India needs a comprehensive National Security Strategy to address the complex challenges it faces in today’s rapidly changing global landscape. With threats ranging from cross-border terrorism, cyberattacks, and internal security issues to geopolitical tensions and economic vulnerabilities, the country requires a clear plan to safeguard its national interests. A well-defined strategy would help coordinate military, diplomatic, and economic efforts to ensure stability and peace. It would also enhance India’s ability to respond to emerging risks, protect its citizens, and strengthen its position on the global stage. By having a robust National Security Strategy, India can effectively manage both current and future threats.
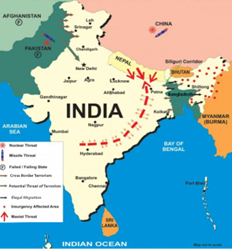
Tags: GS-3,Internal Security-Security Challenges & Management in Border Areas- Security Forces & Agencies Mandate
Contents
- 0.1 Context:
- 0.2 The Concept of National Security and Adopted:
- 0.3 India’s previous efforts to develop a National Security Strategy (NSS):
- 0.4 Need for National Security System (NSS) in India:
- 0.5 The Role of Economic Security in the Formulation of India’s National Security Policy:
- 0.6 What could be the potential benefits of a national security policy in India?
- 0.7 What are the challenges of developing a national security strategy?
- 1 UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 2 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context:
- India, striving to become a $4 trillion economy, faces growing geopolitical challenges as adversaries strengthen and alliances remain uncertain.
- Comprehensive National Security Strategy (NSS) that addresses the complexities of national security in an increasingly complex global environment.
The Concept of National Security and Adopted:
- National Security Concept: National security refers to a state’s ability to protect and defend its citizens.
- United States of America: U.S. focuses on aligning national interests with democratic values, uses its NSS to guide war strategy and global power strategy, and supports authoritarian regimes.
- United Kingdom and France: The U.K. the 2021 survey emphasised cooperation and the Ukraine war shaped Russia- France’s 2022 agenda, which focuses on nuclear solutions and European leadership.
India’s previous efforts to develop a National Security Strategy (NSS):
- Kargil Inquiry Committee Report (2000): After the Kargil conflict in 1999, this report proposed comprehensive recommendations on national security but there was no immediate NSS
- Naresh Chandra Task Force (2012): The task force looked into reforms related to safety reports, but the reports did not result in the publication of a formal NSS document
- National Security Advisory Board (NSAB): NSAB has drafted a number of national security policy documents, but is yet to issue any official document to the NSS.
- General D.S. Hooda’s Document (2019): Lt. Col. Gen. (Retd.) D.S. Hooda’s NSS paper was an important step in formal planning for India.
Need for National Security System (NSS) in India:
- Strategic Uncertainty: Post-Cold War global unpredictability has given rise to new enemies and various security challenges including terrorism, proliferation and non-state actors India needs a strategy to deal with this evolving situation.
- Nuclear Security and Geopolitical Change: India’s nuclear deterrent will have to adapt to threats posed by China, Pakistan and the US. the effects of nuclear energy in the Indian Ocean meet, in the context of changing global dynamics.
- Indo-Pacific Security Framework: As the Indo-Pacific has become the focal point of global politics, India needs a framework for “competitive cooperation” and “social security” in the region.
- Challenges beyond traditional threats: Domestic threats such as left-wing extremism, economic instability and social unrest call for an all-encompassing defensive approach.
- Technological Advancement and Cybersecurity: Rapid technological advances increase capabilities but introduce cyber vulnerabilities, creating the need for strong cybersecurity.
- Biodiversity degradation and climate change: Environmental issues such as melting ice sheets and rising sea levels directly threaten national security.
The Role of Economic Security in the Formulation of India’s National Security Policy:
- Aiming to become a $4 trillion economy, India has to navigate global uncertainty,military capability and flexibility especially from conflicts in Ukraine and Gaza.
- India’s recent economic reforms aim to boost manufacturing, trade & technology and a formal link between these objectives and national security is essential.
- China remains a major trading partner, and India faces a trade deficit of $85 billion, reflecting economic vulnerability amid geopolitical challenges.
What could be the potential benefits of a national security policy in India?
- Comprehensive approach: The entire NSS provides a comprehensive framework for addressing various security challenges, both internal and external.
- Clear objectives: Defines a clear security objective, helps define the assets and interests that need to be protected and identify potential threats.
- Policy Guidance: The NSS provides policy guidance, assisting the government in developing and implementing strategies and policies to protect national security.
- Prioritise: This helps prioritise security concerns, allowing resources and effort to be allocated to the most important issues..
- Distribution: Assists in the distribution of resources, enabling more efficient use of financial and human resources to enhance safety.
- Preventive Measures: Preventive measures can help deter potential adversaries by providing a clear and well thought out approach to national security
- Whole-of-Government Approach: The NSS promotes a “whole-of-government” approach by involving multiple government departments and agencies to ensure coordination and cooperation on security-related issues
What are the challenges of developing a national security strategy?
- Political hesitation: Governments have been reluctant to codify their defence policies, perhaps because of commitment pitfalls, possible criticism, or concerns about rigidity in decision-making
- Legal Framework: Ensuring that NSS complies with existing legal frameworks, including international treaties and domestic laws, is important but can be difficult.
- Resource allocation: Allocating the necessary resources, both financial and human, to implement the NSS effectively can be challenging, especially when there are competing demands on the budget.
- Differences between military and political leadership: Personnel structures in the Ministry of Defense and other government agencies may have different views on the formal NSS
- Changing Threat Landscape: Transforming NSSs is an ongoing challenge to address evolving security threats, such as cyber threats, terrorism, and non-traditional security challenges.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q:1 With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: D
Mains :
Q:1 “The diverse nature of India as a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society is not immune to the impact of radicalism which is seen in her neighbourhood.” Discuss along with strategies to be adopted to counter this environment. (200 words) [2014]
Source: TH
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Learn CSAT – CSAT for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

