- Cyber Fraud Mitigation Centre (CFMC): Established to provide immediate action and seamless cooperation in tackling online financial crimes, exemplifying “Cooperative Federalism” in law enforcement.
- ‘Cyber Commandos’ Program: Creates a special wing of trained ‘Cyber Commandos’ in States/UTs and Central Police Organizations (CPOs) to address cyber security threats.
- Samanvay Platform (Joint Cybercrime Investigation Facilitation System): A web-based portal for cybercrime data repository, sharing, mapping, analytics, and coordination among Law Enforcement Agencies nationwide.
- Cyber Suspect Registry: Developed from the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) in partnership with banks and financial intermediaries to enhance fraud risk management in the financial sector.
Cybersecurity’s Importance in National Security:
- Infrastructure Protection: Essential for safeguarding critical national infrastructure such as power grids, water systems, and transportation networks from digital threats. Example: 2019 malware attack on Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant.
- Economic Security: Crucial for shielding businesses and financial institutions from cyber threats to maintain economic stability. Example: 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack.
- National Defense: Vital for securing military communications, weapons systems, and strategic information from cyber threats. Example: Stuxnet worm attack on Iranian nuclear facilities.
Source: ET
Presbyopia
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- Health
Why in the news?
- On September 10, 2024, Entod Pharmaceuticals, based in Mumbai, announced that the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has approved its new eye drop, PresVu, designed to reduce dependence on reading glasses for individuals suffering from presbyopia.
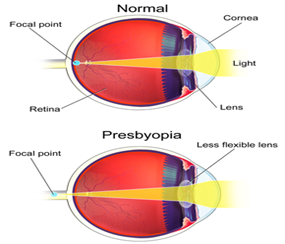
About the Presbyopia:
- About:
- Definition: Presbyopia is an age-related eye condition where the ability to focus on nearby objects gradually diminishes.
- Age of Onset: The condition typically begins around the age of 40. According to medical experts, spectacles remain one of the most effective solutions to manage presbyopia.
- How does PresVu work?
- Active Ingredient: PresVu contains Pilocarpine, which helps the iris muscles contract, allowing the pupil to focus better on nearby objects.
- Technology: It employs “advanced dynamic buffer technology,” which adjusts the solution to the pH of tears, ensuring consistent efficacy and safety for long-term use.
- Usage: PresVu is a prescription medication with effects lasting four to six hours and is not suitable for individuals with iris inflammation.
- Side Effects:
- Common side effects may include itching, redness, eyebrow pain, and muscle spasms in the eyes.
Source: IE
Pahadi Korwa Tribe
Tags: GS-1, Geography- Human Geography- Tribe
Why in the news?
- Recently, 54 settlements of the Pahadi Korwa tribe in northern Chhattisgarh will gain road connectivity under the Prime Minister JANMAN scheme, as per a government announcement.

Pahadi Korwa Tribe:
- About:
- PVTG Classification: The Pahadi Korwa community is recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Chhattisgarh.
- Geographical Spread: Predominantly located in the Korba and Jashpur districts of Chhattisgarh, with smaller populations in Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh.
- Language:
- The tribe’s primary language is Korwa, also called Ernga or Singli, part of the Munda branch of the Austroasiatic language family.
- Sadri and Chhattisgarhi are commonly spoken as second languages.
- Economic Activities:
- They rely on small-scale farming, fishing, hunting, and gathering forest products for their livelihood.
- Their agricultural practice includes Jhoonga Kheti, which involves clearing forests to grow lentils and other crops.
- Families typically follow a nuclear structure, and they relocate after a family member dies in the house, abandoning the old dwelling.
- The tribe manages justice through a community panchayat, where decisions are made collectively based on traditional customs.
- Religious Practices:
- The community practices ancestral worship, with key deities including Sigri Dev, Gauria Dev, Mahadev (Lord Shiva), and their supreme deity, Khudia Rani.
Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN):
- Key Initiatives:
- The program focuses on 11 essential interventions, such as housing, road networks, piped water supply, and skill development centers.
- Additional support comes from ministries like Ayush, which provides wellness centers, and Skill Development, which offers vocational training.
- Funding Plan: The project’s total cost is set at Rs 24,104 crore, with Rs 15,336 crore funded by the central government and Rs 8,768 crore by state governments.
Source: TP
INS Malpe and INS Mulki
Tags: GS-3, Science & Technology- Defence technology
Why in the news?
- Recently, Two anti-submarine warfare shallow watercraft vessels (ASWCWC) of the Indian Navy, INS Malpe and INS Mulki, were launched at Cochin Shipyard.

INS Malpe and INS Mulki:
- About:
- INS Malpe and INS Mulki are Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Watercrafts (ASWCWC) recently launched by the Indian Navy at Cochin Shipyard.
- These vessels represent the fourth and fifth ASWCWC being constructed indigenously for the Navy by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Both vessels belong to the Mahe Class and are intended to replace the current Abhay Class ASW Corvettes.
- Features:
- Primary Roles: These vessels are equipped to perform anti-submarine warfare, mine-laying operations, subsurface surveillance, and search and rescue missions in coastal waters.
- Dimensions: Each vessel is 78.0 metres long and 11.36 metres wide, with a draught of 2.7 metres.
- Specifications:
- Displacement: Approximately 900 tonnes.
- Maximum speed: 25 knots.
- Endurance: 1,800 nautical miles.
- Equipment:
- The ships are fitted with indigenously developed SONARS for advanced underwater surveillance.
- They feature light-weight torpedoes, anti-submarine warfare rockets, close-in weapon systems, and remote-controlled guns for enhanced maritime operations.
Source: TH
Myristica Swamps
Tags: GS-3, Ecology & Environment- Biodiversity – Forest
Why in the news?
- Recently A group of researchers discovered a Myristica swamp forest in Kumbral, Maharashtra, which is protected by the local community.

About the Myristica Swamps:
- About:
- Myristica swamps are freshwater swamps dominated by evergreen trees from the Myristicaceae family, often referred to as living fossils due to their ancient evolutionary origin of approximately 140 million years.
- Key Characteristics:
- The swamps are marked by trees with large protruding roots, emerging from waterlogged soil that remains submerged throughout the year.
- These ecosystems play a crucial role in evolutionary studies due to their primitive nature.
- Geographical distribution in India includes the Western Ghats, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Meghalaya. Historically, they formed a large hydrological network in the Western Ghats.
- Climatic Conditions:
- Myristica swamps require specific abiotic conditions, such as valley shapes, high rainfall (3000 mm average), and year-round water availability.
- These swamps often lie next to rivers, acting as natural water sponges that ensure perennial water availability.
- Ecological Significance:
- They have a high carbon sequestration capacity compared to non-swampy forests.
- Myristica swamps provide stable habitats for various vertebrate and invertebrate species. Notably, the Myristica Swamp Treefrog (Mercurana myristicapalustris) is endemic to small regions in Kerala.
Source: TOI
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

